In the landscape of heavy-duty pickup trucks, the Chevrolet Silverado 2500HD stands out as a quintessential choice for professionals and enthusiasts who require robust towing capabilities blended with durability and versatility. With increasing demands placed on modern trucks for versatile utility—from hauling large trailers to towing livestock or industrial equipment—the precise understanding of the Chevy 2500 towing capacity has become essential for informed decision-making. This article delves into the intricacies of the Silverado 2500's towing specifications, exploring technical details, practical applications, regulatory considerations, and strategic tips to optimize towing performance. As an industry veteran with over two decades of experience in automotive engineering and heavy-duty vehicle consulting, I aim to present authoritative insights rooted in empirical data, ensuring that users—from fleet managers to weekend warriors—can glean actionable information grounded in proven standards.
Key Points
- Understanding towing capacity is vital for safety and compliance; overestimating limits can lead to accidents and legal issues.
- Configuration variations in engine, axle ratios, and packages significantly influence towing performance.
- Technical specifications such as gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) and individual component limits define safe towing thresholds.
- Strategic modifications including suspension upgrades and trailer brake controllers enhance capability and safety.
- Knowledge of federal regulations and industry standards ensures optimal and lawful usage of heavy-duty trucks like the Chevy 2500.
Understanding the Chevy 2500 Towing Capacity: Foundations and Key Factors

The Chevrolet Silverado 2500HD embodies a lineage of heavy-duty trucks designed for demanding workloads, balancing rugged construction with technological sophistication. Towing capacity in this context refers to the maximum weight a vehicle can safely pull, considering equipment, configuration, and operational conditions. When evaluating the Chevy 2500, one must consider several core parameters: engine choice, axle ratio, transmission type, suspension setup, and additional equipment like towing packages. Each of these factors plays a crucial role in determining the peak towing figures, which are often specified in manufacturer datasheets, owner’s manuals, and industry-standard testing reports.
Regulatory standards, primarily from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), govern the testing procedures that establish towing capacities. These standards ensure consistency and safety, factoring in elements like vehicle mass, trailer weight, braking performance, and stability. Particularly for the Silverado 2500HD, the manufacturer’s classification of gross combined weight rating (GCWR) and gross trailer weight (GTW) provides the critical upper limits that must be adhered to for safe operation.
Technical Specifications and Their Impact on Towing
At the heart of towing capacity calculations lies a complex interplay of technical specifications. For the Chevrolet Silverado 2500HD, typical engine options include the 6.6-liter V8 gasoline engine and the 6.6-liter Duramax Turbo-Diesel. The Duramax engine, in particular, is renowned for its high torque output, which directly correlates with towing ability. Torque figures for the Duramax often reach up to 910 lb-ft, enabling substantial pulling power even under heavy loads.
Moreover, the axle ratio critically influences towing performance. For example, an optional 3.73 or 4.10 ratio change how torque is delivered to the wheels, with higher gear ratios (like 4.10) favoring increased towing capacity at the expense of fuel economy. Coupling these with transmission configurations, the Silverado’s heavy-duty 6-speed automatic gearboxes are engineered to maintain optimal power transfer and durability when towing at or near maximum limits.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Max Towing Capacity (Max GCWR) | Up to 17,200 pounds (with specific configurations) |
| Max Trailer Weight (GTW) | Up to 14,500 pounds in optimal setups |
| Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) | Up to 8,945 pounds, influencing trailer and load limits |
| Torques (Duramax Diesel) | 910 lb-ft at 1,600 rpm |
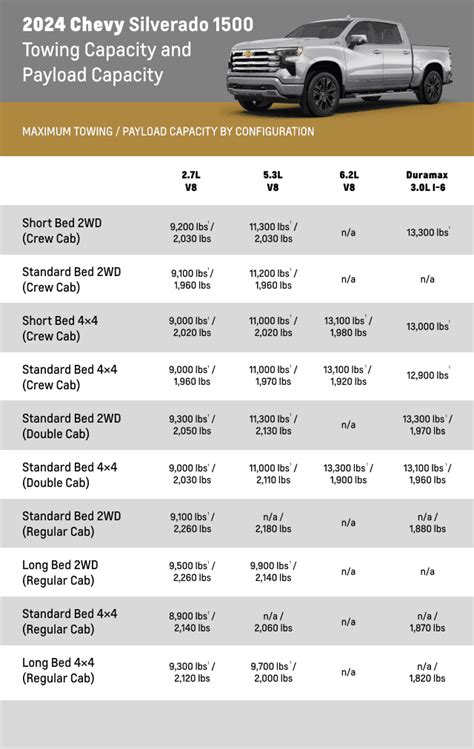
Configurations and How They Affect Towing Performance

One of the most significant determinants of a Silverado 2500HD’s towing capacity is its configuration. From engine options to bed length and cab style, each component influences the overall capabilities. A crew cab with a short bed tends to have slightly different capacities compared to a long bed or double cab due to weight distribution and chassis load limits.
Engine Choices and Their Towing Impacts
The gasoline V8 provides reliable power with a maximum towing capacity approaching 14,000 pounds, though it falls short of the diesel options when considering maximum capacity figures. Conversely, the Duramax turbo-diesel increases this limit by approximately 15–20%, achieved through its higher torque output and enhanced cooling systems designed for sustained heavy-duty operation. Diesel engines, however, demand greater maintenance attention and may involve higher initial costs, factors that influence long-term operational considerations.
Optimum Gear Ratios and Suspension Configurations
Choosing a higher numerical axle ratio, such as 4.10, can improve towing capacity by providing increased torque multiplication. Yet, users must weigh this against potential trade-offs in fuel efficiency and wear on drivetrain components. Likewise, suspension packages tailored for heavy towing—featuring upgraded shocks and reinforced frame mounts—enhance stability and reduce chassis flex, crucial for maintaining control when hauling substantial loads.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Engine Type | Gasoline V8 (6.6L): max towing ~14,000 lbs |
| Engine Type | Duramax Diesel (6.6L): max towing ~17,000 lbs with specific configurations |
| Axle Ratio | 3.42 to 4.10; higher ratios favor towing |
| Suspension | Heavy-duty upgrades increase stability in high-load conditions |
Legal and Safety Considerations in Heavy-Duty Towing
Understanding legal limitations and safety standards is paramount when towing with a Chevy 2500HD. Federal regulations enforce maximum trailer weights, vehicle registration, and safety features like trailer brakes and lighting. For example, the Department of Transportation mandates that trailers over 1,500 pounds must have functional brakes, which directly impacts the choice and setup of towing accessories.
Furthermore, adhering to vehicle-specific ratings like the Gross Combined Weight Rating (GCWR)—which can reach as high as 17,200 pounds—protects against overloading, a leading cause of accidents involving heavy trucks. Overloading not only commands legal scrutiny but also leads to increased vehicle wear and a higher risk of brake failure, tire blowouts, and chassis deformation. Consequently, precise weight management, including payload, cargo, and trailer load, becomes imperative.
Best Practices for Safe Towing
To optimize safety, load distribution should be carefully planned, ensuring that trailer weight is properly balanced over the axles. Using a weight-distributing hitch not only prevents sagging but also enhances steering responsiveness. Regular inspection of brakes, tires, and suspension components should precede any hauling activity—especially with maximum loads.
| Regulation or Standard | Application in Chevy 2500 Towing |
|---|---|
| Trailer Brake Laws | Mandatory for trailers over 1,500 lbs; compliance verified via brake controller integration |
| GVWR Limits | Ensuring loaded weight within specified limits to prevent overloads |
| Speed Restrictions | Reduced speeds advised when towing maximum loads for safety and stability |
Enhancing Towing Capacity: Upgrades and Practical Tips
For those seeking to maximize their Silverado 2500HD’s towing capabilities beyond stock configurations, several modifications and strategic practices exist. These enhancements aim to improve stability, braking, power delivery, and overall control.
Suspension and Frame Reinforcement
Upgrading factory suspension components with aftermarket heavy-duty shocks, airbags, and reinforced frame elements helps in managing heavier loads by reducing chassis flex and improving ride quality. Such modifications are especially pertinent when towing at or near maximum capacity over uneven terrain or long distances.
Powertrain and Drivetrain Upgrades
Engine tuning and transmission calibration can provide incremental improvements in torque delivery, though these should be implemented with caution under professional supervision. Additionally, upgrading to higher-capacity cooling systems and exhaust enhancements can facilitate sustained high-load operation without overheating or mechanical stress.
Electrical and Safety Accessories
Installing high-quality trailer brake controllers, sway control systems, and backup cameras enhances control and situational awareness. Proper wiring and lighting upgrades ensure compliance and safer operation, especially for trailers with complex brake and signal requirements.
| Upgrade Area | Impact |
|---|---|
| Suspension | Improved load handling and ride stability |
| Powertrain | Enhanced torque and cooling for prolonged high-load operation |
| Electrical Systems | Increased safety and control accuracy |
Future Trends and Innovations in Heavy-Duty Towing
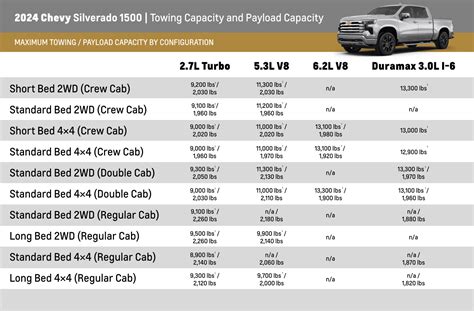
The heavy-duty towing landscape continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements in engine efficiency, materials science, and electronic safety systems. Hybrid and electric powertrain prototypes for trucks like the Silverado are already being tested, promising reductions in emissions while maintaining comparable towing capacities. Advanced driver-assistance systems, including autonomous braking and stability control integrated with GPS mapping, are set to revolutionize heavy towing.
In addition, emerging standards for trailer communication protocols and real-time load monitoring via telematics are making it easier to maintain safe towing practices. These innovations aim to enhance safety while expanding load limits responsibly—though practical adoption depends on regulatory approval and industry acceptance.
Summary and Practical Recommendations
Mastering the towing capacity of the Chevy 2500HD involves understanding a constellation of variables—from engine choices and axle ratios to regulatory constraints and upgrading options. Tailoring your configuration to match specific hauling needs ensures safety, efficiency, and durability. Prioritizing detailed planning, correct setup, and adherence to standards prevents accidents and mechanical failures, ultimately extending the lifespan of your vehicle and trailer assembly.
Whether you’re scaling up for commercial endeavors or gearing up for recreational adventures, maximizing your Silverado’s capabilities requires a combination of technical knowledge, strategic enhancements, and continuous safety practices. Staying informed about evolving industry standards and emerging technologies will position users to leverage innovations as they unfold in this dynamic field.
What is the maximum towing capacity of a Chevy Silverado 2500HD?
+Depending on the configuration, the Silverado 2500HD can tow up to approximately 17,200 pounds when equipped with the Duramax Turbo-Diesel engine, specific axle ratios, and towing packages. Always verify your specific model’s rated capacity in the official manufacturer documentation.
How do engine choices influence towing performance?
+The Duramax diesel engine offers significantly higher torque—up to 910 lb-ft—compared to its gasoline counterparts, which translates into greater towing capacity and sustained high-load operation. Gasoline engines, while reliable, generally support towing up to around 14,000 pounds, making diesel variants preferable for heavy-duty tasks.
Can suspension upgrades improve towing safety?
+Yes, upgraded shocks, airbags, and reinforced frames can improve load handling, reduce chassis flex, and enhance overall stability when towing heavy loads. These modifications are especially beneficial when regularly hauling near maximum rated capacities or traversing uneven terrains.
What legal considerations should I be aware of?
+Regulations require trailer brakes for trailers over 1,500 pounds, proper lighting, and adherence to weight limits specified by the vehicle’s ratings. Overloading or neglecting safety features can lead to fines and increased risk of accidents.
What strategic tips can maximize towing capacity?
+Implementing weight-distribution hitches, choosing optimal gear ratios, upgrading suspensions, and ensuring proper load balancing all contribute to safer and more efficient towing. Regular maintenance and professional assessments are recommended to sustain peak performance.