The terms "capital" and "capitol" are often confused with one another due to their similar spellings and related meanings. However, they have distinct definitions and uses in the English language. Understanding the difference between these two words is essential for effective communication, especially in the context of geography, politics, and architecture. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, examples, and historical contexts of "capital" and "capitol" to clarify their differences and provide a comprehensive guide on their usage.
Key Points
- The term "capital" refers to a city or town that serves as the seat of government, while also denoting wealth or assets.
- "Capitol" specifically refers to a building where a government's legislative body meets, such as the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C.
- Historical context plays a significant role in the development and usage of these terms.
- Understanding the difference between "capital" and "capitol" is crucial for clear and accurate communication in various fields.
- Correct usage of these terms can enhance the credibility and professionalism of written and spoken language.
Definition and Usage of “Capital”

The word “capital” has a broader range of meanings compared to “capitol”. Primarily, it refers to the city or town that serves as the seat of government for a country, state, or province. For instance, Paris is the capital of France, and Sacramento is the capital of California. Beyond its geographical significance, “capital” also denotes wealth, funds, or assets, especially when referring to financial or business contexts. For example, a company’s capital might include its cash reserves, investments, and property. This dual meaning of “capital” underscores its importance in both political and economic spheres.
Historical Context of “Capital”
Historically, the concept of a capital city has been integral to the development of civilizations. The designation of a capital often symbolizes the centralization of power, administration, and culture. The choice of a capital city can be influenced by strategic, economic, and symbolic factors. For instance, the founding of Washington, D.C., as the capital of the United States was a deliberate decision to create a neutral federal district that would not favor any particular state. Understanding the historical context of capital cities can provide insights into the political, social, and economic dynamics of a region.
Definition and Usage of “Capitol”
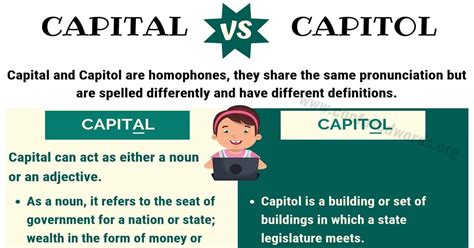
In contrast to “capital”, the term “capitol” has a more specific and limited usage. It refers to the building where a government’s legislative body meets. The most well-known example is the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C., which is the seat of the U.S. Congress. State capitols are the buildings where state legislatures convene. The capitol building often serves as a symbol of the government’s authority and the democratic process. It’s worth noting that while “capitol” always refers to a specific building, “capital” can refer to both a city and financial assets, making the distinction between the two terms crucial for clarity.
Architectural Significance of Capitols
Capitol buildings are not only significant for their political function but also for their architectural and historical value. Many capitol buildings are designed to reflect the history, values, and architectural styles of their respective regions. For example, the United States Capitol features a central dome that symbolizes the unity of the states, while the Texas State Capitol in Austin boasts a stunning Renaissance Revival style. The design and construction of capitol buildings often involve careful consideration of symbolic, functional, and aesthetic factors, making them unique landmarks in their respective capitals.
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital | City or town that serves as the seat of government; wealth or assets | Paris, the capital of France; a company's capital |
| Capitol | Building where a government's legislative body meets | United States Capitol; state capitol |

Conclusion and Future Implications
In conclusion, the terms “capital” and “capitol” are distinct and serve different purposes in the English language. While “capital” encompasses a broader range of meanings, including geographical and financial contexts, “capitol” specifically refers to the building housing a legislative body. The historical, architectural, and symbolic significance of these terms underscores their importance in understanding political, economic, and cultural phenomena. As language continues to evolve, maintaining the distinction between “capital” and “capitol” will remain crucial for clear and effective communication across various disciplines.
What is the primary difference between “capital” and “capitol”?
+The primary difference lies in their definitions: “capital” refers to a city or town that serves as the seat of government or denotes wealth, while “capitol” specifically refers to the building where a government’s legislative body meets.
Can “capital” and “capitol” be used interchangeably in any context?
+No, they cannot be used interchangeably. Using the correct term is essential for clarity and accuracy, especially in formal or professional contexts.
What are the implications of misunderstanding the difference between “capital” and “capitol”?
+Misunderstanding the difference can lead to confusion, miscommunication, and a lack of credibility in written or spoken language, particularly in fields where precision is paramount, such as politics, economics, and architecture.


