Binary ionic compounds are a fundamental concept in chemistry, consisting of two elements: a metal and a nonmetal. These compounds are formed when a metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion, known as a cation, and a nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons to form a negatively charged ion, known as an anion. The electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions holds them together, resulting in the formation of a binary ionic compound. Understanding the properties and behavior of these compounds is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and physics.
The formation of binary ionic compounds can be illustrated by the reaction between sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) to form sodium chloride (NaCl), commonly known as table salt. In this reaction, sodium loses an electron to form a positively charged sodium ion (Na+), while chlorine gains an electron to form a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-). The resulting compound, NaCl, consists of equal numbers of Na+ and Cl- ions, which are arranged in a crystalline lattice structure. This structure is held together by the electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions, resulting in a strong and stable compound.
Key Points
- Binary ionic compounds consist of a metal and a nonmetal.
- The metal atom loses electrons to form a cation, while the nonmetal atom gains electrons to form an anion.
- The electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions holds them together.
- The resulting compound has a crystalline lattice structure.
- Understanding binary ionic compounds is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and physics.
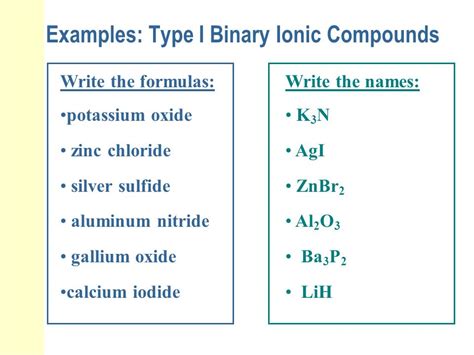
Naming Binary Ionic Compounds

Naming binary ionic compounds involves identifying the cation and anion present in the compound. The name of the cation is typically the same as the name of the metal, while the name of the anion is derived from the name of the nonmetal. For example, the compound formed by the reaction between calcium (Ca) and oxygen (O) is called calcium oxide (CaO). In this case, the cation is calcium (Ca2+), and the anion is oxide (O2-). The suffix “-ide” is added to the root of the nonmetal’s name to form the name of the anion.
Monatomic and Polyatomic Ions
Binary ionic compounds can also involve monatomic and polyatomic ions. Monatomic ions are ions that consist of a single atom, such as the sodium ion (Na+) or the chloride ion (Cl-). Polyatomic ions, on the other hand, are ions that consist of multiple atoms, such as the nitrate ion (NO3-) or the sulfate ion (SO42-). The naming of binary ionic compounds involving polyatomic ions is similar to that of monatomic ions, with the addition of the polyatomic ion’s name to the name of the cation. For example, the compound formed by the reaction between sodium (Na) and nitrate (NO3-) is called sodium nitrate (NaNO3).
| Compound | Cation | Anion |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | Sodium (Na+) | Chloride (Cl-) |
| Calcium oxide (CaO) | Calcium (Ca2+) | Oxide (O2-) |
| Sodium nitrate (NaNO3) | Sodium (Na+) | Nitrate (NO3-) |

Properties of Binary Ionic Compounds

Binary ionic compounds exhibit a range of properties, including high melting and boiling points, brittleness, and conductivity. These properties are a result of the strong electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions, which holds the compound together. The high melting and boiling points of binary ionic compounds are due to the strong ionic bonds between the ions, which require a significant amount of energy to break. The brittleness of these compounds is also a result of the ionic bonds, which can be broken easily, resulting in the formation of cracks and fractures.
Conductivity and Solubility
Binary ionic compounds can also exhibit conductivity and solubility in certain solvents. The conductivity of these compounds is due to the movement of ions, which can carry electrical charge. The solubility of binary ionic compounds in water is also an important property, as it can affect the compound’s reactivity and behavior. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) is highly soluble in water, while calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is insoluble.
The solubility of binary ionic compounds in water can be predicted using the solubility rules, which are based on the properties of the ions involved. For example, compounds containing the nitrate ion (NO3-) are generally soluble in water, while compounds containing the sulfate ion (SO42-) are less soluble. Understanding the solubility properties of binary ionic compounds is essential for various applications, including the development of new materials and technologies.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
+A cation is a positively charged ion, while an anion is a negatively charged ion. Cations are typically formed by the loss of electrons, while anions are formed by the gain of electrons.
How are binary ionic compounds named?
+Binary ionic compounds are named by identifying the cation and anion present in the compound. The name of the cation is typically the same as the name of the metal, while the name of the anion is derived from the name of the nonmetal.
What are the properties of binary ionic compounds?
+Binary ionic compounds exhibit a range of properties, including high melting and boiling points, brittleness, and conductivity. These properties are a result of the strong electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions.