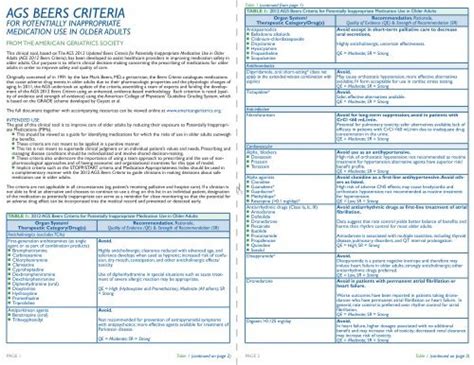
The Beers Criteria, established by Dr. Mark Beers in 1991, is a widely used medication list that identifies potentially inappropriate medications for use in older adults. The criteria are designed to help healthcare professionals make informed decisions about medication use in this population, taking into account the unique physiological changes that occur with aging and the potential for adverse drug reactions. The list is updated regularly to reflect new evidence and changes in medication use.
Introduction to the Beers Criteria
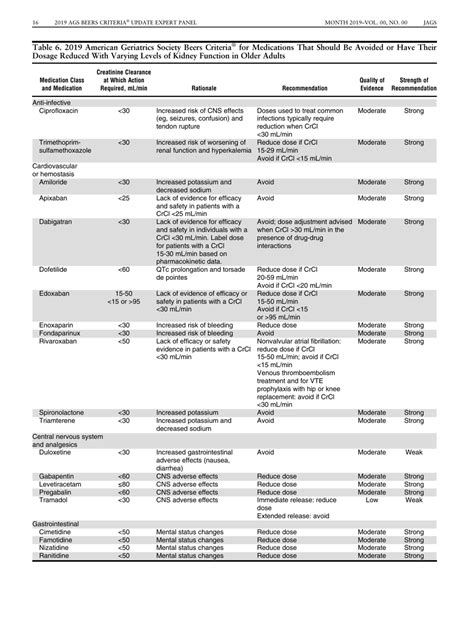
The Beers Criteria medication list is divided into three categories: medications that should be avoided in older adults, medications that are potentially inappropriate but may be used in certain situations, and medications that have a higher risk of adverse effects in older adults. The list is based on a comprehensive review of the literature and takes into account factors such as the medication’s pharmacokinetics, potential for drug interactions, and the presence of age-related diseases.
Key Points
- The Beers Criteria medication list is a valuable tool for healthcare professionals to identify potentially inappropriate medications for use in older adults.
- The list is divided into three categories: medications to avoid, potentially inappropriate medications, and medications with a higher risk of adverse effects.
- The Beers Criteria take into account factors such as pharmacokinetics, potential for drug interactions, and the presence of age-related diseases.
- The list is updated regularly to reflect new evidence and changes in medication use.
- Healthcare professionals should use the Beers Criteria in conjunction with their clinical judgment and consideration of individual patient factors.
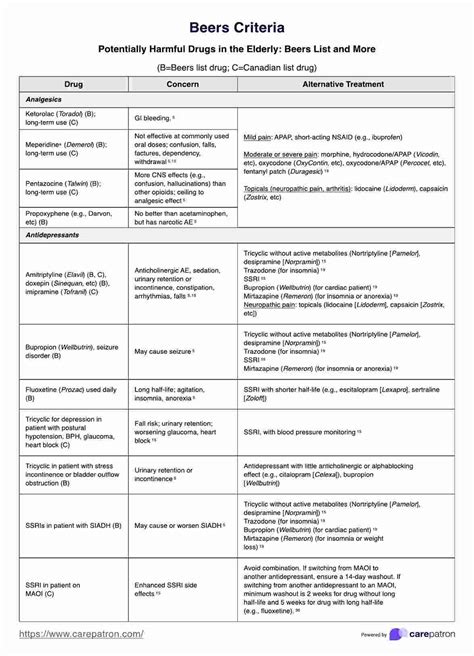
Medications to Avoid in Older Adults
The Beers Criteria identify certain medications that should be avoided in older adults due to their high risk of adverse effects. These medications include:
| Medication Class | Examples |
|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Diphenhydramine, chlorpheniramine |
| Anticholinergics | Oxybutynin, tolterodine |
| Barbiturates | Phenobarbital, secobarbital |
| Benzodiazepines | Alprazolam, diazepam |

These medications can cause a range of adverse effects, including sedation, confusion, dry mouth, and constipation. In older adults, these effects can be particularly problematic, leading to falls, cognitive impairment, and decreased quality of life.
Potentially Inappropriate Medications
The Beers Criteria also identify medications that are potentially inappropriate for use in older adults, but may be used in certain situations. These medications include:
| Medication Class | Examples |
|---|---|
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | Aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen |
| Corticosteroids | Prednisone, dexamethasone |
| Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) | Omeprazole, lansoprazole |
These medications can cause a range of adverse effects, including gastrointestinal bleeding, osteoporosis, and increased risk of infections. However, in certain situations, such as the treatment of inflammatory conditions or gastroesophageal reflux disease, these medications may be necessary.
Medications with a Higher Risk of Adverse Effects
The Beers Criteria also identify medications that have a higher risk of adverse effects in older adults, even when used appropriately. These medications include:
| Medication Class | Examples |
|---|---|
| Anticoagulants | Warfarin, rivaroxaban |
| Antiplatelet agents | Aspirin, clopidogrel |
| Opioid analgesics | Morphine, oxycodone |
These medications can cause a range of adverse effects, including bleeding, thrombocytopenia, and respiratory depression. In older adults, these effects can be particularly problematic, leading to increased morbidity and mortality.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The Beers Criteria medication list has significant implications for clinical practice. Healthcare professionals should use the list to identify potentially inappropriate medications and adjust treatment plans accordingly. This may involve:
- Conducting regular medication reviews to identify potential adverse effects and adjust treatment plans.
- Using alternative medications or therapies that are safer and more effective in older adults.
- Monitoring patients closely for adverse effects and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
- Providing patient education on the potential risks and benefits of medications and the importance of adherence to treatment plans.
Future Directions
The Beers Criteria medication list is continually updated to reflect new evidence and changes in medication use. Future updates may include:
- New medications that have been identified as potentially inappropriate for use in older adults.
- Revised criteria for medications that are currently listed as potentially inappropriate.
- New guidance on the use of medications in older adults with specific medical conditions, such as dementia or chronic kidney disease.
What is the purpose of the Beers Criteria medication list?
+The Beers Criteria medication list is designed to help healthcare professionals identify potentially inappropriate medications for use in older adults and make informed decisions about medication use in this population.
How is the Beers Criteria medication list updated?
+The Beers Criteria medication list is updated regularly to reflect new evidence and changes in medication use. The updates are based on a comprehensive review of the literature and take into account factors such as pharmacokinetics, potential for drug interactions, and the presence of age-related diseases.
What are some examples of medications that should be avoided in older adults?
+Examples of medications that should be avoided in older adults include antihistamines, anticholinergics, barbiturates, and benzodiazepines. These medications can cause a range of adverse effects, including sedation, confusion, dry mouth, and constipation.