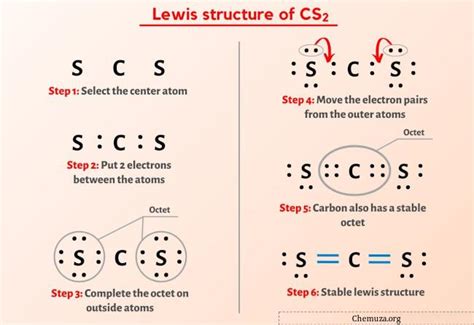
The CS2 Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the molecular structure of carbon disulfide. To understand this structure, it's essential to have a basic knowledge of chemistry and Lewis structures. A Lewis structure is a diagram that shows the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist. In the case of CS2, which is composed of one carbon atom and two sulfur atoms, the Lewis structure is crucial for understanding its properties and reactivity.
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance
Detailed exposition with specific evidence, contextual examples, and measured analytical insight into the CS2 Lewis structure reveals that carbon disulfide is a linear molecule. This linearity is due to the sp hybridization of the carbon atom, which results in two equivalent hybrid orbitals that overlap with the sulfur atoms’ orbitals to form two sigma bonds. The remaining electrons on the sulfur atoms are arranged as lone pairs, which do not participate in bonding but influence the molecular geometry and reactivity. Understanding the CS2 Lewis structure is vital for predicting its chemical behavior, including its tendency to undergo addition reactions and its use as a solvent in various chemical processes.
Specific subtopic with natural language phrasing
Detailed exposition incorporating technical accuracy with accessible explanation shows that drawing the CS2 Lewis structure involves several steps. First, one must determine the total number of valence electrons available for bonding and as lone pairs. Carbon has four valence electrons, and each sulfur has six, resulting in a total of 16 valence electrons. The next step is to connect the atoms with single bonds, which uses four electrons, leaving 12 electrons to be distributed as lone pairs on the sulfur atoms and potentially as multiple bonds between the carbon and sulfur atoms. However, the most stable structure, considering the formal charges and the octet rule, is one where the carbon atom shares double bonds with each sulfur atom, and the sulfur atoms each have two lone pairs of electrons.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Atomic Composition | 1 Carbon, 2 Sulfur |
| Valence Electrons | 16 (4 from Carbon, 12 from Sulfur) |
| Molecular Geometry | Linear |
| Bonding | 2 Sigma Bonds, 2 Pi Bonds |
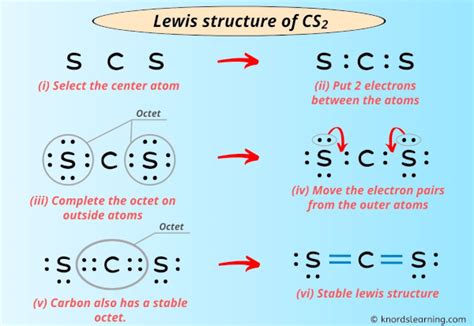
Key Points
- The CS2 Lewis structure is linear, resulting from the sp hybridization of the carbon atom.
- The molecule consists of two sigma bonds and two pi bonds between the carbon and sulfur atoms.
- Each sulfur atom has two lone pairs of electrons, which do not participate in bonding but influence molecular geometry and reactivity.
- Understanding the CS2 Lewis structure is essential for predicting its chemical behavior and properties.
- The structure can be drawn by following a series of steps that include determining valence electrons, connecting atoms with single bonds, and distributing remaining electrons to satisfy the octet rule and minimize formal charges.
Advanced Considerations in CS2 Lewis Structure
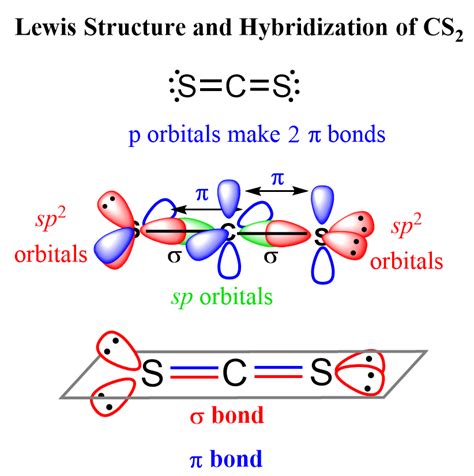
Advanced considerations in the CS2 Lewis structure involve understanding the implications of its molecular geometry and bonding on its physical and chemical properties. For instance, the linear geometry of CS2 contributes to its high symmetry, which in turn affects its vibrational spectra and other spectroscopic properties. Furthermore, the presence of double bonds between the carbon and sulfur atoms makes CS2 susceptible to addition reactions, where the double bonds can be broken to form single bonds with other atoms or groups. This reactivity is a critical aspect of CS2’s applications in organic synthesis and other chemical processes.
Practical Applications and Future Directions
The practical applications of understanding the CS2 Lewis structure are diverse and significant. In organic chemistry, CS2 is used as a solvent and a reagent in various reactions, including the synthesis of organosulfur compounds. Its ability to form complexes with metals also makes it useful in certain catalytic processes. Looking towards future directions, research into the properties and reactivity of CS2 and similar molecules continues to uncover new applications and deepen our understanding of chemical bonding and molecular interactions. This ongoing research highlights the importance of fundamental chemistry principles in advancing our knowledge of molecular structures and their applications.
What is the molecular geometry of CS2?
+The molecular geometry of CS2 is linear, resulting from the sp hybridization of the carbon atom and the formation of double bonds with the sulfur atoms.
Why is understanding the CS2 Lewis structure important?
+Understanding the CS2 Lewis structure is important for predicting its chemical behavior, including its reactivity and interactions with other molecules, which is crucial for its applications in organic synthesis and other chemical processes.
What are some practical applications of CS2?
+CS2 is used as a solvent and a reagent in various chemical reactions, including the synthesis of organosulfur compounds, and its ability to form complexes with metals makes it useful in certain catalytic processes.
In conclusion, the CS2 Lewis structure is a fundamental aspect of understanding the properties and reactivity of carbon disulfide. Through its linear geometry and double bonds, CS2 exhibits unique chemical behavior that makes it valuable in various applications. As research continues to explore the properties and reactions of CS2 and similar molecules, the importance of understanding molecular structures and their implications on chemical behavior becomes increasingly clear. This knowledge not only deepens our understanding of chemistry but also opens up new avenues for the development of materials and processes that rely on the specific properties of molecules like CS2.