Acceleration, a fundamental concept in physics, is often misunderstood as being solely positive. However, acceleration can indeed be negative, and this concept is crucial in understanding various physical phenomena. To grasp this idea, it's essential to revisit the definition of acceleration and explore its implications in different contexts. Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity, which can be positive, negative, or even zero. The direction of acceleration is determined by the direction of the force applied to an object.
Negative Acceleration: A Conceptual Framework
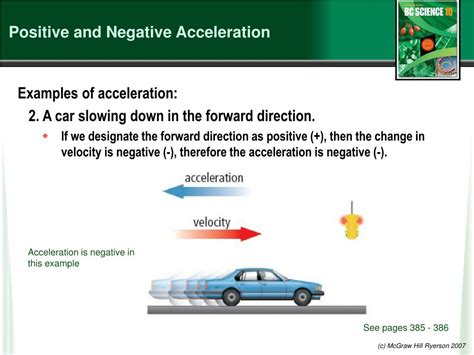
Negative acceleration, also known as deceleration or retardation, occurs when an object’s velocity decreases over time. This happens when a force is applied in the opposite direction of the object’s motion, causing it to slow down. For instance, when a car brakes, the acceleration is negative because the force of friction acts in the opposite direction of the car’s motion, reducing its velocity. Similarly, when a projectile is launched upwards, the acceleration due to gravity is negative, as it opposes the upward motion of the projectile.
Mathematical Representation of Negative Acceleration
In mathematical terms, acceleration is represented as a vector quantity, with both magnitude and direction. The direction of acceleration is indicated by the sign of the acceleration value, with positive acceleration representing an increase in velocity and negative acceleration representing a decrease. For example, if an object is moving at a velocity of 10 m/s and is slowing down at a rate of 2 m/s², its acceleration would be -2 m/s², indicating negative acceleration.
| Acceleration Type | Velocity Change | Force Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Acceleration | Increases | Same as velocity |
| Negative Acceleration (Deceleration) | Decreases | Opposite to velocity |

Key Points
- Acceleration can be negative, representing a decrease in velocity.
- Negative acceleration occurs when a force is applied in the opposite direction of an object's motion.
- The mathematical representation of acceleration uses vectors, with the sign indicating the direction of acceleration.
- Negative acceleration is essential in understanding physical phenomena, such as braking systems in vehicles.
- Recognizing negative acceleration is crucial in designing efficient and safe systems in various fields, including engineering.
Real-World Applications of Negative Acceleration
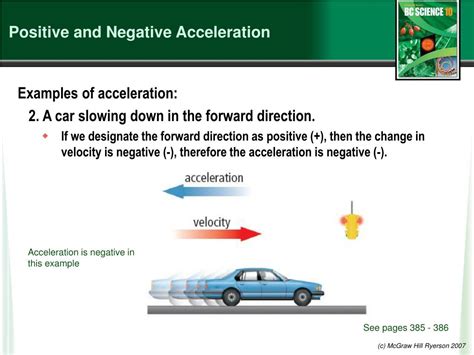
Negative acceleration has numerous real-world applications, from everyday life to complex engineering systems. In the context of transportation, negative acceleration is vital in designing safe and efficient braking systems. For instance, anti-lock braking systems (ABS) rely on the concept of negative acceleration to prevent wheels from locking up during hard braking, ensuring vehicle stability and control. Similarly, in the aerospace industry, negative acceleration plays a critical role in the design of rocket propulsion systems, where it’s essential to manage the deceleration of spacecraft during re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere.
Biological Systems and Negative Acceleration
Biological systems also exhibit negative acceleration in various contexts. For example, during muscle contraction, the acceleration of the muscle fibers can be negative, as they slow down the movement of the joint. This negative acceleration is essential for maintaining control and stability during movement. Furthermore, in the context of neuroscience, negative acceleration is relevant in understanding the mechanisms of motor control, where the brain must regulate the acceleration of muscles to achieve precise movements.
In conclusion, negative acceleration is a fundamental concept in physics, with far-reaching implications in various fields, from engineering to biology. By understanding and recognizing the concept of negative acceleration, we can design more efficient and safe systems, as well as gain insights into the intricate mechanisms of biological systems. As we continue to explore and push the boundaries of human knowledge, the concept of negative acceleration will remain a crucial aspect of our understanding of the physical world.
What is the difference between positive and negative acceleration?
+Positive acceleration represents an increase in velocity, while negative acceleration represents a decrease in velocity. The direction of acceleration determines whether it’s positive or negative, with positive acceleration occurring when the force is applied in the same direction as the velocity, and negative acceleration occurring when the force is applied in the opposite direction.
Can negative acceleration be observed in everyday life?
+Yes, negative acceleration is commonly observed in everyday life. For example, when a car brakes, the acceleration is negative, as the force of friction acts in the opposite direction of the car’s motion, reducing its velocity. Similarly, when a person slows down while walking or running, their acceleration is negative, as their velocity decreases over time.
What are the implications of negative acceleration in engineering design?
+Negative acceleration has significant implications in engineering design, particularly in the development of braking systems, rocket propulsion systems, and other applications where deceleration is critical. By understanding and managing negative acceleration, engineers can create more efficient, safe, and reliable systems that meet the demands of various industries and applications.