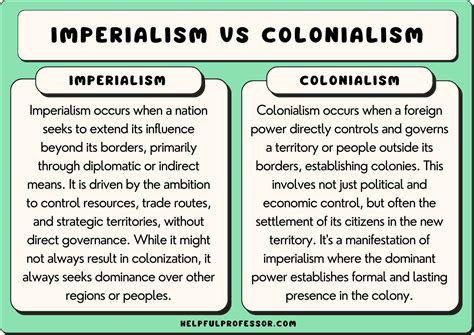
The concepts of colonization and imperialism have been intricately intertwined throughout history, often used interchangeably, yet they possess distinct meanings and implications. To understand the nuances between these two terms, it is essential to delve into their definitions, historical contexts, and the impacts they have had on societies and economies worldwide. Colonization refers to the process by which one country or power establishes a colony, which is a territory under its control, often inhabited by settlers from the colonizing country. This can involve the physical settlement of the colonizing country's citizens in the new territory, as well as the imposition of the colonizer's language, culture, and political and economic systems.
Imperialism, on the other hand, is a broader concept that encompasses not just the physical colonization of territories but also the extension of a country's power and influence through economic, political, and cultural means. Imperialism can manifest without direct colonization, through mechanisms such as economic dependency, cultural hegemony, and political influence. It is a system where one country, often referred to as the imperial power, creates and maintains an empire, which is a large, multi-ethnic state in which one central power holds supreme control over peripheral territories or peoples.
Key Points
- Colonization involves the physical settlement and control of a territory by a foreign power.
- Imperialism is a broader system of influence that can include colonization but also encompasses economic, political, and cultural dominance.
- Historical examples of colonization include the European settlement of the Americas and Australia.
- Imperialism has been exercised through various means, including economic control, as seen in the scramble for Africa, and cultural influence, as observed in the spread of Western culture globally.
- The impacts of colonization and imperialism have been profound, leading to the displacement of indigenous populations, cultural erasure, economic exploitation, and the shaping of global power dynamics.
Historical Contexts of Colonization and Imperialism
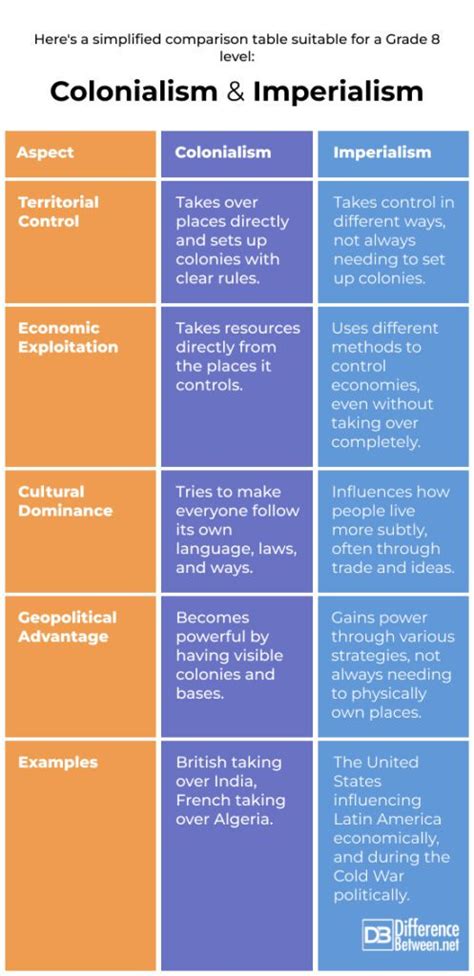
The history of colonization and imperialism stretches back centuries, with ancient civilizations such as the Romans, Greeks, and Chinese engaging in forms of territorial expansion and cultural spread. However, the modern era of colonization and imperialism, particularly from the 15th century onwards, is most closely associated with European powers. The Age of Exploration led to the discovery of new lands, which in turn sparked a wave of colonization across the Americas, Africa, Asia, and the Pacific. European countries such as Spain, Portugal, Britain, France, and the Netherlands established vast colonial empires, imposing their rule over diverse populations and extracting natural resources and labor.
European Colonization of the Americas
The colonization of the Americas by European powers had a devastating impact on indigenous populations. Diseases brought over by Europeans, to which the native populations had no immunity, decimated entire communities. Furthermore, the forced labor, enslavement, and violent conquests led to significant population decline and cultural destruction. The legacy of this colonization continues to affect the social, economic, and political status of indigenous peoples in the Americas today.
| Colonizing Power | Colonized Territories | Impact on Indigenous Populations |
|---|---|---|
| Spain | South and Central America, Caribbean | Significant population decline due to disease and violence |
| Britain | North America, Australia, New Zealand | Forced relocation, cultural suppression, and economic marginalization |
| France | North America, Caribbean, Africa, Asia | Cultural assimilation policies, economic exploitation, and political dominance |

Imperialism Beyond Colonization

Imperialism extends beyond the physical act of colonization, involving the exertion of power and influence over other countries or territories without necessarily establishing direct colonial rule. Economic imperialism, for instance, can involve control over a country’s economy through investments, trade agreements, and debt, without the need for physical occupation. Cultural imperialism refers to the spread and imposition of one culture over another, often through media, education, and cultural exchange programs, which can lead to the erasure of local cultures and identities.
Cultural Imperialism
Cultural imperialism is a subtle yet powerful form of imperialism, where the cultural practices, values, and beliefs of one society are imposed upon another, often through indirect means. This can occur through the global spread of media, the promotion of Western education systems, and the adoption of international languages like English. While cultural exchange can be beneficial, cultural imperialism often results in the suppression of local cultures and the homogenization of global cultural diversity.
In conclusion, while colonization and imperialism are related concepts, they represent different aspects of power dynamics and influence. Colonization refers to the direct control and settlement of territories, whereas imperialism encompasses a broader range of mechanisms through which power is exerted and maintained. Understanding the historical and ongoing impacts of these phenomena is essential for addressing the legacies of colonization and imperialism and for promoting a more equitable and just global order.
What is the primary difference between colonization and imperialism?
+Colonization involves the physical settlement and control of a territory by a foreign power, whereas imperialism is a broader system of influence that can include colonization but also encompasses economic, political, and cultural dominance.
How has cultural imperialism affected local cultures globally?
+Cultural imperialism has led to the suppression of local cultures and the homogenization of global cultural diversity, as the cultural practices, values, and beliefs of dominant societies are imposed upon others through media, education, and cultural exchange programs.
What are the ongoing impacts of colonization and imperialism on contemporary societies?
+The ongoing impacts include social and economic disparities, cultural erasure, political instability, and the continuation of power imbalances between former colonizers and colonized countries, affecting issues such as development, identity, and global governance.