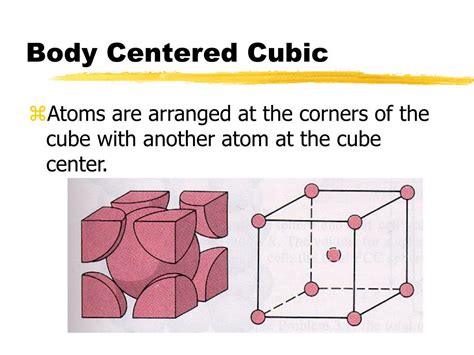
The Body Centered Cubic (BCC) structure is a fundamental concept in materials science and crystallography. It refers to a specific arrangement of atoms within a crystal lattice, where each unit cell consists of a central atom surrounded by eight neighboring atoms at the corners of a cube. This unique arrangement confers distinct properties to materials that exhibit a BCC structure, making them suitable for various applications. In this article, we will delve into five ways Body Centered Cubic works, exploring its characteristics, advantages, and real-world uses.
Key Points
- Body Centered Cubic structure enhances the strength and durability of materials due to its dense packing arrangement.
- BCC materials exhibit high thermal conductivity, making them suitable for applications where heat transfer is critical.
- The BCC structure can be found in various metals, including iron, chromium, and tungsten, each with unique properties and applications.
- Body Centered Cubic materials are often used in high-temperature applications due to their high melting points and resistance to thermal deformation.
- The BCC structure plays a crucial role in the development of advanced materials, such as nanomaterials and composites, with tailored properties for specific applications.
Crystal Structure and Properties

The Body Centered Cubic structure is characterized by its cubic unit cell, with a central atom surrounded by eight nearest neighbors at the corners of the cube. This arrangement results in a dense packing of atoms, with a packing efficiency of approximately 68%. The BCC structure is commonly found in metals, such as iron, chromium, and tungsten, which exhibit high strength, durability, and thermal conductivity. The unique arrangement of atoms in the BCC structure also confers distinct magnetic and electrical properties to these materials.
Thermal Conductivity and Applications
One of the key advantages of Body Centered Cubic materials is their high thermal conductivity. The dense packing arrangement of atoms in the BCC structure enables efficient heat transfer, making these materials suitable for applications where thermal management is critical. For example, BCC materials are often used in heat sinks, thermal interfaces, and high-temperature coatings. The high thermal conductivity of BCC materials also makes them useful in applications where rapid heat dissipation is required, such as in high-power electronics and aerospace components.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
|---|---|
| Iron (BCC) | 80 |
| Chromium (BCC) | 93 |
| Tungsten (BCC) | 173 |
High-Temperature Applications
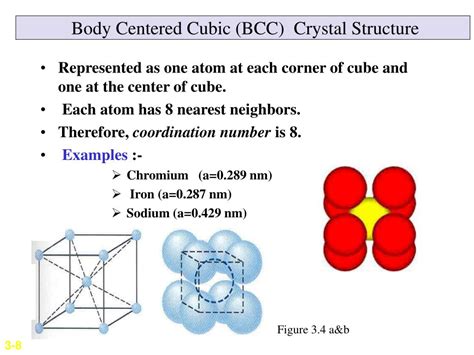
Body Centered Cubic materials are often used in high-temperature applications due to their high melting points and resistance to thermal deformation. The BCC structure is particularly stable at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for applications such as furnace components, heat exchangers, and high-temperature coatings. The high melting points of BCC materials also make them useful in applications where exposure to extreme temperatures is required, such as in aerospace and nuclear applications.
Nanomaterials and Composites
The Body Centered Cubic structure plays a crucial role in the development of advanced materials, such as nanomaterials and composites. By manipulating the BCC structure at the nanoscale, researchers can create materials with tailored properties for specific applications. For example, BCC nanomaterials have been shown to exhibit enhanced mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and optical properties. The BCC structure is also used as a template for the development of composite materials, where the unique arrangement of atoms can be used to create materials with enhanced properties.
What is the packing efficiency of the Body Centered Cubic structure?
+The packing efficiency of the Body Centered Cubic structure is approximately 68%, which is relatively high compared to other crystal structures.
What are some common applications of Body Centered Cubic materials?
+Body Centered Cubic materials are commonly used in high-temperature applications, such as furnace components, heat exchangers, and high-temperature coatings. They are also used in applications where thermal management is critical, such as in high-power electronics and aerospace components.
How does the Body Centered Cubic structure affect the properties of materials?
+The Body Centered Cubic structure confers distinct properties to materials, including high strength, durability, and thermal conductivity. The unique arrangement of atoms in the BCC structure also affects the magnetic and electrical properties of materials.
In conclusion, the Body Centered Cubic structure is a fundamental concept in materials science and crystallography, with distinct properties and applications. The BCC structure is commonly found in metals, such as iron, chromium, and tungsten, which exhibit high strength, durability, and thermal conductivity. The unique arrangement of atoms in the BCC structure also confers distinct magnetic and electrical properties to these materials, making them suitable for various applications. By understanding the properties and applications of Body Centered Cubic materials, researchers and engineers can develop new materials and technologies with tailored properties for specific applications.