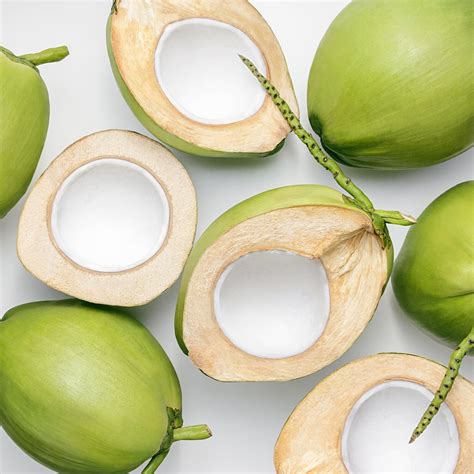
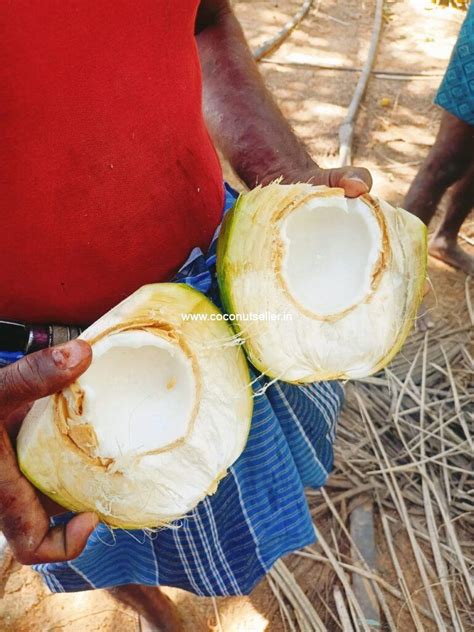
The age-old debate about the classification of coconuts has sparked intense discussion among botanists, nutritionists, and culinary enthusiasts. Is a coconut a nut, a fruit, or something entirely different? To unravel this mystery, it's essential to delve into the botanical, nutritional, and culinary aspects of coconuts. From a botanical perspective, coconuts belong to the family Arecaceae and are the fruit of the coconut palm tree (Cocos nucifera). The coconut fruit consists of three distinct layers: the exocarp (outer layer), mesocarp (middle layer), and endocarp (inner layer). The endocarp surrounds a single seed, which is commonly referred to as the coconut "meat" or "flesh."
Botanical Classification: Coconut as a Fruit

Botanically speaking, a fruit is the mature ovary of a plant, which contains seeds, while a nut is a specific type of fruit that has a hard shell and a single seed. Coconuts meet the criteria for a fruit, as they develop from the ovary of a flower and contain a seed. However, the term “nut” is often used colloquially to refer to any hard, seed-like fruit, including coconuts. This ambiguity has contributed to the ongoing debate about the classification of coconuts. To clarify, coconuts are a type of fruit known as a drupe, which has a hard shell and a single seed, similar to peaches, plums, and olives.
Nutritional Properties: Coconut as a Nutritious Food Source
From a nutritional standpoint, coconuts are an excellent source of healthy fats, protein, and fiber. They contain a unique combination of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which have been shown to have potential health benefits, such as improving cholesterol levels and aiding in weight management. Coconuts are also rich in essential minerals like potassium, magnesium, and iron. The nutritional profile of coconuts is often compared to that of nuts, which are known for their high fat and protein content. However, coconuts are distinct in their composition and offer a unique set of nutritional benefits.
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 375 |
| Protein | 3.3g |
| Fat | 33.5g |
| Carbohydrates | 24.5g |
| Fiber | 9g |

Key Points
- Coconuts are botanically classified as a type of fruit known as a drupe.
- The nutritional profile of coconuts is distinct from that of nuts, with a unique combination of healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Coconuts have been shown to have potential health benefits, including improving cholesterol levels and aiding in weight management.
- The culinary uses of coconuts are diverse, ranging from sweet desserts to savory dishes.
- Coconuts are a rich source of essential minerals like potassium, magnesium, and iron.
Culinary Uses: Coconut in Various Cuisines

Coconuts have been a staple ingredient in many cuisines around the world, particularly in tropical regions where they are abundant. The versatile uses of coconuts range from sweet desserts like coconut cream pie and coconut macaroons to savory dishes like curries, soups, and stir-fries. Coconuts can be used in various forms, including shredded, grated, or as coconut milk, oil, or water. The culinary applications of coconuts are a testament to their unique flavor and nutritional profile, which has captivated the hearts and taste buds of people worldwide.
Practical Applications: Incorporating Coconuts into Daily Life
Incorporating coconuts into daily life can be as simple as adding shredded coconut to oatmeal or yogurt or using coconut oil as a substitute for other oils in cooking. Coconuts can also be used as a natural remedy for various health issues, such as skin and hair care, due to their rich content of antioxidants and fatty acids. The practical applications of coconuts are endless, and their unique properties make them an excellent addition to a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
What is the botanical classification of coconuts?
+Coconuts are botanically classified as a type of fruit known as a drupe.
What are the nutritional benefits of coconuts?
+Coconuts are an excellent source of healthy fats, protein, and fiber, and contain a unique combination of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) that have potential health benefits.
How can coconuts be incorporated into daily life?
+Coconuts can be incorporated into daily life by adding shredded coconut to oatmeal or yogurt, using coconut oil as a substitute for other oils in cooking, or using coconut products as natural remedies for various health issues.
In conclusion, the classification of coconuts as a nut or fruit is not a simple matter of either-or. Instead, coconuts embody characteristics of both, making them a unique and versatile food source. With their distinct nutritional profile, diverse culinary uses, and practical applications, coconuts are an excellent addition to a healthy and balanced lifestyle. As a domain-specific expert, it’s essential to recognize the complexity of coconuts and appreciate their unique properties, which have captivated the hearts and taste buds of people worldwide.