The blue winged wasp, also known as Scolia dubia, is a species of wasp that is commonly found in North America. These wasps are known for their bright blue wings and distinctive habits. In this article, we will explore five interesting facts about the blue winged wasp, including their unique characteristics, behaviors, and habits.
Key Points
- The blue winged wasp is a parasitic wasp that preys on ground-dwelling insects, such as grubs and caterpillars.
- Blue winged wasps are known for their bright blue wings, which are actually a result of the way that light interacts with the microscopic structure of their wings.
- These wasps are important pollinators and are often found in gardens and meadows, where they feed on nectar and pollen.
- Blue winged wasps are generally non-aggressive and do not sting unless they are threatened or provoked.
- These wasps are often considered to be beneficial insects, as they help to control pest populations and maintain the balance of ecosystems.
Natural History of the Blue Winged Wasp
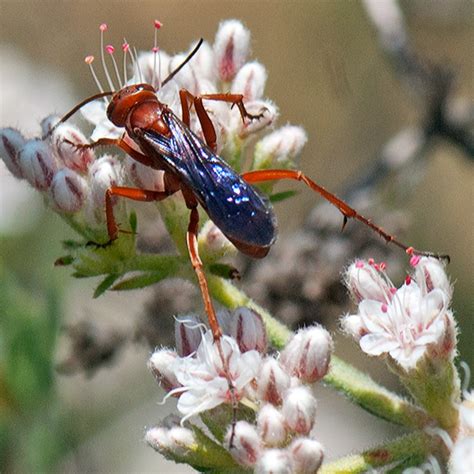

The blue winged wasp is a member of the family Scoliidae, which includes over 300 species of wasps. These wasps are found throughout the world, with the majority of species being found in tropical and subtropical regions. The blue winged wasp is native to North America, where it is commonly found in gardens, meadows, and forests. These wasps are known for their bright blue wings, which are actually a result of the way that light interacts with the microscopic structure of their wings. This phenomenon is known as structural coloration, and it is a common feature of many insects, including butterflies and beetles.
Behavior and Habitat
Blue winged wasps are parasitic wasps, which means that they prey on other insects in order to feed their young. These wasps are known to prey on a variety of ground-dwelling insects, including grubs and caterpillars. They are also important pollinators, and are often found in gardens and meadows, where they feed on nectar and pollen. Blue winged wasps are generally non-aggressive and do not sting unless they are threatened or provoked. They are solitary wasps, which means that they do not live in colonies like some other species of wasps.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Wing Color | Bright blue, due to structural coloration |
| Body Length | Approximately 1-2 inches (2.5-5 cm) |
| Diet | Ground-dwelling insects, such as grubs and caterpillars |
| Habitat | Gardens, meadows, and forests |

Conservation Status
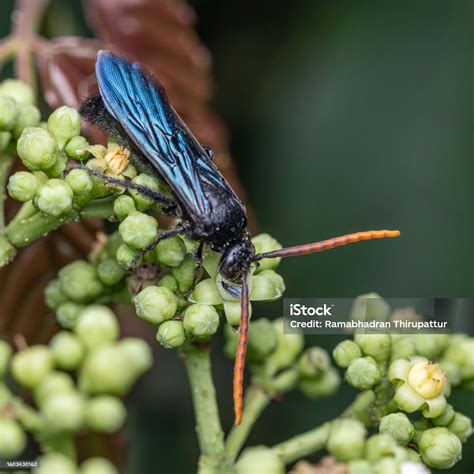

Blue winged wasps are not currently considered to be a threatened species, although their populations are often affected by habitat destruction and the use of pesticides. These wasps are an important part of many ecosystems, and their loss could have significant consequences for the environment. As such, it is essential to take steps to conserve and protect these wasps, such as creating habitat-friendly gardens and reducing the use of pesticides.
Interesting Facts
Here are a few more interesting facts about blue winged wasps:
- These wasps are able to fly at speeds of up to 15 miles per hour (24 km/h), making them some of the fastest flying insects in the world.
- Blue winged wasps are known for their unique stridulation behavior, which involves vibrating their wings to produce a loud buzzing noise.
- These wasps are important indicators of environmental health, as changes in their populations can indicate broader ecosystem problems.
What do blue winged wasps eat?
+Blue winged wasps are parasitic wasps that prey on ground-dwelling insects, such as grubs and caterpillars. They also feed on nectar and pollen, making them important pollinators.
Are blue winged wasps aggressive?
+No, blue winged wasps are generally non-aggressive and do not sting unless they are threatened or provoked.
How can I attract blue winged wasps to my garden?
+You can attract blue winged wasps to your garden by planting a variety of flowers that provide nectar and pollen, such as sunflowers and zinnias. You can also create a habitat-friendly garden by reducing the use of pesticides and providing shelter for these wasps.