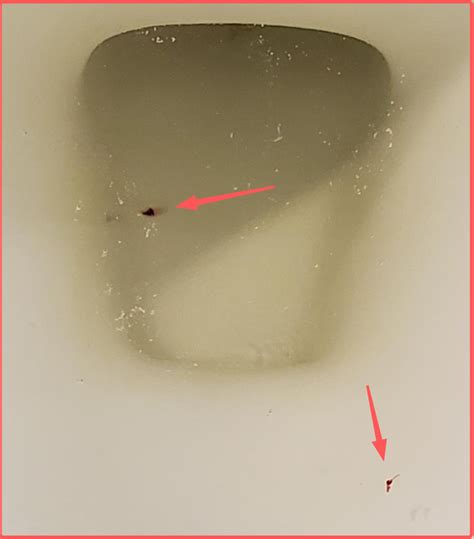
Blood clots in urine, also known as hematuria, can be a concerning and potentially alarming symptom for women. The presence of blood clots in the urine can indicate a range of underlying health issues, from mild to severe. In this article, we will delve into the possible causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for blood clots in urine in females.
Causes of Blood Clots in Urine in Females
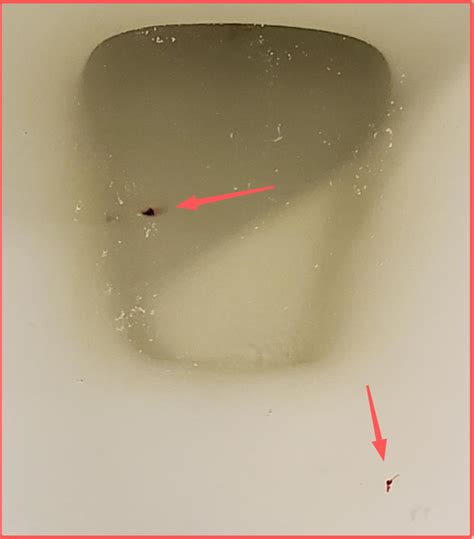

There are several possible causes of blood clots in urine in females, including:
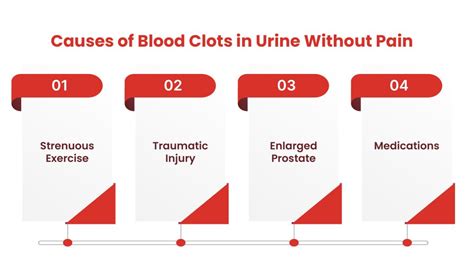
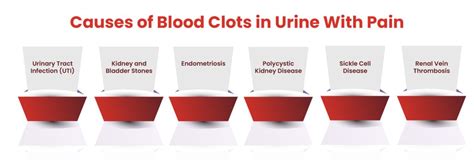
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Bacterial infections in the urinary tract can cause inflammation and bleeding, leading to blood clots in the urine.
- Kidney Stones: Stones in the kidneys or urinary tract can cause bleeding and lead to blood clots in the urine.
- Bladder Infections: Infections in the bladder can cause bleeding and blood clots in the urine.
- Menstruation: In some cases, blood clots in the urine can be related to menstruation, especially if a woman is experiencing heavy or irregular periods.
- Endometriosis: This condition, where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, can cause bleeding and blood clots in the urine.
- Cancer: In rare cases, blood clots in the urine can be a sign of cancer, such as bladder or kidney cancer.
Symptoms of Blood Clots in Urine in Females
The symptoms of blood clots in urine in females can vary, but may include:
- Painful Urination: Discomfort or pain while urinating can be a symptom of blood clots in the urine.
- Frequent Urination: The need to urinate more often than usual can be a sign of a urinary tract infection or other underlying condition.
- Cloudy or Discolored Urine: Urine that is cloudy, dark, or has a strong odor can indicate the presence of blood clots or other underlying conditions.
- Abdominal Pain: Pain in the lower abdomen can be a symptom of a range of conditions, including kidney stones or UTIs.
Key Points
- Blood clots in urine can be a symptom of a range of underlying health issues, from mild to severe.
- Urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and bladder infections are common causes of blood clots in urine in females.
- Symptoms can include painful urination, frequent urination, cloudy or discolored urine, and abdominal pain.
- Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as urinalysis and imaging studies.
- Treatment options depend on the underlying cause, but may include antibiotics, pain management, and in some cases, surgery.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blood Clots in Urine in Females
Diagnosing the cause of blood clots in urine in females typically involves a combination of physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as:
- Urinalysis: A test to analyze the urine for blood, protein, and other substances.
- Imaging Studies: Tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans to visualize the kidneys, bladder, and urinary tract.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure to visually examine the bladder and urinary tract using a flexible scope.
Treatment options for blood clots in urine in females depend on the underlying cause, but may include:
- Antibiotics: To treat bacterial infections, such as UTIs or kidney infections.
- Pain Management: To alleviate discomfort or pain associated with urination or abdominal pain.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove kidney stones, repair damaged tissue, or treat cancer.
| Underlying Cause | Treatment Option |
|---|---|
| Urinary Tract Infections | Antibiotics |
| Kidney Stones | Pain management, surgery to remove stones |
| Bladder Infections | Antibiotics, pain management |
| Menstruation-related | Hormonal therapy, pain management |
Prevention and Management of Blood Clots in Urine in Females
To reduce the risk of developing blood clots in urine, females can take several preventive measures, including:
- Practicing Good Hygiene: Wiping from front to back after using the bathroom, washing hands frequently, and avoiding tight clothing can help prevent UTIs.
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria and other substances that can cause infections.
- Avoiding Certain Foods: Some foods, such as citrus fruits or spicy foods, can irritate the bladder and increase the risk of blood clots in the urine.
What are the most common causes of blood clots in urine in females?
+The most common causes of blood clots in urine in females include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and bladder infections.
How is blood in the urine diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as urinalysis and imaging studies.
What are the treatment options for blood clots in urine in females?
+Treatment options depend on the underlying cause, but may include antibiotics, pain management, and in some cases, surgery.
In conclusion, blood clots in urine can be a symptom of a range of underlying health issues in females. While the causes can vary, prompt medical attention and proper diagnosis are essential for effective treatment and prevention of complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, women can take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce the risk of developing blood clots in their urine.



