Cobalt, a versatile and highly valued metal, plays a crucial role in various industries, including energy, transportation, and construction. With its unique properties and wide range of applications, cobalt has become an essential component in the production of numerous products, from batteries and electronics to alloys and pigments. In this article, we will delve into the world of cobalt, exploring its characteristics, uses, and importance, as well as the challenges and opportunities associated with its extraction and trade.
Key Points
- Cobalt is a key component in lithium-ion batteries, which power many electric vehicles and portable electronics.
- The metal has a high melting point, making it ideal for use in high-temperature applications, such as in the production of jet engine components.
- Cobalt is also used in the manufacture of magnetic alloys, which are used in a variety of applications, including electric motors and generators.
- The metal has a range of medical applications, including its use in radioisotopes for cancer treatment and in orthopedic implants.
- Cobalt is often extracted as a byproduct of copper and nickel mining, with the Democratic Republic of Congo being the largest producer of cobalt.
Cobalt Properties and Applications
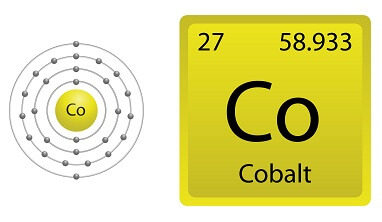
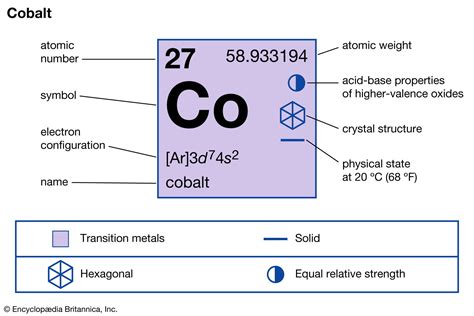
Cobalt is a ferromagnetic metal with a high melting point of 1495°C, making it an ideal material for use in high-temperature applications. Its unique properties also make it a crucial component in the production of lithium-ion batteries, which power many electric vehicles and portable electronics. Additionally, cobalt is used in the manufacture of magnetic alloys, which are used in a variety of applications, including electric motors and generators. The metal’s range of applications also extends to the medical field, where it is used in radioisotopes for cancer treatment and in orthopedic implants.
Cobalt Extraction and Trade
The extraction of cobalt is often associated with copper and nickel mining, with the Democratic Republic of Congo being the largest producer of cobalt. The country’s cobalt mines are estimated to produce over 60% of the world’s cobalt, with China being the largest consumer of the metal. However, the extraction of cobalt has been linked to several environmental and social concerns, including deforestation, water pollution, and child labor. As a result, there is a growing need for more sustainable and responsible cobalt mining practices, as well as increased transparency and regulation in the cobalt trade.
| Country | Cobalt Production (2020) |
|---|---|
| Democratic Republic of Congo | 90,000 metric tons |
| China | 7,200 metric tons |
| Canada | 4,300 metric tons |
| Russia | 2,400 metric tons |
| Australia | 1,900 metric tons |
Cobalt Recycling and Sustainability

As the demand for cobalt continues to grow, there is a growing need for more sustainable and responsible cobalt mining practices. One approach to addressing this challenge is through the development of cobalt recycling technologies, which can help to reduce the amount of waste generated by cobalt mining and decrease the demand for primary cobalt production. Additionally, researchers are exploring new methods for extracting cobalt from secondary sources, such as spent lithium-ion batteries and other electronic waste. By promoting the recycling and reuse of cobalt, we can help to reduce the environmental impacts associated with its extraction and trade.
Cobalt Substitution and Alternative Materials
Another approach to addressing the challenges associated with cobalt extraction and trade is through the development of alternative materials and technologies that can substitute for cobalt in various applications. For example, researchers are exploring the use of other metals, such as nickel and manganese, in the production of lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, there is a growing interest in the development of solid-state batteries, which do not require the use of cobalt or other rare earth metals. By promoting the development and commercialization of these alternative technologies, we can help to reduce our reliance on cobalt and mitigate the environmental and social concerns associated with its extraction and trade.
What are the main applications of cobalt?
+Cobalt is used in a variety of applications, including the production of lithium-ion batteries, magnetic alloys, and pigments. It is also used in the medical field, where it is used in radioisotopes for cancer treatment and in orthopedic implants.
Where is cobalt primarily extracted?
+Cobalt is often extracted as a byproduct of copper and nickel mining, with the Democratic Republic of Congo being the largest producer of cobalt.
What are the environmental and social concerns associated with cobalt extraction?
+The extraction of cobalt has been linked to several environmental and social concerns, including deforestation, water pollution, and child labor. As a result, there is a growing need for more sustainable and responsible cobalt mining practices, as well as increased transparency and regulation in the cobalt trade.
In conclusion, cobalt is a versatile and highly valued metal that plays a crucial role in various industries, including energy, transportation, and construction. However, the extraction of cobalt has been linked to several environmental and social concerns, highlighting the need for more sustainable and responsible cobalt mining practices. By promoting the recycling and reuse of cobalt, as well as the development of alternative materials and technologies, we can help to reduce our reliance on cobalt and mitigate the environmental and social concerns associated with its extraction and trade.