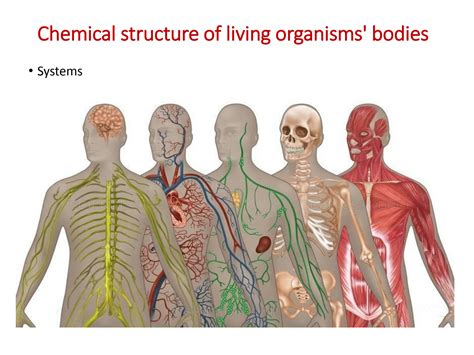
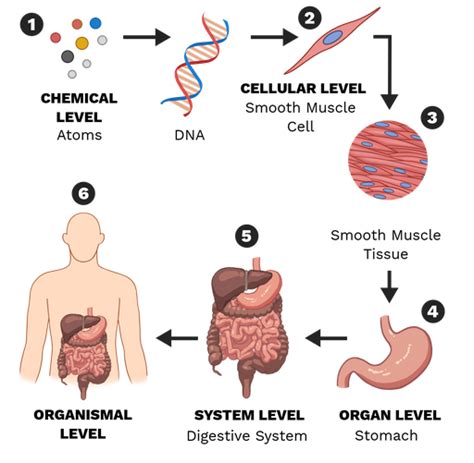
The study of organism bodies structure is a fundamental aspect of biology, as it seeks to understand the complex organization and function of living organisms. From the simplest bacteria to the most complex mammals, all living organisms are composed of cells, which are the basic building blocks of life. The structure and function of these cells, as well as the way they are organized into tissues, organs, and systems, are crucial to understanding how organisms survive, grow, and reproduce.
At the most basic level, cells are composed of a variety of organelles, each with its own unique function. The nucleus, for example, contains the genetic material of the cell, while the mitochondria are responsible for generating energy. The cell membrane, on the other hand, regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell. Understanding the structure and function of these organelles is essential to understanding how cells work, and how they contribute to the overall function of the organism.
As cells are organized into tissues, the structure and function of these tissues become more complex. In animals, for example, there are four primary types of tissue: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Each of these tissues has a unique function, such as protection, support, movement, and control, and they work together to maintain the overall health and function of the organism. In plants, on the other hand, tissues are organized into roots, stems, and leaves, each with its own unique function, such as absorption, transport, and photosynthesis.
Key Points
- Cells are the basic building blocks of life, and are composed of a variety of organelles, each with its own unique function.
- Tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function, such as protection, support, movement, and control.
- Organs are structures that are composed of two or more types of tissue, and work together to perform a specific function, such as the heart, lungs, and liver.
- Systems are groups of organs that work together to maintain the overall health and function of the organism, such as the circulatory, respiratory, and digestive systems.
- Understanding the structure and function of organism bodies is essential to understanding how living organisms survive, grow, and reproduce.
Organism Bodies Structure and Function

As tissues are organized into organs, the structure and function of these organs become even more complex. Organs are structures that are composed of two or more types of tissue, and work together to perform a specific function. In animals, for example, the heart is an organ that is composed of muscle and connective tissue, and works to pump blood throughout the body. The lungs, on the other hand, are organs that are composed of epithelial and connective tissue, and work to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide.
In plants, organs are also composed of multiple types of tissue, and work together to perform specific functions. The roots, for example, are organs that are composed of dermal, vascular, and ground tissue, and work to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. The leaves, on the other hand, are organs that are composed of mesophyll and vascular tissue, and work to photosynthesize and produce energy for the plant.
System Level Organization
At the highest level of organization, organs are organized into systems, which are groups of organs that work together to maintain the overall health and function of the organism. In animals, for example, there are 11 major systems, including the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems. Each of these systems is composed of multiple organs, and works to perform a specific function, such as transporting nutrients and oxygen, exchanging gases, and controlling the body’s functions.
In plants, systems are also organized to perform specific functions, such as the vascular system, which transports water and nutrients throughout the plant, and the root system, which absorbs water and nutrients from the soil. Understanding the structure and function of these systems is essential to understanding how living organisms survive, grow, and reproduce.
| System | Function |
|---|---|
| Circulatory System | Transports nutrients and oxygen to cells, and removes waste products |
| Respiratory System | Exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide through the process of breathing |
| Digestive System | Breaks down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and used by the body |
| Nervous System | Controls the body's functions, including movement, sensation, and cognition |
Evolutionary Development of Organism Bodies Structure
The structure and function of organism bodies has evolved over millions of years, and is shaped by a variety of factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle. In animals, for example, the development of complex body structures, such as the eye and the brain, has allowed for the evolution of complex behaviors and cognitive abilities. In plants, the development of specialized structures, such as roots and leaves, has allowed for the evolution of complex ecosystems and interactions with the environment.
Understanding the evolutionary development of organism bodies structure is essential to understanding how living organisms have adapted to their environments, and how they have evolved over time. By studying the fossil record, comparative anatomy, and developmental biology, we can gain a deeper understanding of the evolutionary history of organism bodies, and how they have changed over time.
Comparative Anatomy
Comparative anatomy is the study of the structure and function of different organisms, and is used to understand the evolutionary relationships between different species. By comparing the anatomy of different organisms, we can identify similarities and differences, and gain a deeper understanding of how different body structures have evolved over time.
For example, the study of comparative anatomy has shown that the human eye is similar in structure and function to the eye of other vertebrates, such as fish and birds. This suggests that the eye has evolved from a common ancestor, and has been modified over time to adapt to different environments and lifestyles.
What is the basic building block of life?
+The basic building block of life is the cell, which is the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently.
What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
+The nucleus is the control center of the cell, and contains the genetic material that determines the cell's functions and characteristics.
What is the difference between a tissue and an organ?
+A tissue is a group of cells that work together to perform a specific function, while an organ is a structure that is composed of two or more types of tissue, and works to perform a specific function.
In conclusion, the study of organism bodies structure is a complex and fascinating field that seeks to understand the organization and function of living organisms. By studying the structure and function of cells, tissues, organs, and systems, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of life, and understand how living organisms survive, grow, and reproduce. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply someone who is interested in learning more about the natural world, the study of organism bodies structure is an essential part of understanding the world around us.