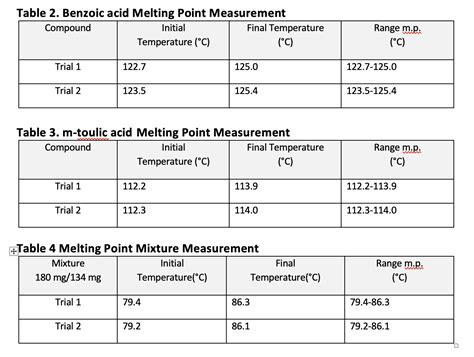
Benzoic acid, a white, crystalline organic compound, is widely used in the production of various chemicals, such as dyes, plastics, and pharmaceuticals. One of the key physical properties of benzoic acid is its melting point, which is a crucial factor in determining its purity and suitability for different applications. The melting point of benzoic acid is typically reported as a range, rather than a single value, due to the potential presence of impurities and variations in experimental conditions.
The standard melting point of benzoic acid is generally considered to be between 121°C and 123°C, with some sources reporting a slightly broader range of 120°C to 124°C. However, it is essential to note that the actual melting point of benzoic acid can vary depending on the specific sample and the method used to determine the melting point. For instance, the melting point of benzoic acid can be affected by the presence of impurities, such as water or other organic compounds, which can lower the melting point. Additionally, the melting point can also be influenced by the rate of heating and the atmospheric pressure during the measurement.
Key Points
- The standard melting point of benzoic acid is between 121°C and 123°C.
- The actual melting point can vary depending on the specific sample and experimental conditions.
- The presence of impurities, such as water or other organic compounds, can lower the melting point.
- The rate of heating and atmospheric pressure can also influence the melting point.
- Benzoic acid is widely used in the production of various chemicals, such as dyes, plastics, and pharmaceuticals.
Factors Affecting the Melting Point of Benzoic Acid
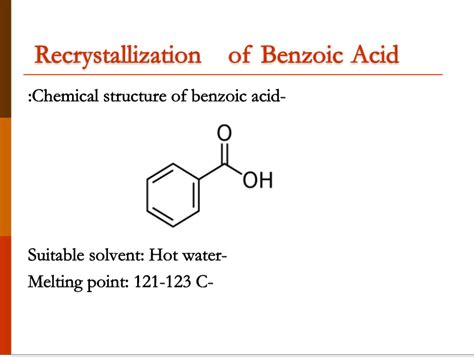
Several factors can affect the melting point of benzoic acid, including the presence of impurities, the rate of heating, and the atmospheric pressure during the measurement. The purity of the sample is a critical factor, as the presence of impurities can significantly lower the melting point. For example, the presence of water can reduce the melting point of benzoic acid by as much as 10°C. Additionally, the rate of heating can also influence the melting point, as rapid heating can cause the sample to melt at a lower temperature than slow heating.
Experimental Methods for Determining the Melting Point of Benzoic Acid
There are several experimental methods that can be used to determine the melting point of benzoic acid, including the capillary tube method, the melting point apparatus method, and the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) method. The capillary tube method involves placing a small sample of benzoic acid in a capillary tube and heating it slowly until the sample melts. The melting point apparatus method uses a specialized instrument to heat the sample and measure the melting point. The DSC method uses a calorimeter to measure the heat flow associated with the melting of the sample, allowing for the determination of the melting point with high accuracy.
| Method | Melting Point Range (°C) |
|---|---|
| Capillary Tube Method | 120-124 |
| Melting Point Apparatus Method | 121-123 |
| Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Method | 122-123 |
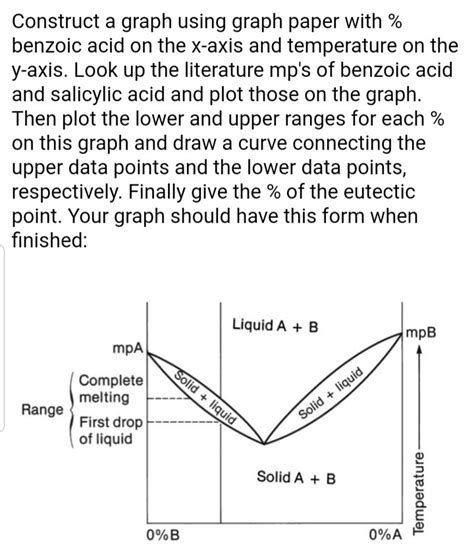
Applications of Benzoic Acid

Benzoic acid has a wide range of applications in various industries, including the production of dyes, plastics, and pharmaceuticals. Its antimicrobial properties make it a popular preservative in food and cosmetics. Additionally, benzoic acid is used as a intermediate in the synthesis of various chemicals, such as benzyl alcohol and benzaldehyde. The melting point of benzoic acid is an essential factor in determining its suitability for these applications, as it affects the physical and chemical properties of the final product.
What is the standard melting point of benzoic acid?
+The standard melting point of benzoic acid is between 121°C and 123°C.
What factors can affect the melting point of benzoic acid?
+The presence of impurities, the rate of heating, and the atmospheric pressure during the measurement can affect the melting point of benzoic acid.
What are the applications of benzoic acid?
+Benzoic acid has a wide range of applications in various industries, including the production of dyes, plastics, and pharmaceuticals, as well as a preservative in food and cosmetics.
In conclusion, the melting point of benzoic acid is a critical physical property that requires careful measurement and interpretation. By understanding the factors that affect the melting point and using appropriate experimental methods, researchers and manufacturers can ensure the purity and quality of benzoic acid for various applications. The melting point range of 121°C to 123°C is a widely accepted standard, but it is essential to consider the potential variations and factors that can influence this value. As a widely used chemical intermediate, benzoic acid continues to play a vital role in various industries, and its melting point remains an essential factor in determining its suitability for different applications.