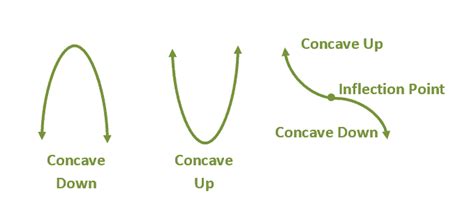
When delving into the realm of calculus and mathematics, understanding the behavior of functions is paramount. One crucial aspect of this understanding involves recognizing whether a function is concave up or down. The terms "concave up" and "concave down" refer to the shape or curvature of a function's graph. This concept is vital in various mathematical and real-world applications, including optimization problems, where identifying whether a function is concave up or down can significantly impact the outcome. In this article, we will explore the definitions, implications, and applications of concave up and down functions, providing a comprehensive overview for those seeking to deepen their understanding of these mathematical concepts.
Key Points
- Understanding the definitions of concave up and concave down functions is crucial for analyzing their behavior and applications.
- The second derivative test is a key tool for determining the concavity of a function.
- Concave up functions have applications in optimization problems where a maximum is sought, while concave down functions are relevant when a minimum is the goal.
- Real-world applications include economics, physics, and engineering, where the curvature of functions can model various phenomena and systems.
- Inflection points mark the transition between concave up and concave down segments of a function and are critical for understanding its overall behavior.
Defining Concave Up and Down Functions
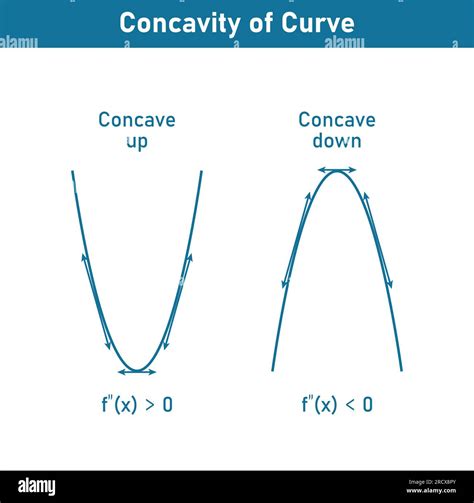
A function is said to be concave up (or convex) on an interval if its graph lies above any line segment connecting two points on the graph. Conversely, a function is concave down (or concave) if its graph lies below any line segment connecting two points on the graph. Mathematically, for a function f(x) to be concave up, the inequality f(y) ≥ f(x) + f’(x)(y - x) must hold for all x and y in the interval, where f’(x) is the derivative of f(x). For a function to be concave down, the inequality is reversed: f(y) ≤ f(x) + f’(x)(y - x). These definitions provide a foundation for understanding the behavior and implications of concave up and down functions.
The Role of the Second Derivative
The second derivative of a function, denoted as f”(x), plays a crucial role in determining its concavity. If the second derivative is positive, f”(x) > 0, the function is concave up. Conversely, if the second derivative is negative, f”(x) < 0, the function is concave down. When the second derivative equals zero, f”(x) = 0, it may indicate an inflection point, where the concavity of the function changes. The second derivative test is a powerful tool for analyzing the concavity of functions and is widely used in calculus and optimization problems.
| Type of Function | Second Derivative | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Concave Up | f''(x) > 0 | Graph lies above any line segment connecting two points. |
| Concave Down | f''(x) < 0 | Graph lies below any line segment connecting two points. |
| Inflection Point | f''(x) = 0 | Change in concavity, from concave up to down or vice versa. |

Applications and Implications
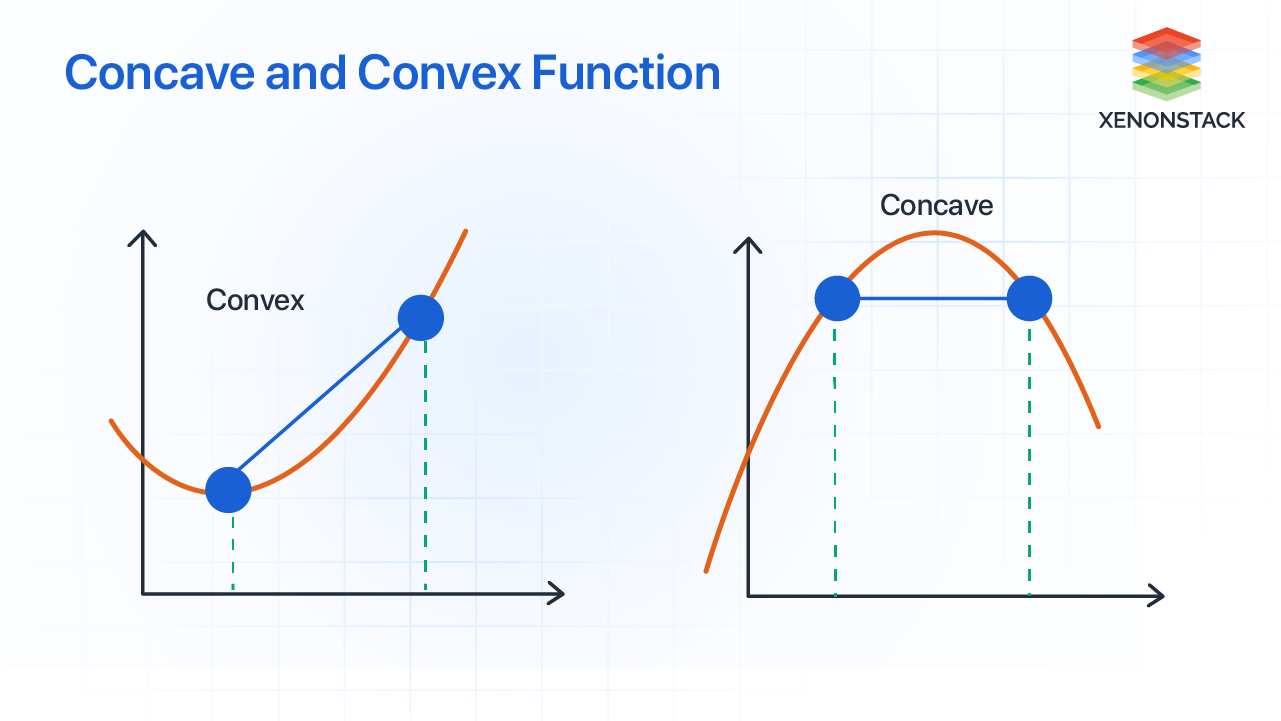
The distinction between concave up and down functions has far-reaching implications in various fields. In economics, for example, the concavity of a utility function can influence how individuals make decisions under uncertainty. In physics and engineering, understanding the concavity of functions can help model complex systems and phenomena, such as the trajectory of projectiles or the stress on materials. The ability to identify and analyze concave up and down functions is, therefore, a critical skill for professionals and researchers in these and related fields.
Optimization Problems
One of the most significant applications of concave up and down functions is in optimization problems. When seeking to maximize a function, a concave down function is relevant, as it ensures that the maximum point is a global maximum. Conversely, for minimization problems, a concave up function is applicable, guaranteeing that the minimum point is a global minimum. The concavity of a function, as determined by its second derivative, is thus a crucial factor in the solution of optimization problems, which are ubiquitous in fields ranging from finance to logistics.
As we conclude our exploration of concave up and down functions, it's clear that understanding these concepts is essential for analyzing and applying mathematical functions in a wide range of contexts. From the theoretical foundations provided by the definitions and the second derivative test to the practical implications in optimization and real-world modeling, the distinction between concave up and down functions is a fundamental aspect of calculus and mathematics. By grasping these concepts, individuals can deepen their understanding of complex systems and phenomena, ultimately contributing to advancements in various fields of study and application.
What is the primary difference between a concave up and a concave down function?
+A concave up function has a graph that lies above any line segment connecting two points on the graph, while a concave down function has a graph that lies below any line segment connecting two points. This difference is determined by the sign of the second derivative of the function.
How does the second derivative test help in identifying concave up and down functions?
+The second derivative test states that if the second derivative of a function is positive, the function is concave up. If the second derivative is negative, the function is concave down. This test provides a straightforward method for determining the concavity of a function based on its second derivative.
What are some real-world applications of understanding concave up and down functions?
+Understanding concave up and down functions has applications in economics, physics, engineering, and optimization problems. In economics, it can influence decision-making under uncertainty. In physics and engineering, it helps model complex systems and phenomena. In optimization, it ensures that the solution found is a global maximum or minimum.