The relationship between yeast infections and menstrual cycles is complex, and there is ongoing debate about whether yeast infections can delay periods. To understand this potential connection, it's essential to delve into the basics of yeast infections, the menstrual cycle, and how they might interact.
Understanding Yeast Infections
Yeast infections, primarily caused by Candida albicans, are a common type of fungal infection that can affect various parts of the body, including the vagina. The symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection can include itching, burning, redness, and a thick, white discharge. These infections are more likely to occur when there is an imbalance in the natural flora of the vagina, which can be due to various factors such as antibiotic use, hormonal changes, or an impaired immune system.
Menstrual Cycle and Yeast Infections
The menstrual cycle is a delicate balance of hormonal changes that prepare the body for a potential pregnancy each month. This cycle is controlled by a complex interplay of hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, which also influence other bodily functions. The connection between yeast infections and the menstrual cycle is primarily through hormonal fluctuations. Some women may experience yeast infections more frequently during certain times of their menstrual cycle, possibly due to changes in hormone levels or the natural pH balance of the vagina.
Can Yeast Infections Delay Periods?

There is limited direct evidence to suggest that yeast infections can delay menstrual periods. However, it’s crucial to consider the broader context of how infections, including yeast infections, can impact the body. Significant stress, whether physical or emotional, can potentially affect the menstrual cycle, leading to irregularities such as delayed periods. This is because stress can influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which plays a role in regulating hormones, including those involved in the menstrual cycle.
Moreover, certain underlying conditions that predispose someone to frequent or severe yeast infections, such as diabetes or immune system disorders, might also contribute to menstrual irregularities, including delayed periods. However, these effects are more likely due to the underlying condition rather than the yeast infection itself.
Addressing Yeast Infections and Menstrual Health
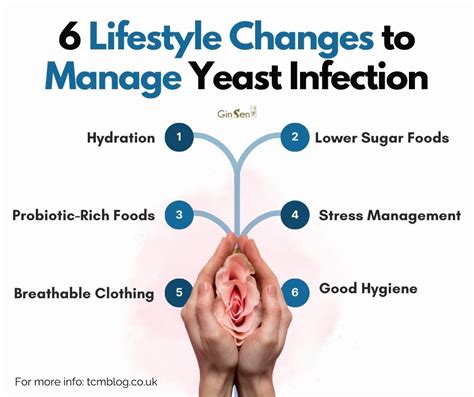
For women experiencing recurrent yeast infections or those concerned about the potential impact on their menstrual cycle, several steps can be taken. Maintaining good genital hygiene, avoiding scented soaps or douching, wearing breathable underwear, and managing stress through relaxation techniques can help prevent yeast infections. If yeast infections are recurrent or severe, consulting a healthcare provider for appropriate treatment and guidance is essential.
| Prevention Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Good Hygiene Practices | Avoiding the use of scented products and douching can help maintain the natural balance of the vagina. |
| Wearing Breathable Clothing | Choosing underwear made from natural fibers can help keep the genital area dry and reduce the risk of yeast infections. |
| Stress Management | Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help mitigate the impact of stress on the menstrual cycle. |
Key Points
- Yeast infections are primarily caused by Candida albicans and can affect the vagina, causing symptoms like itching and discharge.
- Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can influence the risk of yeast infections but are unlikely to be directly caused by them.
- Significant stress, whether from infections or other sources, can potentially impact the menstrual cycle, leading to irregularities.
- Prevention strategies such as good hygiene, breathable clothing, and stress management can help reduce the risk of yeast infections.
- Consulting a healthcare provider for recurrent or severe infections is crucial for proper treatment and guidance.
In conclusion, while there is no direct evidence that yeast infections can delay menstrual periods, the broader impact of infections and underlying health conditions on the body's hormonal balance and stress levels could potentially lead to menstrual irregularities. Maintaining good health practices, managing stress, and seeking medical advice when necessary are key to preventing and treating yeast infections and supporting overall reproductive health.
Can yeast infections affect my menstrual cycle?
+Yeast infections themselves are unlikely to directly affect your menstrual cycle, but underlying conditions that predispose you to infections, or significant stress from recurrent infections, might lead to menstrual irregularities.
How can I prevent yeast infections?
+Practicing good genital hygiene, avoiding scented products, wearing breathable underwear, and managing stress can help prevent yeast infections.
Should I consult a doctor for a yeast infection?
+If you experience recurrent, severe, or persistent yeast infections, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.