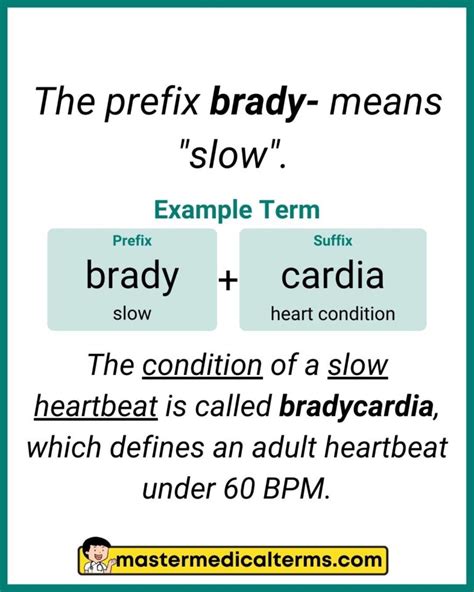
The Brady medical term refers to a condition characterized by an abnormally slow heart rate, typically defined as a rate of less than 60 beats per minute (bpm) in adults. This condition is also known as bradycardia, a term derived from the Greek words "bradys," meaning slow, and "kardia," meaning heart. Bradycardia can be a normal condition in individuals who are physically fit, such as athletes, but it can also be a sign of an underlying medical issue in others.
Key Points
- Bradycardia is a condition characterized by a heart rate of less than 60 bpm in adults.
- The condition can be normal in physically fit individuals but may indicate an underlying medical issue in others.
- Symptoms of bradycardia can include dizziness, fainting, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
- Treatment for bradycardia depends on the underlying cause and may include medication, pacemaker implantation, or other interventions.
- It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Causes and Symptoms of Bradycardia
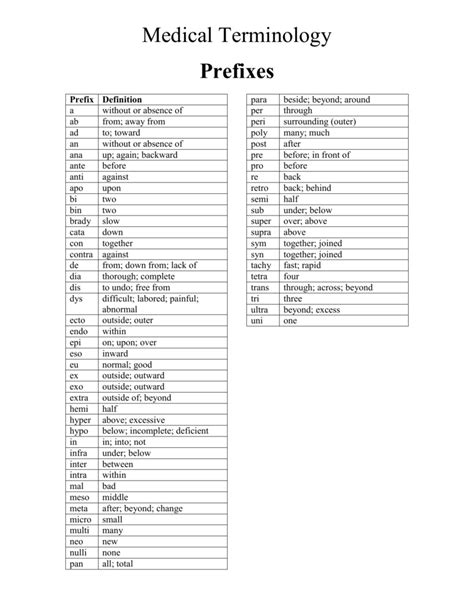
Bradycardia can be caused by a variety of factors, including a congenital heart defect, certain medications, hypothyroidism, or damage to the heart’s electrical system. Symptoms of bradycardia can vary depending on the severity of the condition but may include dizziness, fainting, fatigue, and shortness of breath. In some cases, individuals with bradycardia may not experience any symptoms at all.
Types of Bradycardia
There are several types of bradycardia, including sinus bradycardia, which is characterized by a slow heart rate originating from the sinoatrial node, and atrioventricular (AV) block, which occurs when there is a blockage in the electrical pathway between the atria and ventricles. Other types of bradycardia include sick sinus syndrome, in which the sinoatrial node does not function properly, and bundle branch block, in which there is a blockage in the electrical pathway between the atria and ventricles.
| Type of Bradycardia | Description |
|---|---|
| Sinus Bradycardia | A slow heart rate originating from the sinoatrial node. |
| Atrioventricular (AV) Block | A blockage in the electrical pathway between the atria and ventricles. |
| Sick Sinus Syndrome | The sinoatrial node does not function properly. |
| Bundle Branch Block | A blockage in the electrical pathway between the atria and ventricles. |

Treatment and Management of Bradycardia
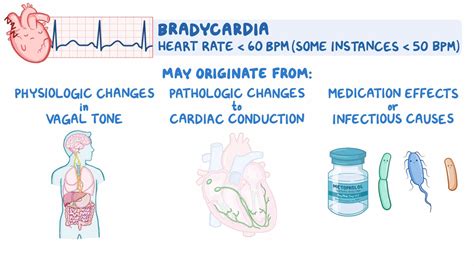
Treatment for bradycardia depends on the underlying cause of the condition. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to regulate the heart rate, while in other cases, a pacemaker may be implanted to help control the heart’s rhythm. Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding certain medications, staying hydrated, and avoiding extreme temperatures, may also be recommended.
Pacemaker Implantation
Pacemaker implantation is a common treatment for bradycardia, particularly in individuals who experience symptoms. A pacemaker is a small device that is implanted under the skin and connected to the heart via electrodes. The device emits electrical impulses that help regulate the heart’s rhythm and maintain a normal heart rate.
In conclusion, bradycardia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally slow heart rate. While it can be a normal condition in physically fit individuals, it can also be a sign of an underlying medical issue. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as untreated bradycardia can lead to serious complications. With proper treatment and management, individuals with bradycardia can lead active and healthy lives.
What is the normal heart rate for an adult?
+A normal heart rate for an adult is typically between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
What are the symptoms of bradycardia?
+Symptoms of bradycardia can include dizziness, fainting, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
How is bradycardia treated?
+Treatment for bradycardia depends on the underlying cause and may include medication, pacemaker implantation, or other interventions.