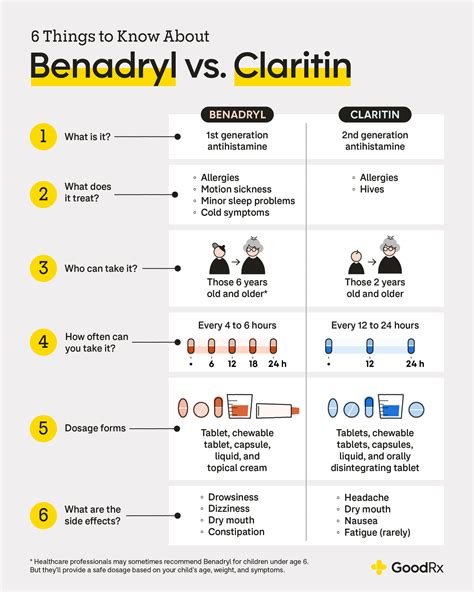
When it comes to treating allergies, two of the most commonly used medications are Claritin and Benadryl. Both are antihistamines, but they belong to different generations and have distinct mechanisms of action, side effect profiles, and indications. Understanding the differences between Claritin and Benadryl is crucial for making informed decisions about allergy treatment. In this article, we will delve into the details of each medication, comparing their efficacy, safety, and suitability for various patients.
Introduction to Claritin and Benadryl
Claritin, also known as loratadine, is a second-generation antihistamine. It is non-sedating, meaning it is less likely to cause drowsiness compared to first-generation antihistamines. Claritin is primarily used to treat symptoms of allergic rhinitis, such as sneezing, runny or itchy nose, and itchy or watery eyes. It works by blocking the action of histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergy symptoms.
Benadryl, also known as diphenhydramine, is a first-generation antihistamine. It is known for its sedating effects, making it useful not only for treating allergies but also for inducing sleep or relieving symptoms of insomnia. Benadryl can be used for a variety of conditions, including allergic reactions, itching, and hives. Like Claritin, it works by blocking histamine receptors, but its broader range of effects includes the central nervous system, contributing to its sedative properties.
Key Points
- Claritin (loratadine) is a second-generation antihistamine with non-sedating properties.
- Benadryl (diphenhydramine) is a first-generation antihistamine known for its sedating effects.
- Both medications are used to treat allergy symptoms but have different side effect profiles and indications.
- Claritin is generally preferred for daytime use due to its non-drowsy formula.
- Benadryl's sedating properties make it suitable for nighttime use or for inducing sleep.
Comparing Efficacy and Safety
The efficacy of Claritin and Benadryl in treating allergy symptoms is well-documented. Both medications are effective in relieving symptoms of allergic rhinitis. However, their safety profiles differ significantly, mainly due to their sedating properties. Claritin, being non-sedating, is generally safer for use during the day, as it is less likely to impair cognitive function or cause drowsiness. This makes it a preferred choice for individuals who need to maintain alertness for work, school, or other daily activities.
Benadryl, on the other hand, can cause significant drowsiness, which may be beneficial for nighttime use but can be a hindrance during the day. Additionally, long-term use of first-generation antihistamines like Benadryl has been associated with cognitive impairment and an increased risk of dementia in elderly patients, although the evidence is not conclusive and more research is needed.
| Medication | Sedating Effects | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Claritin (loratadine) | Non-sedating | Headache, dry mouth, stomach pain |
| Benadryl (diphenhydramine) | Sedating | Drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation, cognitive impairment |
Practical Applications and Considerations

In practical terms, the choice between Claritin and Benadryl depends on several factors, including the severity of allergy symptoms, the patient’s age, and any underlying health conditions. For children and the elderly, second-generation antihistamines like Claritin are often preferred due to their safer side effect profile. For adults with mild to moderate allergy symptoms, Claritin’s non-sedating properties make it a popular choice for managing symptoms without interfering with daily activities.
Benadryl, with its sedating effects, is sometimes used off-label for treating insomnia or as a sleep aid, though this is not its primary indication and should be done under medical supervision due to the risk of dependence and other side effects. Additionally, Benadryl's anticholinergic properties can exacerbate conditions like urinary retention, constipation, and dry mouth, particularly in older adults.
Evolution of Antihistamines and Future Directions
The development of antihistamines has evolved significantly over the years, from the first-generation drugs like Benadryl to the newer, non-sedating options like Claritin. Research continues into the development of antihistamines with improved efficacy and safety profiles. The focus is on creating medications that can effectively relieve allergy symptoms without the sedating or anticholinergic effects associated with older generations of antihistamines.
Furthermore, the understanding of allergic diseases and the mechanisms by which antihistamines work is becoming more nuanced. This includes recognizing the role of histamine in various physiological processes beyond allergy symptoms, such as regulation of the sleep-wake cycle and cognitive functions. As our understanding deepens, so too will the development of targeted therapies that can address specific aspects of allergic responses without broadly affecting the body.
What is the primary difference between Claritin and Benadryl?
+The primary difference is that Claritin is a non-sedating, second-generation antihistamine, whereas Benadryl is a sedating, first-generation antihistamine.
Which medication is safer for children and the elderly?
+Claritin is generally considered safer for children and the elderly due to its non-sedating properties and lower risk of side effects.
Can Benadryl be used as a sleep aid?
+While Benadryl can induce sleep due to its sedating effects, it is not recommended as a primary sleep aid due to the risk of dependence and other side effects. Its use for this purpose should be under medical supervision.
In conclusion, the choice between Claritin and Benadryl depends on a variety of factors, including the patient’s specific needs, lifestyle, and health status. Both medications have their places in the treatment of allergy symptoms, but it’s crucial to understand their differences in terms of efficacy, safety, and side effects to make an informed decision. As research continues to advance our understanding of allergic diseases and the development of antihistamines, patients can look forward to more targeted and effective treatments with fewer side effects.