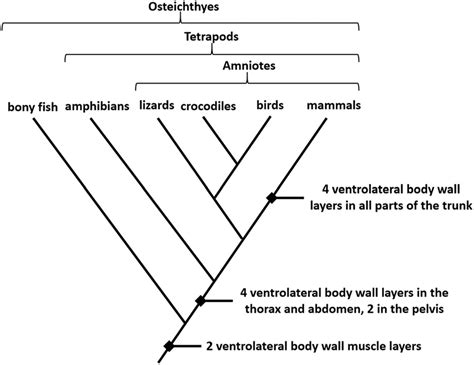
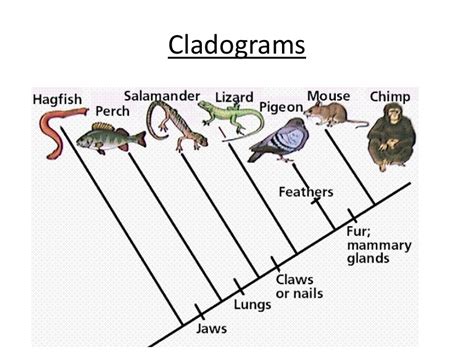
The cladogram, a fundamental tool in phylogenetics, serves as a visual representation of the relationships among different organisms based on their shared derived characteristics. This diagrammatic approach helps scientists to understand the evolutionary history and connections between various species, providing a framework for classifying living things into groups that reflect their evolutionary relationships. By analyzing the patterns of shared characteristics, researchers can infer the most likely sequence of evolutionary events that have led to the diversity of life on Earth. The cladogram's purpose is multifaceted, enabling the reconstruction of phylogenetic trees, the identification of common ancestors, and the tracing of the evolution of specific traits over time.
One of the key aspects of cladogram construction is the identification of homologous characters, which are features that are shared among different species due to a common ancestry. These characters can be morphological, such as the structure of limbs or the shape of leaves, or molecular, such as DNA or protein sequences. By comparing these characters across different species, scientists can determine which ones are most closely related and how they have evolved over time. The cladogram provides a methodical way to organize and analyze these data, allowing for the identification of clades, which are groups of organisms that share a common ancestor.
Key Points
- The cladogram is a visual tool used to represent the evolutionary relationships among different organisms.
- It is based on the analysis of shared derived characteristics, which are features that have evolved from a common ancestor.
- The cladogram helps scientists to reconstruct phylogenetic trees, identify common ancestors, and trace the evolution of specific traits.
- Homologous characters, whether morphological or molecular, are crucial for cladogram construction and phylogenetic analysis.
- The identification of clades, or groups of organisms that share a common ancestor, is a fundamental outcome of cladogram analysis.
Phylogenetic Tree Construction
The process of constructing a phylogenetic tree using a cladogram involves several steps, starting with the selection of taxa, which are the groups of organisms to be analyzed. These taxa can range from different species to higher taxonomic ranks such as genera, families, or even kingdoms. The next step involves the identification and coding of characters, which can be a time-consuming process, especially when dealing with molecular data such as DNA sequences. Each character is then analyzed to determine its state in each taxon, allowing for the construction of a data matrix that summarizes the distribution of character states across all taxa.
Once the data matrix is complete, various methods can be employed to infer the phylogenetic relationships among the taxa. These methods include parsimony, which seeks to find the tree that requires the fewest evolutionary changes, maximum likelihood, which estimates the probability of observing the data given a particular tree, and Bayesian inference, which uses Bayes' theorem to update the probability of a tree given the data. The resulting phylogenetic tree provides a hypothesis of the evolutionary relationships among the taxa, which can then be tested and refined through further analysis and the incorporation of additional data.
Cladogram Interpretation and Applications
Interpreting a cladogram requires an understanding of its components and the relationships they depict. The cladogram is typically depicted as a tree-like diagram, with the root representing the most ancient common ancestor of all the taxa included. The branches of the tree represent the evolutionary lineages, and the nodes where these branches diverge indicate the points at which different groups of organisms shared a common ancestor. The length of the branches can sometimes represent the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred, although this is not always the case.
The applications of cladograms are diverse and significant. In biology, they are essential for understanding the evolution of different traits, such as the development of wings in birds or the evolution of the horse. In medicine, cladograms can be used to trace the spread of diseases and understand the evolutionary relationships among different strains of pathogens. In conservation biology, cladograms can help identify species that are most in need of protection by highlighting their unique evolutionary positions and the potential loss of biodiversity if they become extinct.
| Phylogenetic Analysis Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Parsimony | Seeks the tree that requires the fewest evolutionary changes. |
| Maximum Likelihood | Estimates the probability of observing the data given a particular tree. |
| Bayesian Inference | Uses Bayes' theorem to update the probability of a tree given the data. |

Evolutionary Implications and Future Directions

The study of cladograms and phylogenetic trees has profound implications for our understanding of evolution and the natural world. By tracing the evolutionary history of different species, scientists can gain insights into the processes that have shaped the diversity of life on Earth. This knowledge can also inform strategies for conservation, as understanding the evolutionary relationships among different species can help identify those that are most unique and in need of protection.
Looking to the future, advances in technology and methodology are expected to continue to enhance the field of phylogenetics. The increasing availability of genomic data, for example, is providing unprecedented detail about the evolutionary relationships among different organisms. Additionally, new methods for analyzing these data, such as machine learning algorithms, are being developed to improve the accuracy and efficiency of phylogenetic analysis. As these advances continue, the study of cladograms and phylogenetic trees will remain a vibrant and dynamic field, offering new insights into the evolution of life on Earth and our place within the natural world.
What is the primary purpose of a cladogram in biology?
+The primary purpose of a cladogram is to visually represent the evolutionary relationships among different organisms based on their shared derived characteristics, helping scientists to understand the evolutionary history and connections between various species.
How are homologous characters used in cladogram construction?
+Homologous characters, which are features shared among different species due to a common ancestry, are crucial for cladogram construction. They can be morphological or molecular and are used to determine the evolutionary relationships among taxa, allowing for the identification of clades and the reconstruction of phylogenetic trees.
What are some of the applications of cladograms in different fields?
+Cladograms have diverse applications, including in biology for understanding trait evolution, in medicine for tracing disease spread, and in conservation biology for identifying species in need of protection. They provide a framework for understanding evolutionary relationships, which can inform strategies in these and other fields.