The person-centered theory, developed by Carl Rogers, is a widely recognized and influential approach in the field of psychology. This theory emphasizes the inherent worth and dignity of individuals, and it is based on the idea that people have the capacity for self-actualization and personal growth. Rogers' person-centered theory is considered a humanistic approach, as it focuses on the individual's subjective experience and their inherent tendency towards self-actualization. In this article, we will explore the key concepts and principles of Rogers' person-centered theory, and we will examine the implications of this approach for psychotherapy and personal development.
Key Points
- Carl Rogers' person-centered theory emphasizes the importance of empathy, genuineness, and unconditional positive regard in the therapeutic relationship.
- The theory is based on the idea that individuals have the capacity for self-actualization and personal growth.
- Rogers' approach focuses on the individual's subjective experience and their inherent tendency towards self-actualization.
- The person-centered theory has been influential in the development of humanistic psychology and has been applied in various fields, including education and counseling.
- The theory emphasizes the importance of creating a supportive and non-judgmental environment, where individuals feel free to explore their thoughts and feelings.
The Core Principles of Person-Centered Theory
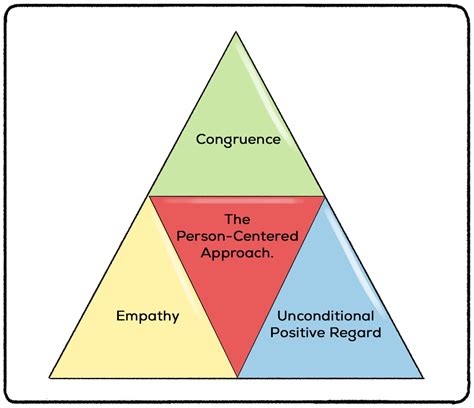
The person-centered theory is based on several core principles, including the idea that individuals have the capacity for self-actualization and personal growth. According to Rogers, people have an inherent tendency to move towards self-actualization, which is the realization of their full potential. This process is facilitated by the presence of certain conditions, such as empathy, genuineness, and unconditional positive regard. Empathy refers to the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person, while genuineness refers to the authenticity and transparency of the therapist. Unconditional positive regard refers to the acceptance and valuing of the individual, regardless of their behavior or circumstances.
The Therapeutic Relationship
The therapeutic relationship is a central component of the person-centered theory. Rogers believed that the relationship between the therapist and the client is essential for facilitating personal growth and self-actualization. The therapist’s role is to create a supportive and non-judgmental environment, where the individual feels free to explore their thoughts and feelings. The therapist’s primary goal is to provide empathy, genuineness, and unconditional positive regard, which helps to establish a sense of trust and rapport with the client. By creating a safe and supportive environment, the therapist can help the individual to feel more comfortable and confident, which can facilitate the process of self-actualization.
| Core Principles | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Empathy | The ability to understand and share the feelings of another person |
| Genuineness | The authenticity and transparency of the therapist |
| Unconditional Positive Regard | The acceptance and valuing of the individual, regardless of their behavior or circumstances |

Criticisms and Limitations

While the person-centered theory has been widely influential, it has also been subject to various criticisms and limitations. Some critics have argued that the theory is too focused on the individual’s subjective experience, and that it neglects the importance of social and cultural factors. Others have argued that the theory is too optimistic, and that it fails to account for the complexity and diversity of human experience. Additionally, some critics have argued that the theory is too vague, and that it lacks a clear and coherent framework for understanding human behavior.
Implications for Psychotherapy
The person-centered theory has been widely influential in the field of psychotherapy, and it has been applied in various forms of therapy, including individual, group, and family therapy. The theory emphasizes the importance of creating a supportive and non-judgmental environment, where individuals feel free to explore their thoughts and feelings. By focusing on the individual’s subjective experience and their inherent tendency towards self-actualization, the person-centered theory has helped to facilitate personal growth and self-actualization. However, the theory’s limitations and criticisms must also be taken into account, and therapists must be aware of the potential pitfalls and challenges of the approach.
What is the core principle of the person-centered theory?
+The core principle of the person-centered theory is the idea that individuals have the capacity for self-actualization and personal growth. This process is facilitated by the presence of certain conditions, such as empathy, genuineness, and unconditional positive regard.
What is the role of the therapist in the person-centered theory?
+The therapist's role is to create a supportive and non-judgmental environment, where the individual feels free to explore their thoughts and feelings. The therapist's primary goal is to provide empathy, genuineness, and unconditional positive regard, which helps to establish a sense of trust and rapport with the client.
What are the limitations and criticisms of the person-centered theory?
+The person-centered theory has been subject to various criticisms and limitations, including the idea that it is too focused on the individual's subjective experience, and that it neglects the importance of social and cultural factors. Others have argued that the theory is too optimistic, and that it fails to account for the complexity and diversity of human experience.
In conclusion, the person-centered theory is a widely recognized and influential approach in the field of psychology. The theory emphasizes the importance of empathy, genuineness, and unconditional positive regard in the therapeutic relationship, and it is based on the idea that individuals have the capacity for self-actualization and personal growth. While the theory has been subject to various criticisms and limitations, it remains a valuable and influential approach in the field of psychotherapy and personal development.