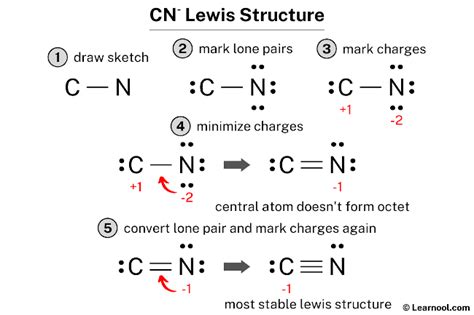
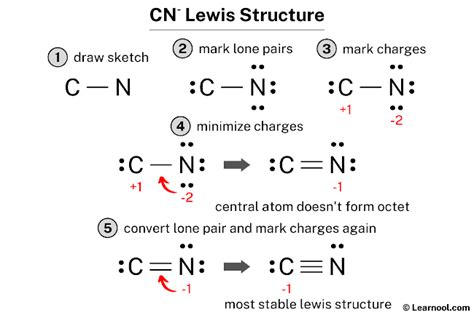
The CN Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the arrangement of electrons in a molecule. To understand the CN Lewis structure, it's essential to have a basic knowledge of chemistry and molecular bonding. The CN molecule, composed of one carbon atom and one nitrogen atom, is a diatomic molecule that exhibits a triple bond between the two atoms. The Lewis structure of CN can be drawn in several ways, but here, we'll explore five different representations, each highlighting a unique aspect of the molecule's electronic structure.
Introduction to Lewis Structures
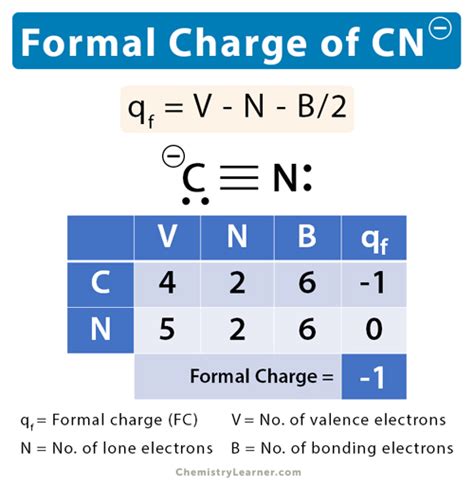
Lewis structures, also known as electron dot diagrams, are a graphical representation of the valence electrons in a molecule. They are used to predict the shape and reactivity of molecules. In the case of the CN molecule, we need to account for the total valence electrons, which are 4 from carbon and 5 from nitrogen, totaling 9 valence electrons. The goal is to arrange these electrons in a way that satisfies the octet rule for both atoms, indicating a stable molecule.
Drawing the First CN Lewis Structure
The first way to draw the CN Lewis structure involves a triple bond between the carbon and nitrogen atoms. This structure satisfies the octet rule for both atoms, with carbon having 4 bonds (one triple bond counts as 3 bonds) and nitrogen also having 4 bonds (including the 3 from the triple bond). The structure looks like this: C≡N. This representation is the most common and straightforward way to depict the CN molecule, emphasizing the strong triple bond between the two atoms.
Alternative Representations of the CN Lewis Structure
Beyond the simple triple bond representation, there are other ways to draw the CN Lewis structure, each highlighting different aspects of the molecule’s electronic configuration. These include structures with less than a triple bond, where formal charges are introduced to satisfy the octet rule for both atoms. For instance, a structure with a double bond and two lone pairs on nitrogen can also be drawn, but this would require assigning formal charges to the atoms to balance the electrons.
Second Representation: Double Bond with Formal Charges
A second way to represent the CN Lewis structure is by drawing a double bond between the carbon and nitrogen, with a lone pair on the nitrogen atom. However, to make this structure valid, we must assign a formal charge to the carbon atom, making it less electronegative than nitrogen. This representation is less common but can be useful in understanding certain reaction mechanisms where the molecule might behave as if it had a double bond character.
| Lone Pairs | Bond Order | Formal Charges |
|---|---|---|
| 1 on N | Double Bond | C(+1), N(-1) |
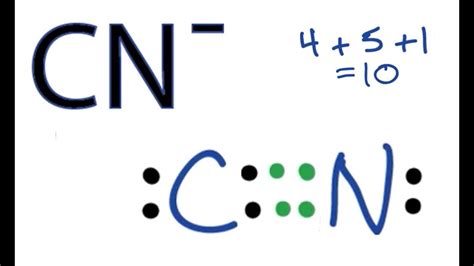
Further Variations of the CN Lewis Structure
In addition to the triple and double bond representations, there are other theoretical structures that can be proposed for the CN molecule, each with its implications for the molecule’s stability and reactivity. These structures might involve different bond orders or arrangements of electrons, always keeping in mind the octet rule and the electronegativities of the atoms involved.
Third Representation: Single Bond with Three Lone Pairs on Nitrogen
A third, less conventional representation could involve a single bond between the carbon and nitrogen, with three lone pairs on the nitrogen atom. This structure would also require the assignment of formal charges to both atoms to balance the electrons, resulting in a less stable and less realistic representation of the molecule.
Key Points
- The CN Lewis structure can be represented in multiple ways, emphasizing different aspects of its electronic configuration.
- The most common representation is a triple bond between the carbon and nitrogen atoms.
- Alternative representations may involve double or single bonds with formal charges assigned to the atoms.
- The choice of representation depends on the context, such as understanding chemical reactivity or molecular stability.
- Each representation must adhere to the octet rule and consider the electronegativities of the atoms.
Implications and Applications of the CN Lewis Structure
The understanding of the CN Lewis structure has significant implications for its chemical properties and reactivity. The molecule’s ability to form a strong triple bond gives it unique characteristics, making it useful in various chemical reactions and applications. For instance, the CN group is a common functional group in organic chemistry, known for its stability and reactivity in forming compounds.
Practical Applications of the CN Group
In practical terms, the CN group is used in the synthesis of many organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, and other specialty chemicals. The stability and reactivity of the CN bond make it an ideal functional group for various chemical transformations, allowing chemists to build complex molecules with specific properties.
What is the significance of the CN Lewis structure in chemistry?
+The CN Lewis structure is crucial for understanding the molecule's stability, reactivity, and chemical properties. It helps in predicting how the molecule will behave in different chemical reactions and environments.
How does the triple bond in CN affect its chemical properties?
+The triple bond gives CN its linear shape and high bond strength, contributing to its stability and reactivity. This strong bond is responsible for many of the chemical properties and applications of the CN group in organic chemistry.
What are some common applications of the CN group in organic chemistry?
+The CN group is used in the synthesis of various organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, and other specialty chemicals. Its stability and reactivity make it a versatile functional group for building complex molecules.
In conclusion, the CN Lewis structure is a foundational concept in chemistry, essential for understanding the molecule’s electronic configuration, stability, and reactivity. Through various representations, chemists can better comprehend the molecule’s behavior in different contexts, from theoretical bonding arrangements to practical applications in organic synthesis. The CN group’s unique characteristics, particularly its strong triple bond, make it a valuable functional group in the construction of complex organic molecules, highlighting the importance of Lewis structures in predicting and explaining chemical properties and reactivity.