The chest tube water seal, a crucial component in the management of pleural space disorders, has been a cornerstone in thoracic surgery and critical care for decades. This simple yet effective device plays a pivotal role in the drainage of air, fluid, or blood from the pleural cavity, thereby facilitating the re-expansion of the lung and restoring normal intrathoracic pressure. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the chest tube water seal, exploring its historical development, technical specifications, clinical applications, and the nuances of its management.
Key Points
- The chest tube water seal is an essential device in thoracic surgery for managing pleural space disorders.
- It functions by creating a one-way valve system, allowing air and fluid to escape from the pleural cavity while preventing external air from entering.
- Proper setup and maintenance of the water seal are critical to prevent complications and ensure effective drainage.
- Clinical monitoring and adjustment of the water seal are necessary to adapt to changing patient conditions.
- Understanding the mechanics and clinical applications of the chest tube water seal is vital for healthcare professionals in thoracic and critical care settings.
Historical Development and Technical Specifications

The concept of using a water seal to manage pleural drainage dates back to the early 20th century, with initial designs focusing on simple, manually operated systems. Over the years, advancements in materials science and medical technology have led to the development of more sophisticated and reliable chest tube water seal devices. These modern systems typically consist of a collection chamber, a water seal chamber, and a manometer for pressure monitoring. The water seal chamber, filled with a specific volume of water, acts as a one-way valve, allowing air and fluid to exit the pleural cavity while preventing external air from entering, thus maintaining a negative intrathoracic pressure that facilitates lung re-expansion.
Clinical Applications and Management
The clinical applications of the chest tube water seal are diverse, ranging from the treatment of pneumothorax and pleural effusions to the management of post-operative thoracic surgical patients. Effective management of the chest tube water seal requires careful consideration of several factors, including the volume of water in the seal chamber, the presence of air leaks, and the patient’s respiratory mechanics. Healthcare professionals must be adept at troubleshooting common issues, such as blockages or malpositioning of the chest tube, and adjusting the water seal as necessary to maintain optimal drainage and prevent complications.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Collection Chamber | Receives drained fluid and air from the pleural cavity |
| Water Seal Chamber | Acts as a one-way valve, preventing air from entering the pleural space |
| Manometer | Monitors intrathoracic pressure and guides adjustments to the water seal |
Complications and Limitations
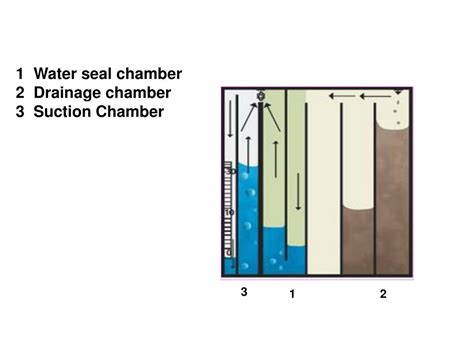
While the chest tube water seal is a highly effective tool in thoracic medicine, it is not without its complications and limitations. Common issues include blockages of the chest tube, infection, and the potential for air leaks around the tube insertion site. Furthermore, the management of the water seal can be complex, particularly in patients with persistent air leaks or those requiring high levels of negative pressure. Addressing these challenges requires a deep understanding of the underlying pathophysiology and the technical specifications of the water seal device.
Future Directions and Innovations
As medical technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see innovations in the design and functionality of chest tube water seal devices. Digital monitoring systems, for example, may offer real-time pressure and flow measurements, allowing for more precise management of pleural drainage. Additionally, the development of new materials and designs may improve the safety, efficacy, and patient comfort associated with these devices. The integration of such advancements into clinical practice will depend on rigorous testing and validation, ensuring that new technologies enhance patient outcomes without introducing unnecessary complexity or risk.
What is the primary function of the chest tube water seal?
+The primary function of the chest tube water seal is to act as a one-way valve, allowing air and fluid to escape from the pleural cavity while preventing external air from entering, thereby facilitating lung re-expansion and maintaining negative intrathoracic pressure.
How does the volume of water in the seal chamber affect the function of the chest tube water seal?
+The volume of water in the seal chamber is critical, as it determines the pressure required to open the valve and allow air or fluid to escape. Too little water may result in inadequate sealing, while too much water can increase the resistance to drainage, potentially hindering lung re-expansion.
What are common complications associated with the chest tube water seal?
+Common complications include blockages of the chest tube, infection, and air leaks around the tube insertion site. Proper setup, maintenance, and monitoring of the water seal, along with adherence to sterile technique and infection control measures, are crucial in preventing these complications.
In conclusion, the chest tube water seal is a vital component in the management of pleural space disorders, offering a simple yet effective means of facilitating lung re-expansion and restoring normal intrathoracic pressure. Through a deep understanding of its technical specifications, clinical applications, and potential complications, healthcare professionals can optimize the use of this device, ultimately improving patient outcomes in thoracic and critical care settings. As medical technology continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see further innovations in the design and functionality of chest tube water seal devices, underscoring the need for ongoing education and adaptation among healthcare providers.


