Understanding the fundamentals of sentence structure is essential for effective communication in writing and speech. Two crucial components of a sentence are the compound and predicate, which work together to convey meaningful information. In this article, we will delve into the world of compounds and predicates, exploring their definitions, functions, and applications in language.
Defining Compounds and Predicates

A compound refers to a word or phrase that is composed of two or more elements, often with a specific meaning that differs from the sum of its individual parts. Compounds can be classified into different types, such as open compounds (e.g., post office), closed compounds (e.g., toothbrush), and hyphenated compounds (e.g., self-made). On the other hand, a predicate is the part of a sentence that contains the verb and tells us what the subject is doing or what is happening to the subject. The predicate is a vital component of a sentence, as it provides essential information about the action or state of being.
Predicate Types and Functions
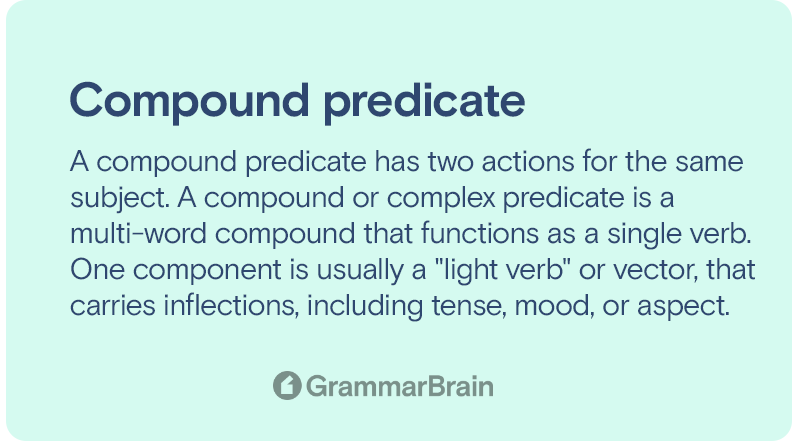
Predicates can be categorized into two main types: simple predicates and compound predicates. A simple predicate consists of a single verb or verb phrase, whereas a compound predicate contains two or more verbs or verb phrases joined by a conjunction. The function of a predicate is to provide insight into the actions, events, or states of being described in a sentence. For instance, in the sentence “She ate breakfast and checked her phone,” the compound predicate “ate breakfast and checked her phone” tells us what the subject (she) is doing.
| Predicate Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Simple Predicate | "She ran." |
| Compound Predicate | "She ran and jumped." |
Compound and Predicate in Sentence Structure

In sentence structure, compounds and predicates work together to create a cohesive and informative unit. A sentence typically begins with a subject, followed by a predicate that tells us what the subject is doing or what is happening to the subject. Compounds can be used within the subject or predicate to add depth and specificity to the sentence. For example, in the sentence “The self-made entrepreneur launched a successful business,” the compound “self-made” is used to describe the subject (entrepreneur), while the predicate “launched a successful business” tells us what the subject is doing.
Applications of Compounds and Predicates
Compounds and predicates have numerous applications in language, including creative writing, technical writing, and everyday communication. By using compounds and predicates effectively, writers and speakers can convey complex ideas, describe actions and events, and add nuance and depth to their language. For instance, in technical writing, compounds and predicates can be used to describe complex systems and processes, while in creative writing, they can be used to craft vivid descriptions and engaging narratives.
Key Points
- Compounds are words or phrases composed of two or more elements with a specific meaning.
- Predicates contain the verb and tell us what the subject is doing or what is happening to the subject.
- Simple predicates consist of a single verb or verb phrase, while compound predicates contain two or more verbs or verb phrases.
- Compounds and predicates work together to create a cohesive and informative sentence structure.
- Effective use of compounds and predicates can convey complex ideas, describe actions and events, and add nuance and depth to language.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, compounds and predicates are essential components of language that work together to convey meaningful information. By understanding the definitions, functions, and applications of compounds and predicates, writers and speakers can create effective and engaging language that communicates complex ideas and actions with precision and clarity. As language continues to evolve, the study of compounds and predicates will remain crucial for developing a deeper understanding of language structure and function.
What is the difference between a simple predicate and a compound predicate?
+A simple predicate consists of a single verb or verb phrase, whereas a compound predicate contains two or more verbs or verb phrases joined by a conjunction.
How are compounds used in sentence structure?
+Compounds can be used within the subject or predicate to add depth and specificity to the sentence, describing actions, events, or states of being.
What are the applications of compounds and predicates in language?
+Compounds and predicates have numerous applications in language, including creative writing, technical writing, and everyday communication, allowing writers and speakers to convey complex ideas, describe actions and events, and add nuance and depth to their language.
Meta description: “Discover the fundamentals of compounds and predicates in language, including their definitions, functions, and applications in sentence structure and communication.”



