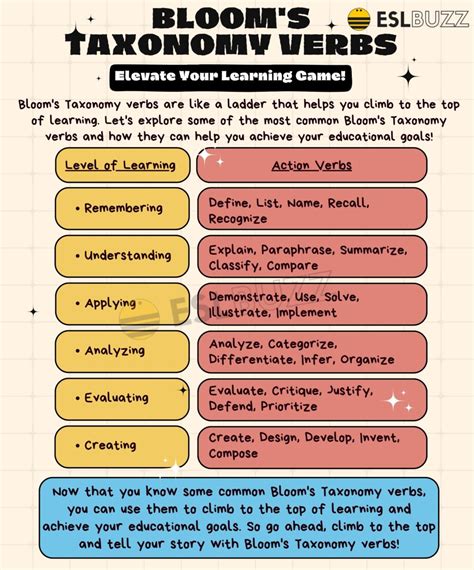
Bloom's Taxonomy is a widely accepted framework used to classify learning objectives into six distinct levels of cognitive complexity. The taxonomy, developed by Benjamin Bloom and his colleagues in 1956, provides a hierarchical structure for understanding and measuring the complexity of learning outcomes. The six levels of Bloom's Taxonomy, listed in order of increasing complexity, are: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating. Each level is associated with specific verbs that describe the cognitive processes involved.
Introduction to Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs

The verbs associated with each level of Bloom’s Taxonomy serve as a guide for educators, instructional designers, and learners to understand the cognitive demands of learning objectives. By using these verbs, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of what is expected at each level of cognitive complexity. The six levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy, along with their associated verbs, are as follows:
Level 1: Remembering
The Remembering level involves recalling previously learned information. Verbs associated with this level include: list, define, describe, identify, recall, and recognize. This level is focused on retrieving information from memory, with little or no processing of the information.
| Verb | Definition |
|---|---|
| List | To recall a series of items or facts |
| Define | To state the meaning of a term or concept |
| Describe | To provide a detailed account of something |
Level 2: Understanding
The Understanding level involves interpreting and explaining the meaning of information. Verbs associated with this level include: interpret, explain, summarize, paraphrase, and describe. This level requires learners to make sense of the information and convey their understanding in their own words.
Level 3: Applying
The Applying level involves using learned information to solve problems or complete tasks. Verbs associated with this level include: apply, use, demonstrate, implement, and execute. This level requires learners to take the information they have learned and use it in a practical context.
Main Section: Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating

The higher levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy involve more complex cognitive processes, including analyzing, evaluating, and creating. These levels require learners to think critically and make judgments about the information they have learned.
Level 4: Analyzing
The Analyzing level involves breaking down information into its component parts and examining the relationships between them. Verbs associated with this level include: analyze, compare, contrast, classify, and differentiate. This level requires learners to identify patterns, themes, and relationships within the information.
Level 5: Evaluating
The Evaluating level involves making judgments about the value or quality of information. Verbs associated with this level include: evaluate, judge, justify, critique, and assess. This level requires learners to consider the strengths and weaknesses of the information and make informed decisions.
Level 6: Creating
The Creating level involves generating new ideas, products, or solutions. Verbs associated with this level include: create, design, develop, compose, and generate. This level requires learners to think creatively and bring new ideas to life.
Key Points
- The six levels of Bloom's Taxonomy are: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating
- Each level has associated verbs that describe the cognitive processes involved
- The levels build upon one another, with higher levels requiring more complex cognitive processes
- Understanding and Applying are critical levels, as they lay the foundation for higher-level cognitive processes
- Creating is the highest level, requiring learners to generate new ideas and solutions
In conclusion, Bloom's Taxonomy verbs provide a framework for understanding the cognitive complexity of learning objectives. By using these verbs, educators and learners can develop a deeper understanding of what is expected at each level of cognitive complexity and create learning experiences that challenge and engage learners.
What are the six levels of Bloom's Taxonomy?
+The six levels of Bloom's Taxonomy are: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating.
What is the difference between Understanding and Applying?
+Understanding involves interpreting and explaining the meaning of information, while Applying involves using learned information to solve problems or complete tasks.
What is the highest level of Bloom's Taxonomy?
+The highest level of Bloom's Taxonomy is Creating, which involves generating new ideas, products, or solutions.
Meta Description: Discover the six levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy and the associated verbs that describe cognitive processes. Learn how to use Bloom’s Taxonomy to create learning experiences that challenge and engage learners. (140-155 characters)



