Betadine and iodine are two antiseptic agents commonly used for skin disinfection and wound care. While both have been widely used for decades, they have distinct differences in terms of their composition, mechanism of action, and indications for use. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of Betadine and iodine, exploring their similarities and differences, as well as their applications in various medical settings.
Key Points
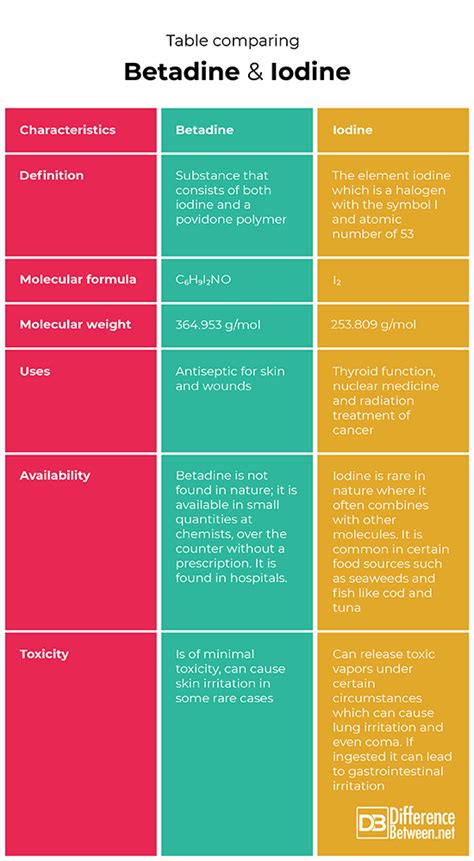
- Betadine is a topical antiseptic containing povidone-iodine, which is a complex of iodine with the polymer povidone.
- Iodine, on the other hand, refers to elemental iodine, which is a potent antiseptic but also highly irritating to tissues.
- Betadine has a broader spectrum of activity against bacteria, viruses, and fungi compared to iodine.
- The mechanism of action of both Betadine and iodine involves the release of free iodine, which disrupts microbial cell membranes and DNA.
- Betadine is generally considered safer and less irritating than iodine, making it preferred for use on broken skin and in wound care.
Composition and Mechanism of Action

Betadine, also known as povidone-iodine, is a topical antiseptic that contains 10% povidone-iodine, which is a complex of iodine with the polymer povidone. This complexation enhances the solubility and stability of iodine, allowing for a more sustained release of free iodine. Iodine, in its elemental form, is highly reactive and irritating to tissues, which limits its direct use on skin and mucous membranes.
The mechanism of action of both Betadine and iodine involves the release of free iodine, which then acts on microbial cells. Free iodine disrupts cell membranes, interferes with protein synthesis, and damages DNA, ultimately leading to the death of the microorganism. This broad-spectrum activity makes both agents effective against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Antimicrobial Spectrum and Efficacy
Betadine has been shown to have a broader spectrum of activity compared to iodine, with efficacy against a wider range of microorganisms. This is due in part to the povidone component, which enhances the penetration of iodine into microbial cells. Studies have demonstrated that Betadine is effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as against certain viruses and fungi.
Iodine, while potent, has a narrower spectrum of activity and is more effective against bacteria and viruses. Its use is often limited to specific applications, such as preoperative skin preparation and water purification, due to its high reactivity and potential for tissue irritation.
| Agent | Composition | Spectrum of Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Betadine | 10% povidone-iodine | Broad-spectrum: bacteria, viruses, fungi |
| Iodine | Elemental iodine | Narrower spectrum: primarily bacteria and viruses |
Clinical Applications and Safety Considerations
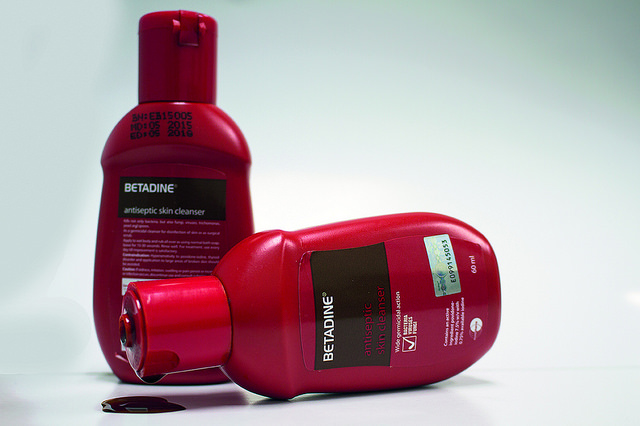

Betadine is widely used in clinical settings for skin disinfection, wound care, and preoperative preparation. Its lower irritation potential and broader spectrum of activity make it preferred for use on broken skin and in situations where a broad-spectrum antiseptic is required. Betadine is available in various formulations, including solutions, swabs, and ointments, which can be selected based on the specific application and patient needs.
Iodine, due to its high reactivity and potential for tissue irritation, is used more selectively. It is often used for water purification, as a disinfectant for surfaces, and in certain medical procedures where its potent antiseptic properties are beneficial and its use can be carefully controlled.
Safety and Allergic Reactions
Both Betadine and iodine can cause allergic reactions or skin irritation in some individuals. However, Betadine is generally considered safer and less irritating than iodine, especially for use on broken skin or in wound care. The povidone component in Betadine helps to reduce the risk of irritation and allergic reactions, making it a preferred choice for patients with sensitive skin or a history of allergic reactions to antiseptics.
What is the primary difference between Betadine and iodine in terms of their composition?
+Betadine is a complex of iodine with the polymer povidone, which enhances the solubility and stability of iodine, whereas iodine refers to elemental iodine.
Which agent has a broader spectrum of antimicrobial activity?
+Betadine has a broader spectrum of activity against bacteria, viruses, and fungi compared to iodine.
What are the primary clinical applications of Betadine and iodine?
+Betadine is used for skin disinfection, wound care, and preoperative preparation, while iodine is used for water purification, as a disinfectant for surfaces, and in certain medical procedures.
In conclusion, while both Betadine and iodine are effective antiseptic agents, their differences in composition, mechanism of action, and clinical applications make them suited for different uses. Understanding these differences is crucial for healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about antiseptic use, ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.