The question of whether octopuses can breathe air has fascinated both marine biologists and the general public for a long time. While octopuses are marine animals that live in water, they do have a unique respiratory system that allows them to extract oxygen from the water. However, this does not necessarily mean they can breathe air like humans do. To answer this question, we need to delve into the anatomy and physiology of octopuses.
Understanding Octopus Respiration

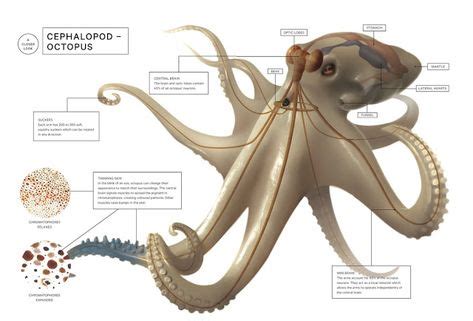
Octopuses have gills, which are specialized organs used for gas exchange in aquatic environments. These gills are highly efficient at extracting oxygen from the water, allowing octopuses to thrive in their underwater habitat. The process involves the extraction of oxygen from the water, which is then transported to the octopus’s body tissues. While this system is excellent for underwater respiration, it is not designed for breathing air.
Octopus Anatomy and Air Exposure
When an octopus is exposed to air, its gills cannot function in the same way they do underwater. Without the buoyancy and support of water, the gills collapse, and the octopus cannot efficiently exchange gases. However, octopuses have been observed to survive out of water for short periods, suggesting they have some mechanism to cope with air exposure, albeit not in the form of breathing air like terrestrial animals.
One key adaptation that allows octopuses to survive brief periods out of water is their ability to store oxygen in their bodies. This stored oxygen, combined with their slow metabolism when not actively moving, can help them survive for a short time without the need for continuous gas exchange. This is not the same as breathing air but rather a unique physiological adaptation that allows them to endure temporary exposure to air.
| Physiological Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| Oxygen Storage | Ability to store oxygen in body tissues for short-term use during air exposure |
| Slow Metabolism | Reduced metabolic rate when not actively moving, conserving stored oxygen |

Implications and Observations

Observations of octopuses moving across land or surviving out of water have led to misconceptions about their ability to breathe air. These instances, however, are rare and usually occur in specific contexts, such as moving between tide pools or escaping predators. The primary takeaway is that while octopuses can tolerate brief air exposure, they do not breathe air in the way terrestrial animals do.
Furthermore, the study of octopus behavior and physiology has broader implications for our understanding of marine life and the adaptability of species. It highlights the complexity and diversity of life in the ocean and encourages further research into the unique adaptations of marine animals.
Key Points
- Octopuses have a unique respiratory system adapted for underwater gas exchange, not for breathing air.
- Their gills are highly efficient in water but collapse and are ineffective in air.
- Octopuses can survive brief periods out of water due to oxygen storage and a reduced metabolic rate, not air breathing.
- Observations of octopuses on land are rare and usually involve specific circumstances like moving between habitats.
- Understanding octopus physiology encourages further research into marine life adaptations and diversity.
Conclusion and Future Research
In conclusion, while octopuses cannot breathe air in the traditional sense, their unique physiological adaptations allow them to survive brief exposures to air. This distinction is crucial for understanding the behavior, ecology, and conservation of these fascinating creatures. Future research should continue to explore the complex adaptations of marine animals, providing insights into the intricate relationships between species and their environments.
Can octopuses really survive out of water?
+Yes, octopuses can survive for short periods out of water due to their ability to store oxygen and reduce their metabolic rate. However, this is not the same as breathing air and is typically seen in specific contexts such as moving between tide pools.
How do octopuses breathe underwater?
+Octopuses breathe underwater using gills, which are highly efficient at extracting oxygen from the water. This process involves the extraction of oxygen from the water, which is then transported to the octopus’s body tissues.
What are the implications of octopus adaptations for marine biology research?
+The study of octopus adaptations highlights the complexity and diversity of life in the ocean, encouraging further research into the unique adaptations of marine animals and their implications for our understanding of marine ecosystems.