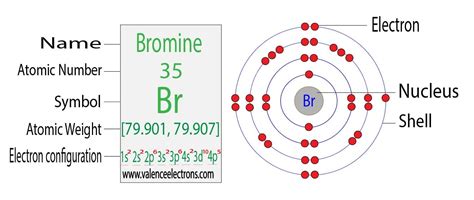
The bromine electron configuration is a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the arrangement of electrons in a bromine atom. To understand this configuration, it's essential to delve into the basics of atomic structure and electron arrangement. Bromine, with its atomic number of 35, is a halogen located in group 17 of the periodic table. Its electron configuration plays a crucial role in determining its chemical properties and reactivity.
Introduction to Electron Configuration
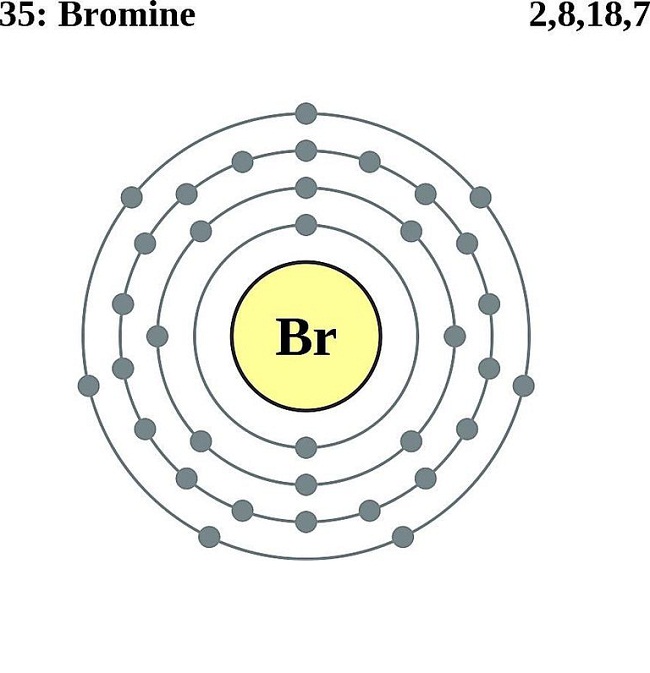
Electron configuration refers to the distribution of electrons in an atom’s orbitals. It’s a way of describing how the electrons are arranged around the nucleus, which consists of protons and neutrons. The electron configuration is typically written in a shorthand notation, which indicates the energy level (or shell) and the type of orbital (s, p, d, f) where the electrons are located. Understanding electron configuration is vital for predicting an element’s chemical behavior, including its ability to form bonds with other elements.
Bromine’s Position in the Periodic Table
Bromine is situated in the seventh row and the seventeenth column of the periodic table. Its position provides clues about its electron configuration, particularly the outermost energy level, which is crucial for chemical reactivity. As a halogen, bromine has seven electrons in its outermost shell, making it highly reactive and prone to forming a single covalent bond with other atoms to achieve a stable noble gas configuration.
| Element | Atomic Number | Group | Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bromine | 35 | 17 | 4 |
Key Points
- Bromine's atomic number is 35, indicating it has 35 protons and 35 electrons in a neutral atom.
- Its position in group 17 of the periodic table signifies that it has seven electrons in its outermost energy level.
- The electron configuration of bromine is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5, following the Aufbau principle and the Pauli Exclusion Principle.
- Bromine's reactivity is high due to its tendency to gain one electron to achieve a stable noble gas configuration, similar to that of krypton.
- The understanding of bromine's electron configuration is crucial for predicting its chemical properties and reactions.
Electron Configuration of Bromine
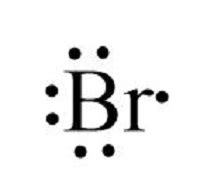
The electron configuration of bromine can be determined by following the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill the lowest available energy levels. Starting from the lowest energy level, the configuration is as follows: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p5. This configuration can also be written in a condensed form as [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5, where [Ar] represents the electron configuration of argon, the noble gas that precedes bromine in the periodic table.
Understanding the Electron Configuration Notation
The notation [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5 signifies that bromine’s electrons are arranged as follows: the inner electrons are arranged like those of argon (a stable noble gas configuration), and the outer electrons are in the 3d, 4s, and 4p orbitals, with 10 electrons in the 3d orbital, 2 in the 4s, and 5 in the 4p. This specific arrangement of electrons is what gives bromine its unique chemical properties and reactivity.
Chemical Properties and Reactivity
Bromine’s chemical properties and reactivity are significantly influenced by its electron configuration. With seven electrons in its outermost shell, bromine is highly reactive and tends to form a single covalent bond with other atoms to achieve a stable noble gas configuration. This reactivity makes bromine useful in a variety of applications, including the manufacture of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and flame retardants. Additionally, bromine’s ability to form compounds with other elements is crucial in many industrial and biological processes.
Applications of Bromine
Bromine and its compounds have numerous applications across various industries. In the chemical industry, bromine is used as a reactant and intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals. In the pharmaceutical industry, bromine is used in the production of certain medications. Furthermore, bromine compounds are used as disinfectants in swimming pools and as flame retardants in textiles and plastics, highlighting the diversity of bromine’s applications and the importance of its electron configuration in determining its chemical properties.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Synthesis | Bromine serves as a reactant and intermediate in producing other chemicals. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Bromine is used in the synthesis of certain medications. |
| Disinfectants | Bromine compounds are used to disinfect swimming pools. |
| Flame Retardants | Bromine compounds are used to reduce the flammability of materials. |
What is the electron configuration of bromine?
+The electron configuration of bromine is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5.
Why is bromine highly reactive?
+Bromine is highly reactive because it has seven electrons in its outermost shell, making it prone to forming a single covalent bond with other atoms to achieve a stable noble gas configuration.
What are some common applications of bromine?
+Bromine and its compounds are used in the chemical industry, pharmaceuticals, as disinfectants in swimming pools, and as flame retardants in textiles and plastics.
In conclusion, the electron configuration of bromine is a critical aspect of its chemical properties and reactivity. Understanding this configuration is essential for predicting how bromine will behave in different chemical reactions and for appreciating its role in various industrial and biological processes. As research and technology continue to evolve, the importance of bromine and its compounds in innovative applications will likely grow, underscoring the need for a deep understanding of its electron configuration and chemical properties.