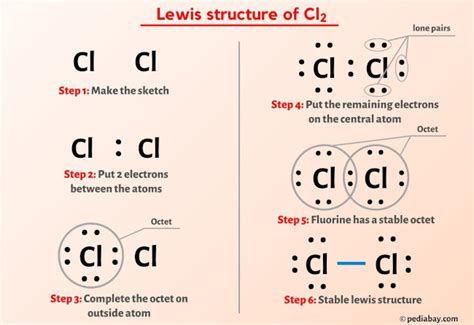
The Cl2 Lewis structure diagram is a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the molecular structure of chlorine gas. To understand this, we first need to grasp what a Lewis structure is. A Lewis structure, also known as an electron dot diagram, is a graphical representation of the electron configuration of molecules. It shows how electrons are arranged around the atoms in a molecule, including both bonding and lone pairs of electrons.
Understanding the Cl2 Molecule

Chlorine gas, denoted by the chemical formula Cl2, consists of two chlorine atoms covalently bonded together. Each chlorine atom has 7 electrons in its outermost shell, which is the valence shell. According to the octet rule, atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer shell, which typically has 8 electrons for non-noble gas atoms. In the case of Cl2, each chlorine atom shares one pair of electrons with the other chlorine atom to form a covalent bond, thereby achieving a stable octet configuration.
Constructing the Cl2 Lewis Structure
To construct the Lewis structure for Cl2, we follow these steps:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons: Since each chlorine atom has 7 valence electrons, the total number of valence electrons in Cl2 is 7 + 7 = 14.
- Draw the skeleton of the molecule: The Cl2 molecule consists of two chlorine atoms. We draw these atoms side by side.
- Connect the atoms with a single bond: This uses 2 electrons, leaving 12 electrons to be distributed.
- Distribute the remaining electrons: We distribute the remaining 12 electrons around the atoms so that each atom achieves an octet. Since the bond between the two chlorine atoms uses 2 electrons, we have 12 electrons left. Each chlorine atom will have 3 lone pairs of electrons (6 electrons) and share 2 electrons in the covalent bond, thereby achieving the stable octet configuration.
| Atom | Valence Electrons | Lone Pairs | Bonding Electrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cl | 7 | 3 pairs (6 electrons) | 2 electrons (1 bond) |
| Cl | 7 | 3 pairs (6 electrons) | 2 electrons (1 bond) |
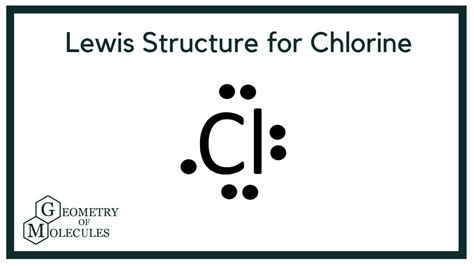
Key Points About the Cl2 Lewis Structure
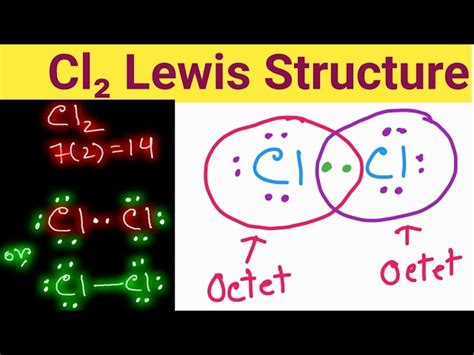
Key Points
- The Cl2 molecule consists of two chlorine atoms covalently bonded together.
- Each chlorine atom in Cl2 has 3 lone pairs of electrons and shares 2 electrons in a covalent bond.
- The Lewis structure of Cl2 shows that each chlorine atom achieves a stable octet configuration.
- The covalent bond in Cl2 is a single bond, using 2 electrons.
- Understanding the Lewis structure of Cl2 is essential for predicting its chemical properties and reactivity.
Implications of the Cl2 Lewis Structure
The Cl2 Lewis structure has significant implications for understanding the chemical behavior of chlorine gas. The presence of three lone pairs on each chlorine atom suggests that chlorine is capable of forming additional bonds, which is indeed observed in its reactions. For instance, chlorine can react with other elements or compounds to form chlorides, where it donates or shares its electrons to achieve a more stable configuration. The Cl2 molecule’s reactivity can be predicted based on its Lewis structure, making it a fundamental tool in chemistry for understanding and predicting chemical reactions.
What does the Cl2 Lewis structure represent?
+The Cl2 Lewis structure represents the arrangement of electrons in a chlorine molecule, showing how the atoms share electrons to form a covalent bond and achieve a stable octet configuration.
How many lone pairs of electrons does each chlorine atom have in Cl2?
+Each chlorine atom in Cl2 has 3 lone pairs of electrons, in addition to sharing 2 electrons in a covalent bond with the other chlorine atom.
What is the significance of the Cl2 Lewis structure in understanding chemical reactions?
+The Cl2 Lewis structure is significant because it helps predict the reactivity of chlorine gas. By understanding the arrangement of electrons, chemists can anticipate how chlorine will react with other elements or compounds to form new bonds.
In conclusion, the Cl2 Lewis structure diagram provides valuable insights into the molecular structure and chemical properties of chlorine gas. By understanding how electrons are arranged in the Cl2 molecule, chemists can better predict its reactivity and behavior in various chemical reactions, underscoring the importance of Lewis structures in chemistry.