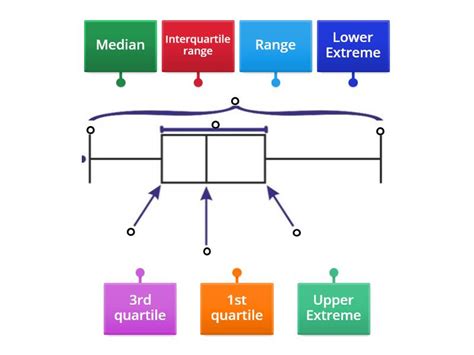
Box plots, also known as box-and-whisker plots, are a type of graphical representation used to display the distribution of a set of data. They are particularly useful for comparing the distribution of different datasets or for identifying outliers and skewness in a single dataset. A box plot typically consists of a box that represents the interquartile range (IQR), which is the difference between the 75th percentile (Q3) and the 25th percentile (Q1), and two whiskers that extend from the edges of the box to show the range of the data. Here, we will discuss 5 ways to label a box plot, enhancing its readability and utility for both novice and expert users.
Key Points
- Understanding the components of a box plot, including the median, quartiles, and whiskers.
- Labeling the axes appropriately to provide context for the data being represented.
- Including a legend to distinguish between different datasets when multiple box plots are displayed together.
- Adding numerical values to the plot for key statistics, such as the median and quartiles.
- Using annotations to highlight significant features, such as outliers or significant differences between groups.
Understanding Box Plot Components
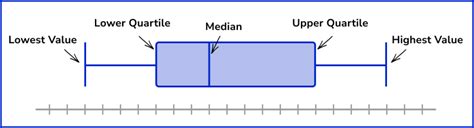
A box plot is labeled by understanding its components. The box itself represents the IQR, with the line inside the box indicating the median (50th percentile) of the data. The whiskers represent the range of the data, excluding outliers. Any data point beyond 1.5 times the IQR away from the first quartile or third quartile is considered an outlier and is plotted individually. Labeling these components clearly is essential for understanding the data distribution.
Labeling Axes and Including a Legend
For clarity, the vertical axis (y-axis) should be labeled with the unit of measurement of the data, and the horizontal axis (x-axis) should indicate the different groups or categories being compared. If multiple box plots are shown on the same graph, a legend is necessary to distinguish between them. This is particularly important in comparative studies where the goal is to visualize differences or similarities between groups.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Median | The middle value of the data when it is ordered from smallest to largest. |
| Quartiles | Divide the data into four equal parts: the first quartile (Q1), median (Q2), and third quartile (Q3). |
| Whiskers | Represent the range of the data, excluding outliers. |
| Outliers | Data points that are significantly different from other observations. |
Adding Numerical Values and Annotations

To enhance the box plot further, adding numerical values for key statistics such as the median, Q1, and Q3 can be beneficial. Annotations can also be used to highlight significant features, such as outliers that may indicate errors in data collection or interesting patterns that warrant further investigation. These additions make the box plot more informative and facilitate a deeper understanding of the data.
Best Practices for Labeling
Best practices for labeling a box plot include ensuring that all components are clearly labeled, using a legend when necessary, and providing enough context so that the plot can be understood without needing to refer to external information. Additionally, the plot should be scaled appropriately so that the data can be easily interpreted, and any annotations or additional information should be concise and relevant.
What are the main components of a box plot?
+The main components of a box plot include the box (which represents the interquartile range), the median line inside the box, and the whiskers that extend from the box to show the range of the data.
Why is labeling important in a box plot?
+Labeling is important because it provides clarity and context to the data being represented, making it easier for viewers to understand the distribution, central tendency, and dispersion of the data.
How can annotations be used in a box plot?
+Annotations can be used to highlight significant features such as outliers, to provide additional information about the data, or to draw attention to specific patterns or trends in the data.
In conclusion, labeling a box plot effectively is crucial for communicating the insights and trends within a dataset. By understanding the components of the box plot, labeling axes appropriately, including legends when necessary, adding numerical values for key statistics, and using annotations to highlight significant features, one can create a clear, informative, and useful graphical representation of data.