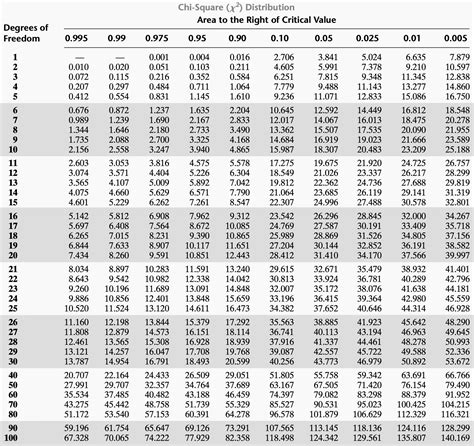
The Chi distribution, also known as the Chi-squared distribution, is a widely used probability distribution in statistics, particularly in hypothesis testing and confidence interval construction. The Chi distribution table, also known as the Chi-squared table or Chi-square distribution table, is a statistical table that provides the critical values of the Chi-squared distribution for various degrees of freedom and significance levels. In this guide, we will explore the Chi distribution table, its application, and provide a comprehensive overview of how to use it.
Understanding the Chi Distribution Table
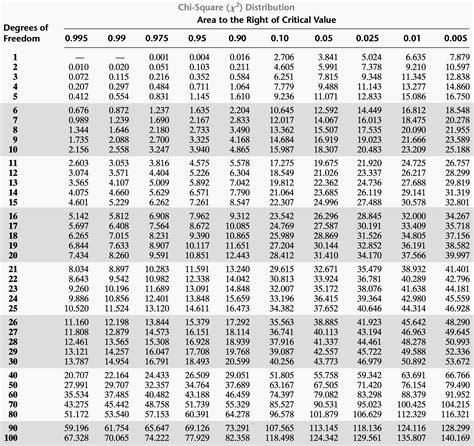
The Chi distribution table is a table of critical values that correspond to specific degrees of freedom and significance levels. The table is used to determine the critical region for a hypothesis test, which is the region where the null hypothesis is rejected. The critical values in the table are calculated using the Chi-squared distribution, which is a continuous probability distribution that is commonly used in statistical analysis.
Components of the Chi Distribution Table
A typical Chi distribution table consists of the following components:
- Degrees of freedom (df): The number of independent pieces of information used to calculate a statistic. In the context of the Chi-squared distribution, the degrees of freedom are usually denoted by the symbol k.
- Significance level (α): The probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. The significance level is usually denoted by the symbol α.
- Critical value: The value of the test statistic that corresponds to the specified significance level and degrees of freedom.
| Degrees of Freedom (df) | Significance Level (α) | Critical Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 | 3.841 |
| 2 | 0.05 | 5.991 |
| 3 | 0.05 | 7.815 |
Using the Chi Distribution Table
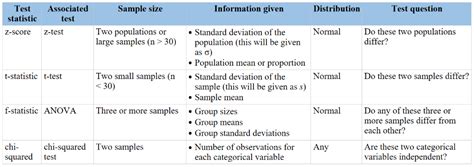
The Chi distribution table is used to determine the critical region for a hypothesis test. To use the table, follow these steps:
- Specify the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Choose a significance level (α) for the test.
- Determine the degrees of freedom (df) for the test statistic.
- Look up the critical value in the Chi distribution table that corresponds to the specified significance level and degrees of freedom.
- Compare the calculated test statistic to the critical value. If the test statistic is greater than the critical value, reject the null hypothesis.
Interpreting the Chi Distribution Table
The Chi distribution table provides critical values for various degrees of freedom and significance levels. The critical values in the table are calculated using the Chi-squared distribution, which is a continuous probability distribution. To interpret the table, follow these steps:
- Identify the degrees of freedom (df) for the test statistic.
- Choose a significance level (α) for the test.
- Look up the critical value in the Chi distribution table that corresponds to the specified significance level and degrees of freedom.
- Compare the calculated test statistic to the critical value. If the test statistic is greater than the critical value, reject the null hypothesis.
Key Points
- The Chi distribution table is a statistical table that provides critical values of the Chi-squared distribution for various degrees of freedom and significance levels.
- The table is used to determine the critical region for a hypothesis test.
- To use the table, specify the null and alternative hypotheses, choose a significance level, determine the degrees of freedom, and look up the critical value in the table.
- Interpret the table by identifying the degrees of freedom, choosing a significance level, and comparing the calculated test statistic to the critical value.
- Correct specification of the degrees of freedom and significance level is essential to ensure accurate conclusions and results.
Common Applications of the Chi Distribution Table
The Chi distribution table has numerous applications in statistical analysis, including:
- Hypothesis testing: The Chi distribution table is used to determine the critical region for a hypothesis test, which is essential in making conclusions about a population based on sample data.
- Confidence interval construction: The table is used to construct confidence intervals for population parameters, such as the population mean and proportion.
- Regression analysis: The Chi distribution table is used in regression analysis to test the significance of regression coefficients and to construct confidence intervals for the regression coefficients.
Limitations of the Chi Distribution Table
While the Chi distribution table is a powerful tool in statistical analysis, it has some limitations, including:
- Assumes normality: The Chi distribution table assumes that the data follows a normal distribution, which may not always be the case.
- Requires large sample sizes: The table requires large sample sizes to ensure accurate results.
- Does not account for non-random sampling: The table does not account for non-random sampling, which can lead to biased results.
What is the purpose of the Chi distribution table?
+The Chi distribution table is used to determine the critical region for a hypothesis test, which is essential in making conclusions about a population based on sample data.
How do I use the Chi distribution table?
+To use the table, specify the null and alternative hypotheses, choose a significance level, determine the degrees of freedom, and look up the critical value in the table.
What are the limitations of the Chi distribution table?
+The table assumes normality, requires large sample sizes, and does not account for non-random sampling, which can lead to biased results.
Meta description suggestion: “Learn how to use the Chi distribution table in statistical analysis, including hypothesis testing and confidence interval construction. Understand the components, interpretation, and limitations of the table.” (149 characters)