The molar mass of a compound is a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the mass of one mole of that substance. In the case of calcium fluoride (CaF2), understanding its molar mass is crucial for various chemical calculations and applications. The molar mass of CaF2 can be determined by summing the atomic masses of its constituent elements: calcium (Ca) and fluorine (F). Here, we will delve into the calculation of the molar mass of CaF2 and explore its significance in different contexts.
Understanding Atomic Masses

To calculate the molar mass of CaF2, we first need to know the atomic masses of calcium and fluorine. The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the isotopes of that element. For calcium, the atomic mass is approximately 40.078 g/mol, and for fluorine, it is about 18.998 g/mol. Given that CaF2 consists of one calcium atom and two fluorine atoms, we can proceed to calculate its molar mass.
Calculation of Molar Mass
The molar mass of CaF2 is calculated as follows: the atomic mass of one calcium atom (40.078 g/mol) plus the atomic mass of two fluorine atoms (2 * 18.998 g/mol). This calculation yields a molar mass of 40.078 g/mol + 37.996 g/mol = 78.074 g/mol for CaF2.
| Element | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Number of Atoms in CaF2 | Total Mass Contribution (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium (Ca) | 40.078 | 1 | 40.078 |
| Fluine (F) | 18.998 | 2 | 37.996 |
| Total | - | - | 78.074 |
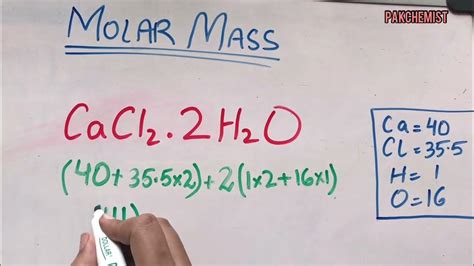
Applications and Significance

The molar mass of CaF2 has various applications in chemistry and materials science. Calcium fluoride is used in a range of industries, from optics to electronics, due to its unique properties such as its transparency over a wide range of wavelengths and its high melting point. Knowing the molar mass of CaF2 is essential for calculating the amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions involving this compound, as well as for determining its concentration in solutions.
Practical Considerations
In practical terms, the molar mass of CaF2 is crucial for the synthesis of materials that incorporate calcium fluoride. For instance, in the production of fluorescent lighting, CaF2 is used as a host material for europium, which emits light. The precise control of the molar ratios of the components is critical for achieving the desired optical properties, making the molar mass of CaF2 a key piece of information.
Key Points
- The molar mass of CaF2 is calculated by summing the atomic masses of one calcium atom and two fluorine atoms.
- The atomic mass of calcium is approximately 40.078 g/mol, and that of fluorine is about 18.998 g/mol.
- The molar mass of CaF2 is approximately 78.074 g/mol.
- Understanding the molar mass of CaF2 is essential for various chemical calculations and applications, including the synthesis of materials and the determination of concentrations in solutions.
- The compound has unique properties, such as transparency over a wide range of wavelengths and a high melting point, making it valuable in industries like optics and electronics.
The calculation and understanding of the molar mass of compounds like CaF2 underscore the importance of fundamental principles in chemistry. By grasping these concepts, scientists and engineers can develop new materials and technologies with specific properties, driving innovation in various fields.
What is the significance of the molar mass of CaF2 in chemical reactions?
+The molar mass of CaF2 is crucial for calculating the amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions, ensuring stoichiometric ratios are maintained for optimal reaction conditions and product yields.
How is the molar mass of CaF2 applied in materials science?
+The molar mass of CaF2 is essential in materials science for the synthesis of compounds with specific properties, such as in the production of fluorescent materials where CaF2 acts as a host for activator ions like europium.
What role does the atomic mass of constituent elements play in determining the molar mass of CaF2?
+The atomic masses of calcium and fluorine are directly used to calculate the molar mass of CaF2, with the atomic mass of one calcium atom and two fluorine atoms being summed to obtain the total molar mass of the compound.