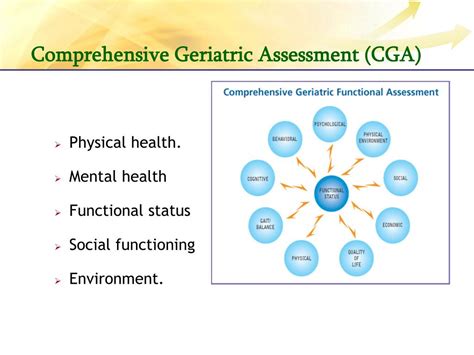
The Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA) is a multifaceted, interdisciplinary approach to evaluating the health and well-being of older adults. This holistic assessment tool is designed to identify the complex needs of geriatric patients, taking into account their physical, functional, cognitive, emotional, and social health. As the global population ages, the importance of CGA in providing person-centered care and improving health outcomes for older adults has become increasingly recognized. In this article, we will delve into the components, benefits, and implementation of CGA, as well as its role in shaping healthcare policies and practices for older adults.
Components of Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment
A comprehensive geriatric assessment typically involves a team of healthcare professionals, including geriatricians, nurses, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and social workers. The assessment process encompasses a broad range of domains, including:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A thorough review of the patient’s medical history, including current and past illnesses, medications, and allergies, as well as a comprehensive physical examination to identify any underlying health issues.
- Functional Assessment: An evaluation of the patient’s ability to perform daily activities, such as bathing, dressing, and managing finances, to determine their level of independence and need for support.
- Cognitive and Mental Health Assessment: A assessment of the patient’s cognitive function, including memory, attention, and decision-making abilities, as well as their mental health, including symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other psychiatric conditions.
- Social and Environmental Assessment: An examination of the patient’s social support network, including family and friends, as well as their living environment, to identify potential risks and opportunities for intervention.
- Nutritional and Pharmacological Assessment: An evaluation of the patient’s nutritional status and medication regimen, including potential interactions and side effects, to optimize their health and well-being.
Benefits of Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment
The benefits of CGA are numerous and well-documented. By providing a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s needs and health status, CGA can help to:
- Improve Health Outcomes: CGA has been shown to reduce hospital readmissions, improve functional status, and enhance overall quality of life for older adults.
- Enhance Patient Safety: By identifying potential risks and hazards, CGA can help to prevent falls, medication errors, and other adverse events.
- Optimize Healthcare Utilization: CGA can help to reduce unnecessary hospitalizations, emergency department visits, and other healthcare services, resulting in cost savings and improved resource allocation.
- Support Caregivers: CGA can provide valuable information and support to family caregivers, helping to reduce their burden and improve their overall well-being.
| Domain | Assessment Tool |
|---|---|
| Functional Status | Activities of Daily Living (ADL) scale |
| Cognitive Function | Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) |
| Mental Health | Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) |
| Social Support | Social Support Questionnaire (SSQ) |
| Nutritional Status | Mini-Nutritional Assessment (MNA) |

Key Points
- Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA) is a multifaceted, interdisciplinary approach to evaluating the health and well-being of older adults.
- CGA encompasses a broad range of domains, including medical history, functional status, cognitive and mental health, social support, and nutritional status.
- The benefits of CGA include improved health outcomes, enhanced patient safety, optimized healthcare utilization, and support for caregivers.
- CGA can be implemented in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and community-based programs.
- Geriatricians and other healthcare professionals play a critical role in leading and coordinating CGA teams.
Implementation of Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment
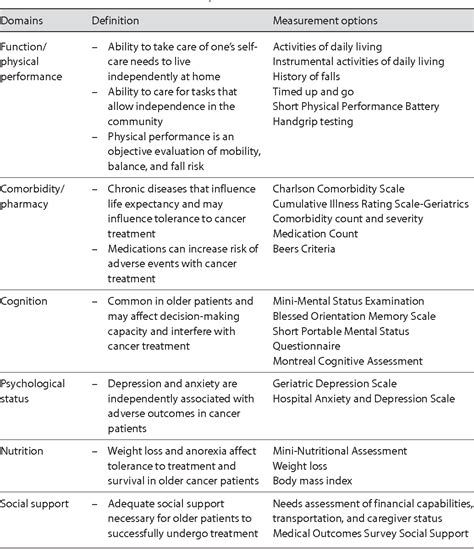
Implementing CGA requires a team-based approach, with geriatricians and other healthcare professionals working together to assess and address the complex needs of older adults. The following steps can help to facilitate the implementation of CGA:
- Establish a CGA Team: Assemble a team of healthcare professionals, including geriatricians, nurses, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and social workers, to provide comprehensive assessment and care.
- Develop a CGA Protocol: Establish a standardized protocol for CGA, including assessment tools, procedures, and guidelines for referral and follow-up.
- Provide Education and Training: Offer education and training to healthcare professionals on the principles and practice of CGA, including assessment tools, communication skills, and care planning.
- Ensure Accessibility and Availability: Ensure that CGA services are accessible and available to all older adults, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status.
Challenges and Limitations of Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment
While CGA has been shown to be effective in improving health outcomes and enhancing patient safety, there are several challenges and limitations to its implementation, including:
- Lack of Standardization: CGA protocols and assessment tools may vary widely across different healthcare settings and organizations.
- Insufficient Resources: CGA teams may face challenges in terms of staffing, funding, and infrastructure, particularly in rural or underserved areas.
- Complexity of Care: Older adults often have multiple comorbidities and complex care needs, requiring careful coordination and communication among healthcare professionals.
What is the primary goal of Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment?
+The primary goal of CGA is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the patient's needs and health status, in order to develop a personalized care plan that addresses their unique needs and preferences.
How is Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment different from other assessment tools?
+CGA is a multifaceted, interdisciplinary approach to assessment that takes into account the patient's physical, functional, cognitive, emotional, and social health, rather than focusing on a single domain or aspect of care.
What are the benefits of Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment for caregivers?
+CGA can provide valuable information and support to family caregivers, helping to reduce their burden and improve their overall well-being, as well as provide guidance on how to care for their loved one.
In conclusion, Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment is a vital tool in providing person-centered care and improving health outcomes for older adults. By taking a multifaceted, interdisciplinary approach to assessment, we can identify the complex needs of geriatric patients and develop personalized care plans that address their unique needs and preferences. As the global population ages, the importance of CGA in shaping healthcare policies and practices for older adults will only continue to grow.