The Cobb-Douglas production function model is a fundamental concept in economics, particularly in the field of microeconomics. It is a mathematical representation of the relationship between inputs and outputs in a production process. The model was first introduced by Charles Cobb and Paul Douglas in 1928 and has since become a widely used tool for analyzing the behavior of firms and industries.
Introduction to the Cobb-Douglas Production Function
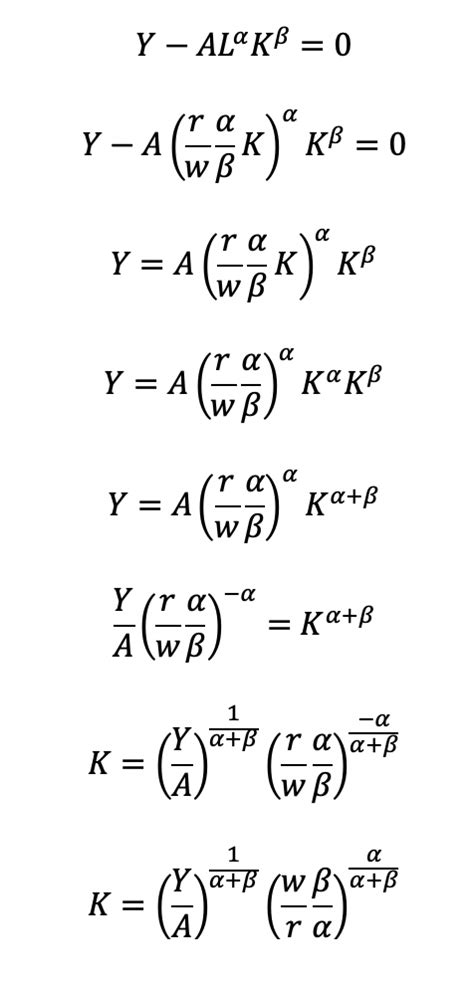
The Cobb-Douglas production function is a neoclassical model that assumes a firm’s output is a function of two main inputs: labor (L) and capital (K). The model is represented by the following equation:
Q = A * L^α * K^β
where Q is the output, A is a constant representing the total factor productivity, L is the labor input, K is the capital input, and α and β are the output elasticities of labor and capital, respectively. The output elasticities represent the percentage change in output resulting from a 1% change in the corresponding input, while holding all other inputs constant.
Key Characteristics of the Cobb-Douglas Production Function
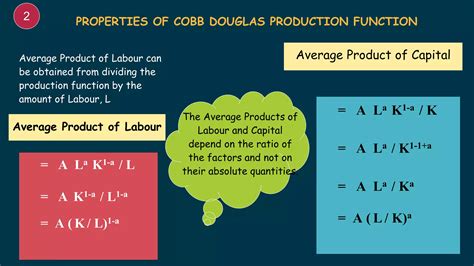
The Cobb-Douglas production function has several key characteristics that make it a useful tool for analyzing production processes. Some of these characteristics include:- Constant Returns to Scale: The Cobb-Douglas production function exhibits constant returns to scale, meaning that if all inputs are increased by a given percentage, output will increase by the same percentage.
- Diminishing Marginal Productivity: The model also exhibits diminishing marginal productivity, meaning that as more of one input is added, while holding all other inputs constant, the marginal product of that input will eventually decrease.
- Homogeneity: The Cobb-Douglas production function is homogeneous of degree one, meaning that if all inputs are increased by a given percentage, output will increase by the same percentage.
| Input | Output Elasticity |
|---|---|
| Labor (L) | α |
| Capital (K) | β |
Key Points
- The Cobb-Douglas production function is a mathematical representation of the relationship between inputs and outputs in a production process.
- The model assumes a firm's output is a function of two main inputs: labor (L) and capital (K).
- The output elasticities of labor and capital represent the percentage change in output resulting from a 1% change in the corresponding input.
- The Cobb-Douglas production function exhibits constant returns to scale and diminishing marginal productivity.
- The model is homogeneous of degree one, meaning that if all inputs are increased by a given percentage, output will increase by the same percentage.
Estimation and Application of the Cobb-Douglas Production Function
The Cobb-Douglas production function can be estimated using various econometric techniques, such as ordinary least squares (OLS) or maximum likelihood estimation (MLE). Once estimated, the model can be used to analyze the behavior of firms and industries in a variety of contexts.
Technical Specifications and Interpretation
The technical specifications of the Cobb-Douglas production function are as follows:- Parameters: The model has three parameters: A, α, and β.
- Inputs: The model has two inputs: labor (L) and capital (K).
- Output: The model produces one output: Q.
The interpretation of the model’s parameters is as follows:
- A: The total factor productivity, which represents the overall efficiency of the production process.
- α: The output elasticity of labor, which represents the percentage change in output resulting from a 1% change in labor.
- β: The output elasticity of capital, which represents the percentage change in output resulting from a 1% change in capital.
What is the Cobb-Douglas production function?
+The Cobb-Douglas production function is a mathematical representation of the relationship between inputs and outputs in a production process.
What are the key characteristics of the Cobb-Douglas production function?
+The Cobb-Douglas production function exhibits constant returns to scale, diminishing marginal productivity, and homogeneity of degree one.
How is the Cobb-Douglas production function estimated?
+The Cobb-Douglas production function can be estimated using various econometric techniques, such as ordinary least squares (OLS) or maximum likelihood estimation (MLE).
In conclusion, the Cobb-Douglas production function is a powerful tool for analyzing the behavior of firms and industries. By understanding the key characteristics and technical specifications of the model, firms can make informed decisions about the optimal combination of inputs to produce a given level of output. The model’s parameters, including the total factor productivity and output elasticities of labor and capital, provide valuable insights into the production process and can be used to inform strategic decision-making.