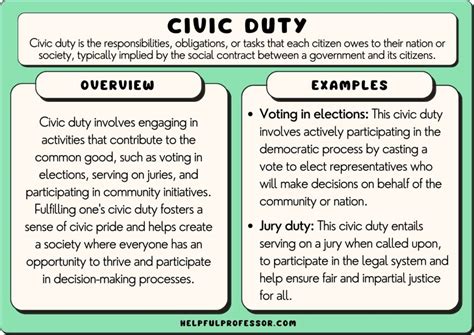
The concept of civic duty is a cornerstone of democratic societies, emphasizing the responsibility of citizens to contribute to the well-being and prosperity of their communities. At its core, civic duty encompasses a range of activities and behaviors that demonstrate a citizen's commitment to the common good. This includes participation in the electoral process, adherence to the rule of law, and engagement in voluntary service that benefits the broader community. Understanding the meaning and significance of civic duty is essential for fostering a sense of shared responsibility and promoting the health of democratic institutions.
Historically, the notion of civic duty has evolved alongside the development of democratic systems. In ancient Greece, for example, citizenship was deeply intertwined with the concept of civic responsibility, where citizens were expected to participate in the governance of the city-state. Similarly, in modern times, the idea of civic duty has been influenced by the principles of civic republicanism, which emphasizes the importance of active citizenship and the common good. Today, civic duty is recognized as a vital component of democratic citizenship, encouraging individuals to look beyond their personal interests and work towards the betterment of society as a whole.
Key Points
- Civic duty involves participation in the electoral process and adherence to the rule of law.
- Voluntary service and community engagement are crucial aspects of civic duty.
- Civic duty promotes a sense of shared responsibility and contributes to the health of democratic institutions.
- The concept of civic duty has historical roots in ancient democratic systems and continues to evolve.
- Active citizenship and the pursuit of the common good are central to the idea of civic duty.
The Components of Civic Duty
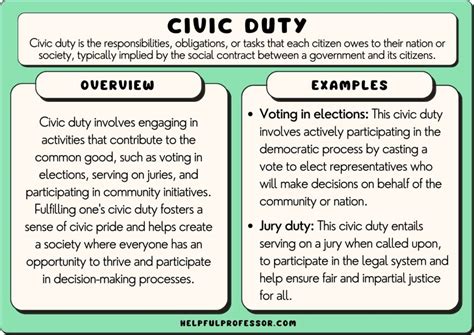
Civic duty is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various dimensions of citizen engagement. One of the primary components is political participation, which includes activities such as voting, joining political parties, and engaging in public debates. By participating in the political process, citizens can influence policy decisions and hold their elected representatives accountable. Furthermore, civic duty involves respect for the law, recognizing the importance of legal frameworks in maintaining social order and protecting individual rights. This respect is not limited to obeying laws but also extends to engaging in civic activism, where citizens may peacefully protest or advocate for changes in laws and policies that they believe are unjust or in need of reform.
Civic Engagement and Voluntary Service
Beyond political participation and respect for the law, civic duty also encompasses civic engagement and voluntary service. Civic engagement refers to the various ways in which citizens contribute to the public sphere, such as participating in community meetings, joining civic organizations, or engaging in public service. Voluntary service, on the other hand, involves donating one’s time and skills to help others, whether through non-profit organizations, community groups, or individual initiatives. Both civic engagement and voluntary service are essential for building strong, cohesive communities and addressing social issues that require collective action.
| Category of Civic Duty | Examples of Activities |
|---|---|
| Political Participation | Voting, joining political parties, public debates |
| Respect for the Law | Obeying laws, civic activism, legal advocacy |
| Civic Engagement | Community meetings, civic organizations, public service |
| Voluntary Service | Non-profit work, community volunteering, individual initiatives |

Challenges to Civic Duty
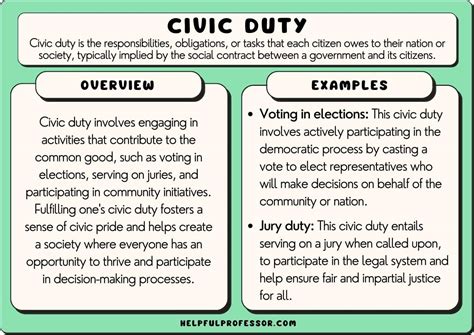
Despite its importance, the practice of civic duty faces several challenges in contemporary society. One of the significant obstacles is civic apathy, where individuals feel disconnected from the political process and lack the motivation to engage in civic activities. Additionally, socio-economic inequalities can hinder certain groups’ ability to participate fully in civic life, either due to lack of access to resources, information, or opportunities. Furthermore, the polarization of political discourse can discourage citizens from engaging in constructive dialogue and collective problem-solving, undermining the foundations of civic duty.
Promoting Civic Duty in Modern Society
To overcome these challenges and promote a culture of civic duty, it is essential to educate and empower citizens. This can be achieved through civic education programs that teach the values and practices of democratic citizenship, as well as initiatives that enhance civic literacy and provide citizens with the skills and knowledge necessary to participate effectively in civic life. Moreover, community-based initiatives that foster a sense of belonging and shared responsibility can encourage more individuals to embrace their civic duties and work towards the common good.
What is the primary goal of civic duty?
+The primary goal of civic duty is to promote the common good and contribute to the well-being of society through active citizenship and community engagement.
How can individuals promote civic duty in their communities?
+Individuals can promote civic duty by participating in local elections, joining community organizations, volunteering for public service, and engaging in respectful and informed dialogue with others about civic issues.
Why is civic education important for civic duty?
+Civic education is crucial because it equips citizens with the knowledge, skills, and values necessary to participate effectively in civic life, make informed decisions, and contribute to the democratic process.
In conclusion, civic duty is a foundational concept in democratic societies, emphasizing the importance of citizen engagement and contribution to the common good. Through a deeper understanding of its components, challenges, and promotion strategies, individuals can foster a stronger sense of civic responsibility and work towards creating more vibrant, inclusive, and equitable communities. As society continues to evolve, the practice of civic duty will remain a critical component of maintaining healthy democratic institutions and ensuring the well-being of future generations.