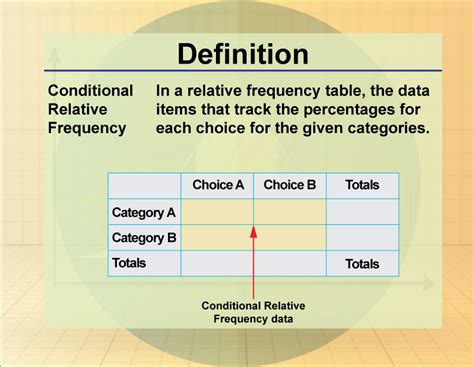
Conditional relative frequency is a statistical concept that plays a crucial role in understanding the relationships between variables in a dataset. It measures the frequency of a particular outcome or event given that another condition or event has occurred. This concept is essential in various fields, including data analysis, machine learning, and probability theory. In this article, we will delve into the world of conditional relative frequency, exploring its definition, calculation, and applications, as well as providing examples to illustrate its usage.
Key Points
- Conditional relative frequency measures the frequency of an event given that another condition has occurred.
- It is calculated by dividing the number of occurrences of the event given the condition by the total number of occurrences of the condition.
- Conditional relative frequency is used in probability theory, statistics, and data analysis to understand relationships between variables.
- It has applications in machine learning, decision-making, and risk assessment.
- Understanding conditional relative frequency is essential for making informed decisions based on data.
Definition and Calculation
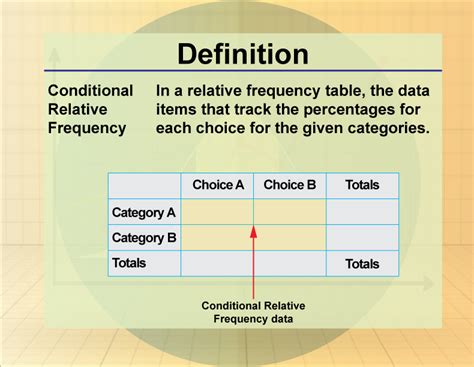
Conditional relative frequency is defined as the proportion of times an event occurs given that another condition or event has occurred. It is calculated using the formula: P(A|B) = (Number of occurrences of A and B) / (Total number of occurrences of B), where A and B are events. This formula provides a measure of the likelihood of event A occurring given that event B has occurred.
For example, consider a dataset of students who have taken a mathematics test. We want to calculate the conditional relative frequency of students who scored above 80 given that they attended a math tutorial. Let's say there are 100 students who attended the tutorial, and 30 of them scored above 80. The conditional relative frequency would be 30/100 = 0.3, indicating that 30% of students who attended the tutorial scored above 80.
Applications and Examples
Conditional relative frequency has numerous applications in various fields. In machine learning, it is used to calculate the probability of a class label given a set of features. For instance, in spam detection, we can calculate the conditional relative frequency of spam emails given certain keywords or features. This helps in developing more accurate spam detection algorithms.
In decision-making, conditional relative frequency is used to assess the likelihood of different outcomes given certain conditions. For example, in finance, we can calculate the conditional relative frequency of stock prices increasing given certain economic indicators. This helps investors make informed decisions about their investments.
| Event | Condition | Conditional Relative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Stock prices increasing | Economic indicators positive | 0.7 |
| Students scoring above 80 | Attending math tutorial | 0.3 |
| Spam emails | Certain keywords present | 0.9 |

Probability Theory and Statistics
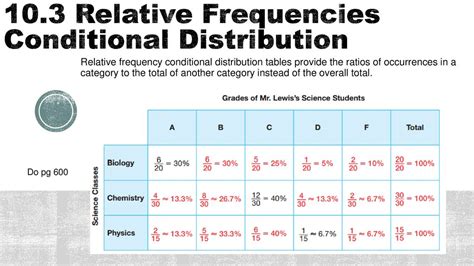
Conditional relative frequency is closely related to probability theory and statistics. In probability theory, it is used to calculate the probability of an event given that another event has occurred. This is known as conditional probability. Conditional probability is a fundamental concept in probability theory and is used to model uncertain events.
In statistics, conditional relative frequency is used to analyze the relationships between variables. It is used to calculate the correlation coefficient, which measures the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables. Conditional relative frequency is also used in regression analysis to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
Machine Learning and Data Analysis
Conditional relative frequency is used in machine learning to develop predictive models. It is used to calculate the probability of a class label given a set of features. This is known as classification. Conditional relative frequency is also used in clustering, which is a type of unsupervised learning. Clustering involves grouping similar data points into clusters based on their features.
In data analysis, conditional relative frequency is used to analyze and visualize data. It is used to create contingency tables, which are used to analyze the relationships between categorical variables. Conditional relative frequency is also used to create heat maps, which are used to visualize the relationships between variables.
What is conditional relative frequency?
+Conditional relative frequency is a statistical concept that measures the frequency of an event given that another condition or event has occurred.
How is conditional relative frequency calculated?
+Conditional relative frequency is calculated using the formula: P(A|B) = (Number of occurrences of A and B) / (Total number of occurrences of B), where A and B are events.
What are the applications of conditional relative frequency?
+Conditional relative frequency has numerous applications in machine learning, data analysis, probability theory, and statistics. It is used to calculate the probability of an event given that another event has occurred, and to analyze the relationships between variables.
In conclusion, conditional relative frequency is a powerful statistical concept that has numerous applications in various fields. By understanding conditional relative frequency, we can gain insights into the relationships between variables and make more accurate predictions. Whether you are a data analyst, machine learning engineer, or statistician, conditional relative frequency is an essential concept to master.
As we continue to collect and analyze large datasets, the importance of conditional relative frequency will only continue to grow. By applying conditional relative frequency to real-world problems, we can develop more accurate predictive models, make informed decisions, and drive business success. With its wide range of applications and versatility, conditional relative frequency is an essential tool for anyone working with data.