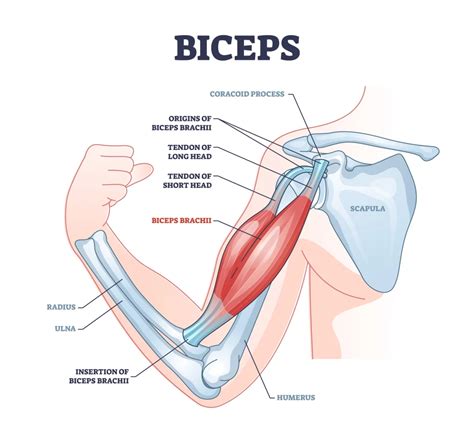
The biceps, one of the most iconic and recognizable muscles in the human body, plays a crucial role in our daily lives, from simple actions like lifting and carrying to more complex movements that require strength, flexibility, and coordination. The biceps brachii, as it is scientifically known, consists of two heads (the short head and the long head) that converge to form a single muscle belly. This unique anatomy allows for a wide range of motion and functionality. Understanding the biceps goes beyond mere aesthetics; it involves delving into its anatomy, function, and the various ways it can be developed and maintained.
Understanding Biceps Anatomy

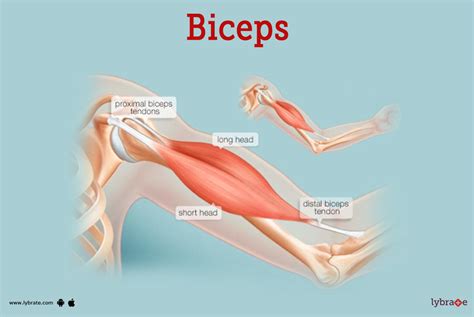
The anatomy of the biceps is fascinating, with its two heads originating from different parts of the scapula (shoulder blade). The long head originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, while the short head originates from the coracoid process. Both heads then merge to form a single muscle belly that attaches to the radial tuberosity and the bicipital aponeurosis, a fascial layer that also merges with the deep fascia of the forearm. This intricate structure is what gives the biceps its remarkable ability to flex the elbow and supinate the forearm. The biceps tendon, which connects the muscle to the bones, is also noteworthy for its strength and resilience, though it is not immune to injury, especially in activities that involve repetitive strain or sudden force.
Biceps Function and Movement
The primary functions of the biceps include elbow flexion (bending at the elbow) and forearm supination (turning the palm upwards). These movements are critical for a variety of daily activities and athletic performances. For instance, lifting a heavy object requires not just the flexion of the elbow but also the supination of the forearm to orient the object correctly in the hand. Moreover, the biceps work in harmony with other muscles of the arm, such as the triceps and brachialis, to ensure smooth and efficient movement. Understanding the interplay between these muscles can provide insights into the prevention and treatment of injuries, as well as strategies for strengthening and conditioning.
| Muscle Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Elbow Flexion | Bending at the elbow joint, reducing the angle between the forearm and the upper arm. |
| Forearm Supination | Rotating the forearm so that the palm faces upwards or forwards. |

Key Points
- The biceps brachii consists of two heads (long and short) that merge into a single muscle belly.
- Its primary functions include elbow flexion and forearm supination.
- The biceps work in coordination with other arm muscles for efficient movement.
- A balanced exercise routine is essential for strengthening and conditioning the biceps.
- Injury prevention and treatment often involve understanding the interplay between the biceps and other muscles of the arm.
Training and Conditioning
Training the biceps effectively involves a combination of weightlifting exercises and bodyweight movements. Dumbbell curls, barbell curls, and preacher curls are popular choices for targeting the biceps from different angles. However, it’s also important to incorporate exercises that work the biceps as part of a larger movement pattern, such as pull-ups, which engage the biceps along with the back and shoulder muscles. Conditioning the biceps for endurance and strength can be achieved through a mix of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and steady-state exercises. For athletes and individuals with specific performance goals, customized training programs that address weaknesses and imbalances can be particularly beneficial.
Injury Prevention and Management
Injuries to the biceps, such as strains or tendonitis, can be painful and debilitating. Prevention strategies include gradual progression of exercise intensity, proper warm-up routines, and avoiding repetitive strain. For existing injuries, management often involves a period of rest, physical therapy to maintain flexibility and strength, and in some cases, medical intervention. Understanding the signs of overuse or impending injury, such as persistent pain or decreased performance, is critical for taking proactive steps towards prevention and early intervention.
| Exercise | Target | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dumbbell Curls | Biceps Brachii | Isolation of biceps for focused strengthening. |
| Pull-ups | Latissimus Dorsi, Biceps | Compound exercise for overall upper body strength. |
As we continue to explore the complexities of the human body, the biceps stand out as a remarkable example of functional anatomy and the potential for strength and resilience through dedicated training and care. By understanding its structure, function, and the ways in which it can be developed and protected, we can appreciate the intricate beauty of human physiology and strive for optimal health and performance.
What are the primary functions of the biceps brachii?
+The primary functions of the biceps brachii include elbow flexion (bending at the elbow) and forearm supination (turning the palm upwards). These movements are essential for a variety of daily activities and athletic performances.
How can I prevent injuries to my biceps?
+Prevention strategies include gradual progression of exercise intensity, proper warm-up routines, avoiding repetitive strain, and ensuring a balanced training program that strengthens the biceps and surrounding muscles.
What exercises are best for strengthening the biceps?
+A combination of isolation exercises (like dumbbell curls) and compound movements (such as pull-ups) is recommended. This approach ensures well-rounded development and enhances overall upper body strength and resilience.