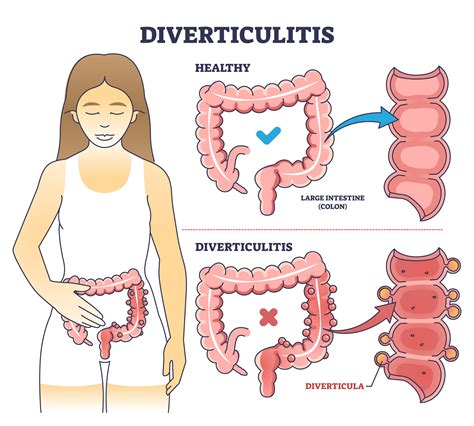
Diverticulitis, a condition characterized by the inflammation of diverticula in the digestive tract, primarily affects the large intestine. The diverticula are small, bulging pouches that can form in the walls of the intestine, and when they become inflamed, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including severe abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, and fever. One of the lesser-known symptoms of diverticulitis is back pain, which can be a source of confusion for both patients and healthcare providers. In this article, we will explore the relationship between diverticulitis and back pain, discussing the possible causes, diagnostic challenges, and treatment options.
Key Points
- Diverticulitis can cause back pain due to the proximity of the inflamed diverticula to the back muscles and nerves.
- The location and severity of the back pain can vary depending on the site of the inflamed diverticula.
- Diagnosing diverticulitis as the cause of back pain can be challenging and requires a comprehensive medical evaluation.
- Treatment options for diverticulitis-induced back pain include antibiotics, pain management, and in severe cases, surgery.
- Preventing diverticulitis through a high-fiber diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of developing back pain associated with this condition.
Understanding Diverticulitis and Back Pain
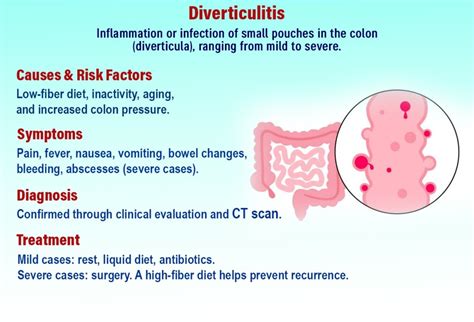
The exact mechanism by which diverticulitis causes back pain is not fully understood, but several theories have been proposed. One possibility is that the inflammation of the diverticula can irritate the surrounding muscles and nerves, leading to referred pain in the back. The location of the back pain can provide clues about the site of the inflamed diverticula, with pain in the lower back often associated with diverticula in the sigmoid colon.
Diagnostic Challenges
Diagnosing diverticulitis as the cause of back pain can be challenging due to the non-specific nature of the symptoms. Back pain is a common complaint with many possible causes, and diverticulitis is often not considered as a potential cause until other more common conditions have been ruled out. A comprehensive medical evaluation, including a physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies such as CT scans or MRI, is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of diverticulitis.
| Diagnostic Test | Description |
|---|---|
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | A blood test to check for signs of infection or inflammation. |
| CT Scan | An imaging test to visualize the diverticula and assess the extent of inflammation. |
| Colonoscopy | A procedure to visually examine the inside of the colon and rectum for diverticula. |
Treatment Options for Diverticulitis-Induced Back Pain
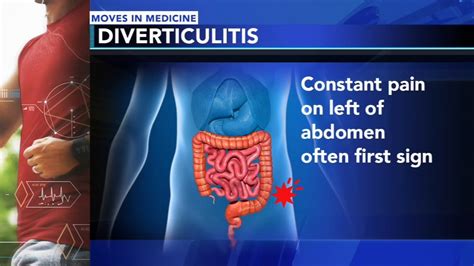
Treatment for diverticulitis-induced back pain depends on the severity of the condition and the presence of any complications. Mild cases of diverticulitis can be managed with antibiotics, pain management, and bowel rest. In more severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to receive intravenous antibiotics and fluids. In rare cases, surgery may be required to remove the affected portion of the colon.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
Preventing diverticulitis through lifestyle modifications can reduce the risk of developing back pain associated with this condition. A high-fiber diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk of diverticulitis. Additionally, avoiding foods that can irritate the digestive tract, such as spicy or fatty foods, and managing stress through techniques such as meditation or yoga can also be beneficial.
Can diverticulitis cause chronic back pain?
+Yes, diverticulitis can cause chronic back pain if left untreated or if the inflammation is severe. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe back pain.
How can I prevent diverticulitis?
+Preventing diverticulitis involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a high-fiber diet, regular exercise, and managing stress. Avoiding foods that can irritate the digestive tract and staying hydrated can also help to reduce the risk of diverticulitis.
Can diverticulitis be treated without surgery?
+Yes, mild cases of diverticulitis can be treated without surgery using antibiotics, pain management, and bowel rest. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected portion of the colon.
In conclusion, diverticulitis can cause back pain due to the inflammation of the diverticula and the proximity of the affected area to the back muscles and nerves. Diagnosing diverticulitis as the cause of back pain can be challenging and requires a comprehensive medical evaluation. Treatment options for diverticulitis-induced back pain include antibiotics, pain management, and in severe cases, surgery. Preventing diverticulitis through lifestyle modifications, such as a high-fiber diet and regular exercise, can reduce the risk of developing back pain associated with this condition. If you experience persistent or severe back pain, it is essential to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.