The Earth's circumference is a fundamental concept in geography and astronomy, representing the distance around the Earth at the equator or at any other latitude. Understanding the Earth's circumference is crucial for various applications, including navigation, cartography, and climate modeling. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate or utilize the Earth's circumference, highlighting the significance of this parameter in different fields.
Key Points
- The Earth's circumference is approximately 40,075 kilometers at the equator.
- Calculating the Earth's circumference involves using the Earth's radius or diameter.
- Different methods, such as Eratosthenes' technique, satellite imaging, and geodetic surveys, can be used to estimate the Earth's circumference.
- Understanding the Earth's circumference is essential for navigation, climate modeling, and geospatial analysis.
- Advances in technology have improved the accuracy of Earth circumference measurements over time.
Historical Method: Eratosthenes’ Technique
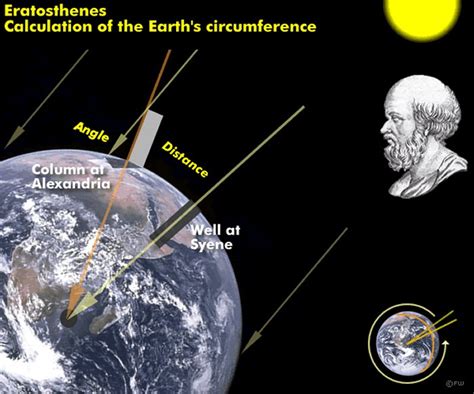
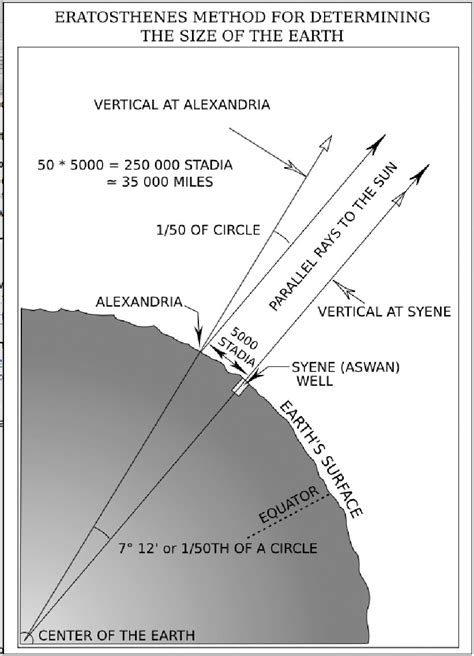
In the 3rd century BCE, the Greek mathematician Eratosthenes developed a method to estimate the Earth’s circumference. By measuring the angles of shadows cast by the Sun at different latitudes, Eratosthenes was able to calculate the circumference with remarkable accuracy. His technique involved using the angles of shadows in Alexandria and Syene (modern-day Aswan) to estimate the circumference, which he calculated to be approximately 40,000 kilometers. This method, although primitive by modern standards, demonstrated a profound understanding of the Earth’s geometry and laid the foundation for later measurements.
Geodetic Surveys and Satellite Imaging
With the advent of modern geodetic surveys and satellite imaging, the measurement of the Earth’s circumference has become increasingly accurate. Geodetic surveys involve measuring the distances and angles between reference points on the Earth’s surface, allowing for the calculation of the Earth’s shape and size. Satellite imaging, on the other hand, provides high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface, enabling the measurement of the Earth’s circumference with unprecedented accuracy. These methods have led to a refined estimate of the Earth’s circumference, which is currently accepted to be approximately 40,075 kilometers at the equator.
| Method | Estimated Circumference (km) |
|---|---|
| Eratosthenes' Technique | 40,000 |
| Geodetic Surveys | 40,069 |
| Satellite Imaging | 40,075 |
Practical Applications: Navigation and Cartography
The Earth’s circumference is a critical parameter in navigation and cartography, as it enables the calculation of distances and positions on the Earth’s surface. In navigation, the Earth’s circumference is used to determine the distance between two points on the Earth’s surface, allowing for the calculation of routes and travel times. In cartography, the Earth’s circumference is used to create accurate maps and charts, which are essential for a wide range of applications, including urban planning, natural resource management, and emergency response.
Climate Modeling and Geospatial Analysis
The Earth’s circumference is also essential in climate modeling and geospatial analysis, as it provides a fundamental parameter for understanding the Earth’s energy balance and climate dynamics. By analyzing the Earth’s circumference and its variations over time, scientists can gain insights into the Earth’s climate system and predict future changes. Additionally, the Earth’s circumference is used in geospatial analysis to study the distribution of natural resources, population dynamics, and environmental phenomena, providing valuable information for sustainable development and environmental management.
What is the significance of the Earth's circumference in navigation?
+The Earth's circumference is essential in navigation, as it enables the calculation of distances and positions on the Earth's surface, allowing for the determination of routes and travel times.
How is the Earth's circumference used in climate modeling?
+The Earth's circumference is used in climate modeling to understand the Earth's energy balance and climate dynamics, providing insights into the Earth's climate system and predicting future changes.
What are the different methods used to estimate the Earth's circumference?
+The different methods used to estimate the Earth's circumference include Eratosthenes' technique, geodetic surveys, and satellite imaging, each providing a unique approach to measuring the Earth's size and shape.
In conclusion, the Earth’s circumference is a fundamental parameter with significant implications for various fields, including navigation, cartography, climate modeling, and geospatial analysis. By understanding the Earth’s circumference and its applications, we can gain valuable insights into the Earth’s geometry, climate system, and natural resources, ultimately contributing to sustainable development and environmental management.