When exploring the realm of geometry, one of the fundamental concepts that students encounter is the properties of angles formed by parallel lines and transversals. Among these properties, consecutive interior angles play a crucial role in understanding the relationships between angles and the geometric figures they form. In this article, we will delve into the world of consecutive interior angles, exploring their definition, properties, and practical applications, with a focus on providing a comprehensive understanding for those seeking to deepen their knowledge of geometric principles.
Key Points
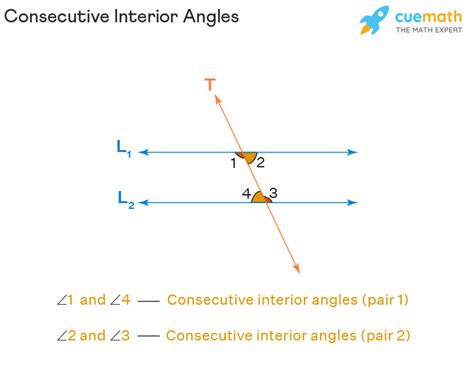
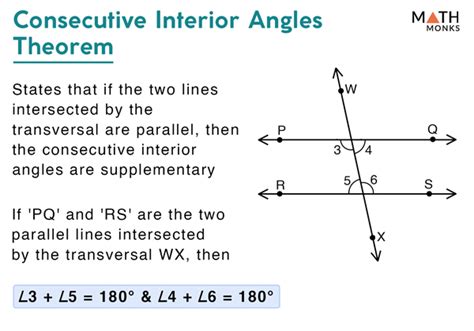
- Consecutive interior angles are angles that lie on the same side of a transversal and inside two lines that the transversal intersects.
- When two lines are parallel, consecutive interior angles are supplementary, meaning they add up to 180 degrees.
- The sum of consecutive interior angles can be used to determine if two lines are parallel or not.
- Consecutive interior angles have numerous applications in geometry, architecture, and engineering, particularly in designing shapes and structures.
- Understanding consecutive interior angles is essential for solving problems related to parallel lines and transversals.
Understanding Consecutive Interior Angles
Consecutive interior angles are defined as the angles that are formed on the same side of a transversal and inside two lines that the transversal intersects. These angles are crucial in geometry because they help in identifying parallel lines and understanding the properties of angles formed when a transversal intersects two lines. For instance, when a transversal intersects two parallel lines, the consecutive interior angles are supplementary, meaning they add up to 180 degrees. This property is a fundamental principle in geometry and is used extensively in solving problems related to parallel lines and transversals.
Properties of Consecutive Interior Angles
The properties of consecutive interior angles are closely related to the properties of parallel lines. When two lines are parallel, the consecutive interior angles formed by a transversal are supplementary. This means that if one angle is x degrees, the other angle will be (180 - x) degrees. This property can be used to determine if two lines are parallel or not. For example, if the sum of two consecutive interior angles is 180 degrees, it indicates that the lines are parallel. On the other hand, if the sum is not 180 degrees, the lines are not parallel.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Supplementary Angles | Consecutive interior angles of parallel lines are supplementary, adding up to 180 degrees. |
| Parallel Lines | If the sum of consecutive interior angles is 180 degrees, the lines are parallel. |
| Non-Parallel Lines | If the sum of consecutive interior angles is not 180 degrees, the lines are not parallel. |
Applications of Consecutive Interior Angles
Consecutive interior angles have numerous applications in various fields, including geometry, architecture, and engineering. In geometry, understanding consecutive interior angles is essential for solving problems related to parallel lines and transversals. Architects use the properties of consecutive interior angles to design buildings and structures, ensuring that the lines and angles are proportionate and aesthetically pleasing. Engineers also apply the principles of consecutive interior angles in designing bridges, roads, and other infrastructure, taking into account the properties of parallel lines and transversals to ensure stability and safety.
Real-World Examples
In real-world scenarios, consecutive interior angles are used in various ways. For instance, when designing a bridge, engineers need to ensure that the lines and angles are proportionate and stable. By applying the principles of consecutive interior angles, they can determine the nature of the lines and ensure that the structure is safe and durable. Similarly, in architecture, the properties of consecutive interior angles are used to design buildings with proportionate lines and angles, creating a visually appealing and stable structure.
What are consecutive interior angles?
+Consecutive interior angles are angles that lie on the same side of a transversal and inside two lines that the transversal intersects.
What is the sum of consecutive interior angles of parallel lines?
+The sum of consecutive interior angles of parallel lines is 180 degrees.
How are consecutive interior angles used in real-world applications?
+Consecutive interior angles are used in various fields, including geometry, architecture, and engineering, to design and build structures with proportionate lines and angles, ensuring stability and safety.
In conclusion, consecutive interior angles are a fundamental concept in geometry, and understanding their properties and applications is essential for solving problems related to parallel lines and transversals. By recognizing the relationship between these angles, one can determine the nature of the lines and apply geometric principles to solve complex problems. The applications of consecutive interior angles are diverse, ranging from geometry and architecture to engineering, and their principles are used to design and build structures that are stable, safe, and aesthetically pleasing.