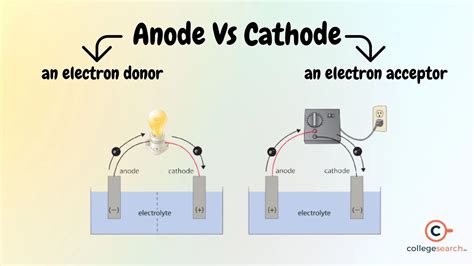
The terms cathode and anode are fundamental concepts in the realm of electrochemistry, electronics, and physics. Understanding the difference between these two terms is essential for grasping the principles of various devices and systems, including batteries, electrolysis, and semiconductors. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, roles, and applications of cathodes and anodes, highlighting their distinct characteristics and importance in different fields.
Key Points
- The cathode is the negatively charged electrode where reduction occurs, typically receiving electrons.
- The anode is the positively charged electrode where oxidation occurs, typically releasing electrons.
- The difference in charge and function between cathode and anode is crucial for the operation of batteries, electrolysis, and electronic devices.
- Understanding the cathode-anode relationship is vital for designing and optimizing electronic circuits, electrochemical systems, and energy storage devices.
- The terminology and principles related to cathodes and anodes are applied across various disciplines, including chemistry, physics, materials science, and engineering.
Definition and Function of Cathode and Anode
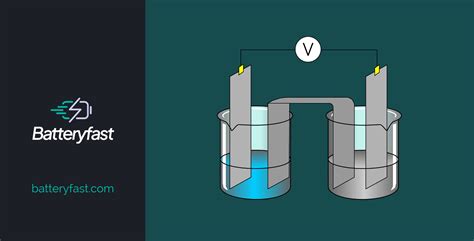
In electrochemistry, the cathode and anode are electrodes that play critical roles in the transfer of electrons. The cathode is defined as the electrode where reduction occurs, meaning it is the site where electrons are gained, typically resulting in a negative charge. Conversely, the anode is the electrode where oxidation occurs, involving the loss of electrons and usually carrying a positive charge. This fundamental difference in their functions underlies the operation of various electrochemical cells and devices.
Role in Electrochemical Reactions
During an electrochemical reaction, the cathode and anode facilitate the transfer of electrons, enabling the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa. At the cathode, reduction reactions occur, where the gain of electrons leads to the formation of a new species. In contrast, at the anode, oxidation reactions take place, involving the loss of electrons and resulting in the formation of a different species. The balanced flow of electrons between the cathode and anode is essential for maintaining the electrochemical reaction and the overall efficiency of the system.
| Electrode | Charge | Reaction Type | Direction of Electron Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cathode | Negative | Reduction | Gain Electrons |
| Anode | Positive | Oxidation | Loss of Electrons |
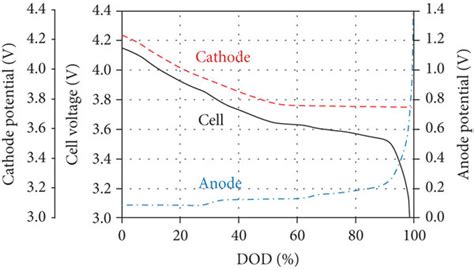
Applications in Batteries and Electrolysis

The concepts of cathode and anode are particularly relevant in the context of batteries and electrolysis. In a battery, the cathode and anode are the terminals that facilitate the flow of electrons, enabling the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy. The cathode is typically the positive terminal, while the anode is the negative terminal. During discharge, electrons flow from the anode, through the external circuit, and back to the cathode, driving the electrochemical reaction and producing electricity.
Electrolysis Process
In electrolysis, an electric current is used to drive a chemical reaction, often for the purpose of decomposing a compound into its elements. The process involves the application of an electric potential difference between the anode and cathode, causing electrons to flow through the electrolyte and facilitating the oxidation and reduction reactions at the respective electrodes. The choice of materials for the anode and cathode, as well as the conditions under which the electrolysis is performed, can significantly influence the efficiency and outcome of the process.
The understanding of cathode and anode principles is crucial for optimizing the performance of electrolysis cells, which have applications in various industries, including the production of hydrogen, the extraction of metals, and the treatment of wastewater. Moreover, the development of more efficient and sustainable electrolysis technologies relies on advancements in electrode materials and electrochemical engineering, further highlighting the importance of the cathode-anode relationship.
What is the primary difference between a cathode and an anode?
+The primary difference lies in their functions: the cathode is where reduction occurs and electrons are gained, while the anode is where oxidation occurs and electrons are lost.
How do cathodes and anodes work in batteries?
+In batteries, the cathode and anode facilitate the flow of electrons, enabling the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy. The cathode is typically the positive terminal, and the anode is the negative terminal.
What are some applications of electrolysis?
+Electrolysis has applications in the production of hydrogen, the extraction of metals, and the treatment of wastewater, among others. It involves the use of an electric current to drive chemical reactions.
In conclusion, the distinction between cathode and anode is a foundational aspect of electrochemistry and electronics, with significant implications for the design, operation, and optimization of various devices and systems. By understanding the roles and relationships of these electrodes, researchers and engineers can develop more efficient, sustainable, and innovative technologies that transform the way we generate, store, and utilize energy.