Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that can be deadly in high concentrations. It is produced by the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, such as gasoline, natural gas, and propane, and can be found in various environments, including homes, vehicles, and industrial settings. The importance of detecting and measuring CO levels cannot be overstated, as prolonged exposure to this gas can lead to serious health effects, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, and even death. In this article, we will delve into the world of carbon monoxide testing, exploring the different methods and devices used to detect and measure CO levels, as well as the importance of regular testing and maintenance.
Understanding Carbon Monoxide Poisoning

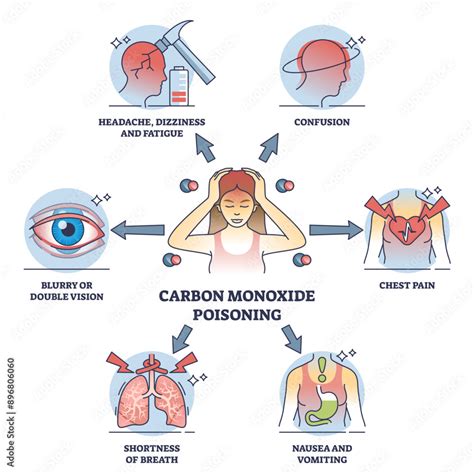
Carbon monoxide poisoning occurs when CO is inhaled and binds to hemoglobin in the blood, forming carboxyhemoglobin (COHb). This binding process reduces the amount of oxygen that can be carried to the body’s tissues, leading to hypoxia and potentially serious health effects. The symptoms of CO poisoning can be non-specific and may resemble those of other conditions, such as the flu or food poisoning. However, if you suspect that you or someone else has been exposed to CO, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. In severe cases, CO poisoning can cause long-term health effects, including brain damage, heart problems, and even death.
Methods of Carbon Monoxide Testing
There are several methods of carbon monoxide testing, each with its own advantages and limitations. Some of the most common methods include:
- Biomarker testing: This involves measuring the levels of COHb in the blood, which can indicate the extent of CO exposure.
- Ambient air testing: This involves measuring the levels of CO in the air, which can help identify potential sources of CO and assess the risk of exposure.
- Device-based testing: This involves using specialized devices, such as CO detectors or meters, to measure CO levels in the air or in the blood.
| Method | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biomarker testing | Measures COHb levels in the blood | Accurate, non-invasive | Requires blood sample, may not detect acute exposure |
| Ambient air testing | Measures CO levels in the air | Quick, easy to use | May not detect intermittent or localized exposure |
| Device-based testing | Uses CO detectors or meters to measure CO levels | Convenient, real-time results | May be affected by interference or calibration issues |
Key Points
- Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that can be deadly in high concentrations.
- CO poisoning can cause serious health effects, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, and even death.
- Regular testing and maintenance are essential to detect and prevent CO exposure.
- There are several methods of carbon monoxide testing, including biomarker testing, ambient air testing, and device-based testing.
- A comprehensive approach to CO testing can help identify potential sources of CO exposure and reduce the risk of CO poisoning.
Importance of Regular Testing and Maintenance

Regular testing and maintenance are essential to detect and prevent CO exposure. This includes:
- Installing CO detectors: CO detectors can alert individuals to the presence of CO in the air and provide an early warning system for potential exposure.
- Inspecting fuel-burning appliances: Regular inspection and maintenance of fuel-burning appliances, such as furnaces and water heaters, can help identify potential sources of CO and prevent exposure.
- Testing for CO: Regular testing for CO can help identify potential sources of exposure and reduce the risk of CO poisoning.
Technical Specifications for CO Detectors
When selecting a CO detector, it is essential to consider the technical specifications, including:
- Sensitivity: The detector should be able to detect CO levels as low as 10 parts per million (ppm).
- Response time: The detector should be able to respond quickly to changes in CO levels, ideally within 1-2 minutes.
- Interference resistance: The detector should be resistant to interference from other gases and devices.
What are the symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning?
+The symptoms of CO poisoning can be non-specific and may resemble those of other conditions, such as the flu or food poisoning. Common symptoms include headaches, dizziness, nausea, and fatigue.
How can I prevent carbon monoxide exposure?
+To prevent CO exposure, it is essential to install CO detectors, inspect fuel-burning appliances regularly, and test for CO. Additionally, never use generators or fuel-burning appliances indoors, and always follow the manufacturer's instructions for use and maintenance.
What are the different types of carbon monoxide detectors?
+There are several types of CO detectors, including biomimetic, metal oxide, and electrochemical detectors. Each type has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of detector will depend on the specific application and environment.
Meta description suggestion: “Learn about the importance of carbon monoxide testing and detection, including methods, devices, and technical specifications. Get expert insights and tips on how to prevent CO exposure and reduce the risk of CO poisoning.” (145 characters)