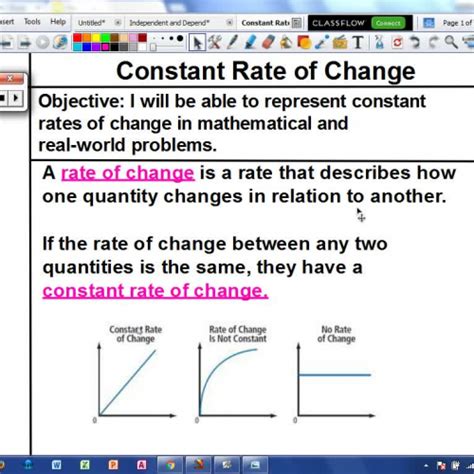
The concept of a constant rate is fundamental in various fields, including physics, chemistry, and economics. It refers to a rate that remains unchanged over a specific period or under certain conditions. Understanding constant rates is crucial for analyzing and predicting phenomena in these fields. Here are five ways constant rates manifest and their significance:
Key Points
- Constant rates in chemical reactions and their importance in understanding reaction kinetics.
- The role of constant rates in economic models, particularly in the context of inflation and interest rates.
- Constant rates of change in calculus and their application in optimizing functions.
- The principle of constant rates in physics, especially in the context of motion and forces.
- Constant rates in biological processes, such as population growth and decay, and their significance in ecology and epidemiology.
Chemical Reactions and Constant Rates
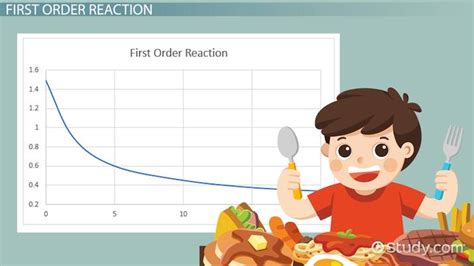
In chemistry, a constant rate of reaction is crucial for understanding and predicting the behavior of reactants and products. The rate of a chemical reaction can be influenced by several factors, including concentration, temperature, and the presence of catalysts. By maintaining a constant rate, chemists can better analyze the kinetics of a reaction, which is essential for designing and optimizing industrial processes. For instance, the Haber-Bosch process for ammonia synthesis relies on maintaining specific conditions to achieve a constant rate of reaction, ensuring efficiency and safety.
Zero-Order Reactions
A particular type of chemical reaction that exhibits a constant rate is the zero-order reaction. In a zero-order reaction, the rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of the reactants. This means that the reaction proceeds at a constant rate until the reactants are depleted. Zero-order reactions are relatively rare but are significant in certain industrial processes and in understanding complex reaction mechanisms.
Economic Models and Constant Rates

In economics, constant rates are used in various models to predict economic behavior and outcomes. For example, the concept of a constant rate of inflation is crucial for monetary policy decisions. Central banks often aim to maintain a low, constant rate of inflation to promote economic stability and growth. Similarly, constant interest rates are used in economic models to analyze the impact of borrowing costs on consumption and investment. The use of constant rates in economic models simplifies complex interactions and allows for more accurate predictions and policy decisions.
Interest Rates and Economic Growth
Constant interest rates play a vital role in influencing economic growth. By maintaining a constant interest rate, central banks can stimulate or slow down economic activity. Lower constant interest rates can encourage borrowing and spending, thereby boosting economic growth, while higher rates can have the opposite effect by increasing the cost of borrowing. The balance between stimulating growth and controlling inflation is a delicate one, and constant interest rates are a key tool in achieving this balance.
Calculus and Constant Rates of Change
In calculus, the concept of a constant rate of change is fundamental. It is represented by the derivative of a function, which gives the rate at which the function changes as its input changes. A constant rate of change means that the derivative of the function is constant over a given interval. This concept is crucial for optimizing functions, which is essential in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics. By finding where a function has a constant rate of change, one can identify maxima, minima, and points of inflection, which are critical for understanding the behavior of complex systems.
Optimization Problems
Constant rates of change are particularly useful in solving optimization problems. These problems involve finding the maximum or minimum of a function subject to certain constraints. In many cases, the optimal solution occurs at a point where the rate of change of the function is constant. For example, in economics, firms may seek to maximize profits by producing at a level where the marginal revenue (the rate of change of total revenue with respect to output) equals the marginal cost (the rate of change of total cost with respect to output), which often corresponds to a constant rate of change in the profit function.
Physics and Constant Rates
In physics, constant rates are observed in various phenomena, including motion and forces. For instance, an object moving at a constant velocity has a constant rate of change of its position with respect to time. This concept is fundamental in understanding kinematics and dynamics. Moreover, forces that act at a constant rate can result in constant accelerations, which are crucial for understanding the motion of objects under the influence of gravity or other forces.
Uniform Motion
Uniform motion, where an object moves at a constant velocity, is a key concept in physics. It is characterized by a constant rate of change of the object’s position. This type of motion is significant because it allows for the application of simple and straightforward mathematical models to predict the object’s future position and velocity. Understanding uniform motion is essential for analyzing more complex types of motion and for applying physical principles to real-world problems.
Biological Processes and Constant Rates

In biology, constant rates are observed in various processes, including population growth and decay. The logistic growth model, for example, assumes a constant rate of growth that decreases as the population approaches its carrying capacity. This model is useful for predicting the growth of populations in ecology and for understanding the spread of diseases in epidemiology. Constant rates in biological processes can help scientists understand the dynamics of complex systems and make predictions about future outcomes.
Population Dynamics
The study of population dynamics often involves modeling the growth or decline of populations over time. Constant rates of growth or decay can be used to simplify these models and make predictions about future population sizes. For instance, the exponential growth model assumes a constant rate of growth, which can be used to estimate the future size of a population under ideal conditions. Understanding these constant rates is essential for managing populations, whether in the context of conservation biology or public health.
What is the significance of constant rates in chemical reactions?
+Constant rates in chemical reactions are significant because they allow chemists to understand and predict the behavior of reactants and products, which is crucial for designing and optimizing industrial processes.
How do constant interest rates influence economic growth?
+Constant interest rates can stimulate or slow down economic activity by influencing borrowing costs. Lower constant interest rates can encourage borrowing and spending, thereby boosting economic growth, while higher rates can increase the cost of borrowing and have the opposite effect.
What is the role of constant rates of change in calculus?
+Constant rates of change in calculus are represented by the derivative of a function and are crucial for optimizing functions. They help in identifying maxima, minima, and points of inflection, which are critical for understanding the behavior of complex systems.
How are constant rates observed in physics?
+Constant rates in physics are observed in phenomena such as uniform motion, where an object moves at a constant velocity, and in forces that act at a constant rate, resulting in constant accelerations.
What is the significance of constant rates in biological processes?
+Constant rates in biological processes, such as population growth and decay, are significant because they help scientists understand the dynamics of complex systems and make predictions about future outcomes, which is essential for managing populations and understanding the spread of diseases.