Confucianism, a philosophical and ethical system based on the teachings of Confucius, has been a cornerstone of East Asian culture for centuries. With its emphasis on moral values, personal and governmental ethics, and correctness of social relationships, Confucianism has attracted a significant following worldwide. As of 2022, it is estimated that there are approximately 6 million people who identify as Confucians, with the majority residing in China, Taiwan, Korea, and other parts of East Asia. However, the influence of Confucianism extends far beyond these regions, with its principles and values being studied and applied by people from diverse cultural backgrounds.
The global distribution of Confucianism followers is not strictly limited to East Asia. There are notable communities in Southeast Asia, particularly in Singapore and Malaysia, where Confucianism has been influential in shaping local customs and traditions. Furthermore, the Chinese diaspora has played a significant role in spreading Confucianism to other parts of the world, including the Americas, Europe, and Australia. In these regions, Confucianism often blends with other cultural and religious practices, giving rise to unique and hybrid forms of expression.
Key Points
- Approximately 6 million people worldwide identify as Confucians, primarily in East Asia.
- Confucianism's influence extends globally, with its principles being studied and applied across diverse cultures.
- The Chinese diaspora has contributed significantly to the spread of Confucianism beyond East Asia.
- Confucianism often integrates with other cultural and religious practices, leading to diverse expressions worldwide.
- The ethical and moral teachings of Confucianism appeal to people seeking a philosophical framework for living.
Historical Development and Spread of Confucianism

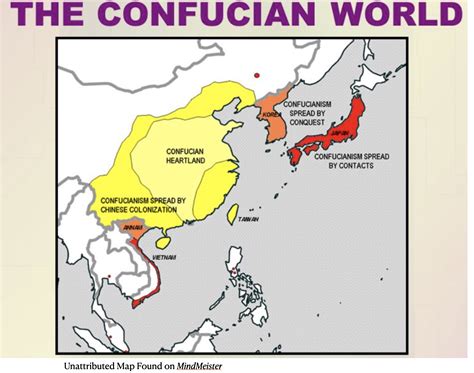
Confucianism originated in China during the 6th century BCE, based on the teachings of Confucius (551-479 BCE). Initially, it was not a religion but a philosophical and ethical system aimed at promoting social harmony and personal moral development. Over time, Confucianism spread throughout East Asia, particularly during the Han Dynasty (206 BCE-220 CE), when it became a state-supported philosophy. The spread of Confucianism was facilitated by scholars, officials, and traders who carried its teachings to Korea, Japan, and Vietnam. Today, Confucianism remains a vital part of the cultural heritage in these countries, with its teachings influencing education, family values, and social norms.
Global Reach and Diversity of Confucianism
The global reach of Confucianism is evident in its adaptation and interpretation by different cultures. For instance, in Korea, Confucianism was deeply ingrained during the Joseon Dynasty (1392-1910), leading to a distinct form of Confucian practice that emphasized social hierarchy and moral obligations. In Japan, Confucianism was introduced from China and Korea, influencing the development of Bushido, the code of conduct for the samurai class. The diversity of Confucianism is also reflected in its fusion with other religions, such as Buddhism and Taoism, resulting in unique philosophical and religious practices.
| Region | Estimated Confucian Population |
|---|---|
| China | 4 million |
| Taiwan | 1 million |
| Korea | 500,000 |
| Other East Asian countries | 200,000 |
| Rest of the world | 300,000 |

Practices and Beliefs of Confucianism
At the heart of Confucianism are its teachings on human nature, morality, and the ideal society. Confucians believe in the inherent goodness of human beings and the potential for self-cultivation and moral development. The core principles of Confucianism include ren (benevolence), yi (righteousness), and li (propriety), which guide individuals in their interactions with others and their community. Rituals and ceremonies, such as the ancestral worship and the Spring and Autumn festivals, are integral parts of Confucian practice, serving as reminders of social obligations and the importance of respecting tradition.
Education and Personal Development in Confucianism
Education is highly valued in Confucianism, seen as a means of personal development and social mobility. The Confucian classics, which include the Analects, the Mencius, and the Xunzi, among others, are considered essential texts for moral and intellectual cultivation. Through the study of these classics and the practice of self-reflection and self-improvement, individuals aim to become junzi, or gentlemen, embodying the virtues of wisdom, courage, and integrity. This emphasis on education and personal development has contributed to the resilience and adaptability of Confucianism in the face of changing societal values and technological advancements.
As Confucianism continues to evolve and spread globally, its followers face the challenge of balancing tradition with modernity. The incorporation of Confucian values into contemporary life requires a nuanced understanding of its historical context and philosophical depth. By embracing this complexity, individuals can harness the wisdom of Confucianism to navigate the complexities of the modern world, fostering a more harmonious and ethical society for all.
What are the core principles of Confucianism?
+The core principles of Confucianism include ren (benevolence), yi (righteousness), and li (propriety), which guide individuals in their interactions with others and their community.
How has Confucianism influenced education?
+Confucianism has placed a strong emphasis on education as a means of personal development and social mobility. The study of Confucian classics is considered essential for moral and intellectual cultivation.
What is the significance of rituals and ceremonies in Confucianism?
+Rituals and ceremonies, such as ancestral worship and the Spring and Autumn festivals, are integral parts of Confucian practice, serving as reminders of social obligations and the importance of respecting tradition.
How does Confucianism contribute to personal development?
+Confucianism promotes personal development through the practice of self-reflection, self-improvement, and the pursuit of becoming a junzi, or gentleman, embodying the virtues of wisdom, courage, and integrity.
What is the global reach of Confucianism?
+Confucianism has a significant following in East Asia, particularly in China, Taiwan, and Korea, but its influence extends globally, with communities and adherents in Southeast Asia, the Americas, Europe, and Australia.
Meta Description: Discover the global reach and diversity of Confucianism, a philosophical and ethical system that has shaped East Asian culture and beyond, with its emphasis on moral values, education, and personal development.



