The electron configuration of an atom is a crucial concept in chemistry, as it determines the chemical properties and behavior of an element. In this guide, we will delve into the electron configuration of Bromine (Br), exploring its atomic structure, electron arrangement, and the implications of its configuration on its chemical properties.
Key Points
- Bromine's atomic number is 35, which means it has 35 protons and 35 electrons in its neutral state.
- The electron configuration of Bromine is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5, which indicates that the outermost energy level is partially filled.
- Bromine is a halogen, and its electron configuration is characteristic of this group, with a tendency to gain one electron to form a stable anion.
- The electron configuration of Bromine influences its chemical properties, such as its reactivity, electronegativity, and ability to form compounds.
- Understanding the electron configuration of Bromine is essential for predicting its behavior in chemical reactions and its interactions with other elements.
Introduction to Electron Configuration
Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in an atom, which is determined by the atom’s atomic number and the principles of quantum mechanics. The electron configuration of an atom is typically represented using the Aufbau principle, the Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule. These principles dictate that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels, and each energy level can hold a specific number of electrons.
Atomic Structure of Bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the atomic number 35, which means it has 35 protons in its nucleus and 35 electrons in its neutral state. The atomic structure of Bromine consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons, which are arranged in energy levels or shells. The energy levels are further divided into subshells, which are designated by the letters s, p, d, and f.
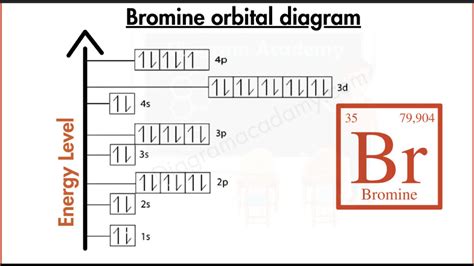
The electron configuration of Bromine can be written as [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5, which indicates that the outermost energy level is partially filled. The [Ar] notation represents the electron configuration of Argon, which is the noble gas that precedes Bromine in the periodic table. The 3d10, 4s2, and 4p5 notations represent the number of electrons in the respective subshells.
Electron Configuration and Chemical Properties
The electron configuration of Bromine has a significant impact on its chemical properties. As a halogen, Bromine has a tendency to gain one electron to form a stable anion, which is characteristic of this group. The partially filled outermost energy level of Bromine also makes it highly reactive, as it readily forms bonds with other elements to achieve a stable configuration.
The electron configuration of Bromine also influences its electronegativity, which is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond. Bromine has an electronegativity of 2.96, which is relatively high compared to other elements. This high electronegativity makes Bromine prone to forming polar covalent bonds, where the electrons are not shared equally between the atoms.
Implications of Electron Configuration on Chemical Behavior
The electron configuration of Bromine has significant implications for its chemical behavior. As a highly reactive element, Bromine readily forms compounds with other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. The electron configuration of Bromine also determines its ability to form ions, such as the bromide ion (Br-), which is a common ion in many chemical compounds.
In conclusion, the electron configuration of Bromine is a crucial aspect of its chemistry, as it determines its chemical properties and behavior. Understanding the electron configuration of Bromine is essential for predicting its behavior in chemical reactions and its interactions with other elements.
| Energy Level | Subshell | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1s | 2 |
| 2 | 2s | 2 |
| 2 | 2p | 6 |
| 3 | 3s | 2 |
| 3 | 3p | 6 |
| 3 | 3d | 10 |
| 4 | 4s | 2 |
| 4 | 4p | 5 |

FAQs
What is the electron configuration of Bromine?
+The electron configuration of Bromine is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5.
Why is Bromine highly reactive?
+Bromine is highly reactive due to its partially filled outermost energy level, which makes it prone to forming bonds with other elements to achieve a stable configuration.
What is the electronegativity of Bromine?
+The electronegativity of Bromine is 2.96, which is relatively high compared to other elements.
Meta Description: Learn about the electron configuration of Bromine, including its atomic structure, electron arrangement, and the implications of its configuration on its chemical properties. Discover how the electron configuration of Bromine influences its reactivity, electronegativity, and ability to form compounds.