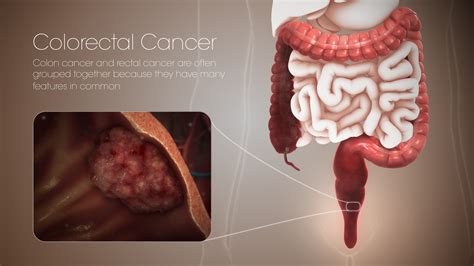
Colorectal cancer, also known as bowel cancer, is a type of cancer that affects the large intestine (colon) and the rectum. It is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, with over 1.8 million new cases diagnosed each year, according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Understanding the visual characteristics of colorectal cancer can aid in early detection and diagnosis, potentially improving treatment outcomes. This article will delve into the various aspects of colorectal cancer, including its symptoms, stages, treatment options, and the importance of early detection through screenings and awareness of the disease's visual manifestations.
Understanding Colorectal Cancer

Colorectal cancer typically begins as small, noncancerous (benign) clumps of cells called polyps that form on the inside of the colon or rectum. Over time, some of these polyps can become colon cancers. The exact cause of colorectal cancer is not known, but certain risk factors have been identified, including age (with most cases occurring in people over 50), a family history of colorectal cancer, a personal history of inflammatory bowel disease, and lifestyle factors such as a low-fiber diet and lack of physical activity. The disease progresses through several stages, from Stage 0 (the earliest stage) to Stage IV (the most advanced stage), with treatment options and prognosis varying significantly depending on the stage at diagnosis.
Symptoms and Detection
Symptoms of colorectal cancer can vary depending on the location and size of the tumor. Common symptoms include changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation, blood in the stool, persistent abdominal discomfort, weakness or fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. However, many people with early-stage colorectal cancer do not experience any symptoms, highlighting the importance of regular screenings for early detection. Visual examinations, such as colonoscopies, allow doctors to look inside the colon for polyps and cancer. During a colonoscopy, any polyps found can be removed, and tissue samples (biopsies) can be taken for further examination.
| Colorectal Cancer Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Stage 0 | Cancer is in the earliest stage and has not grown beyond the inner lining of the colon or rectum. |
| Stage I | Cancer has grown through the inner lining of the colon or rectum but has not spread beyond the colon or rectum wall. |
| Stage II | Cancer has grown through the wall of the colon or rectum but has not reached nearby lymph nodes. |
| Stage III | Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body. |
| Stage IV | Cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs, or distant lymph nodes. |

Key Points
- Colorectal cancer is a common type of cancer that affects the large intestine and rectum, with over 1.8 million new cases diagnosed annually.
- The disease often starts as small, noncancerous polyps that can become cancerous over time, emphasizing the importance of early detection through screenings.
- Symptoms can include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, abdominal discomfort, weakness, and unexplained weight loss, though many cases are asymptomatic in the early stages.
- Visual examinations like colonoscopies are critical for detecting and removing polyps before they become cancerous, with the procedure allowing for the removal of polyps and the taking of tissue samples for biopsy.
- Treatment options vary based on the stage of cancer at diagnosis, with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy being common approaches, and the importance of discussing screening options with a healthcare provider, especially for those with a family history or other risk factors.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for colorectal cancer depends on the stage of the disease, the overall health of the patient, and the preferences of the patient. Surgery is often the primary treatment for early-stage colorectal cancer, aiming to remove the cancer and a portion of healthy tissue around it. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may also be used, either before surgery to shrink the tumor or after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are newer approaches that are being used in some cases, offering hope for more effective treatments with fewer side effects. The choice of treatment should be made in consultation with a healthcare team, considering all available options and the patient’s specific situation.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention
While some risk factors for colorectal cancer cannot be changed, such as age and family history, there are lifestyle changes that can reduce the risk. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption are all recommended. Additionally, participating in regular screenings as recommended by healthcare guidelines can help detect colorectal cancer at an early stage when it is most treatable. Awareness and education about the risks and symptoms of colorectal cancer can also encourage individuals to take preventive measures and seek medical attention if they experience any unusual symptoms.
What are the most common symptoms of colorectal cancer?
+Common symptoms include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, persistent abdominal discomfort, weakness or fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. However, many people with early-stage colorectal cancer may not experience any symptoms.
How is colorectal cancer typically diagnosed?
+Diagnosis often involves a combination of visual examinations like colonoscopies, where polyps can be removed and biopsied, and other tests such as blood tests and imaging studies like CT scans.
Can colorectal cancer be prevented?
+While not all cases can be prevented, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can reduce the risk. Regular screenings are also crucial for early detection and removal of precancerous polyps.
In conclusion, colorectal cancer is a significant health concern that can often be detected early through screenings and managed effectively with appropriate treatment. Understanding the visual characteristics, symptoms, and stages of colorectal cancer, as well as the importance of lifestyle changes and preventive measures, can empower individuals to take proactive steps in protecting their health. By promoting awareness and encouraging discussions about colorectal cancer, we can work towards reducing its incidence and improving outcomes for those affected by this disease.