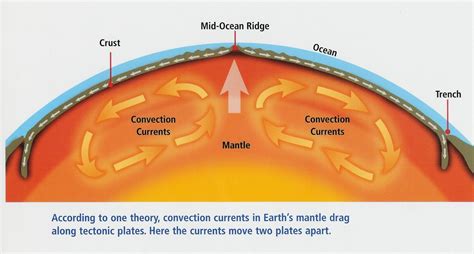
Mantle convection is a fundamental process that drives plate tectonics, shaping the Earth's surface over millions of years. This complex phenomenon involves the movement of hot, viscous rock in the Earth's mantle, which is the layer between the crust and the core. Understanding how mantle convection works is crucial for grasping the dynamics of the Earth's interior and its impact on the planet's surface. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of mantle convection, exploring its mechanisms, processes, and effects on the Earth's surface.
Key Points
- Mantle convection is driven by heat from the Earth's core and radioactive decay in the mantle.
- There are two primary types of mantle convection: whole-mantle convection and layered convection.
- The process involves the movement of hot, viscous rock in the mantle, which drives plate tectonics.
- Mantle convection is responsible for the creation of mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes.
- Understanding mantle convection is essential for predicting geological events and mitigating natural hazards.
Introduction to Mantle Convection
Mantle convection is a slow, continuous process that occurs over geological timescales. It is driven by the heat generated by the Earth’s core and the radioactive decay of elements in the mantle. This heat causes the mantle rock to expand and become less dense than the surrounding material, leading to its ascent. As the hot rock rises, it cools and becomes denser, eventually sinking back down to the bottom of the mantle. This circulation of hot and cold rock creates a convective cell, which drives the movement of the tectonic plates.
Types of Mantle Convection
There are two primary types of mantle convection: whole-mantle convection and layered convection. Whole-mantle convection involves the circulation of rock throughout the entire mantle, from the core-mantle boundary to the Earth’s surface. This type of convection is thought to be the dominant mechanism driving plate tectonics. Layered convection, on the other hand, involves the circulation of rock in distinct layers within the mantle. This type of convection is less well understood and is thought to occur in specific regions of the mantle.
| Type of Convection | Description |
|---|---|
| Whole-Mantle Convection | Circulation of rock throughout the entire mantle |
| Layered Convection | Circulation of rock in distinct layers within the mantle |
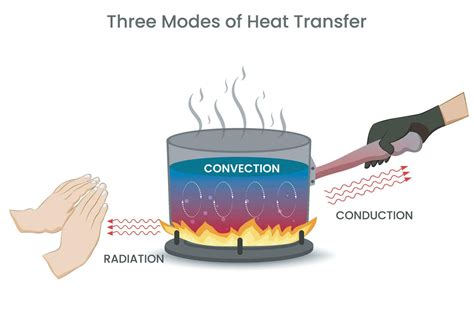
Process of Mantle Convection

The process of mantle convection involves several key stages. First, the heat generated by the Earth’s core and radioactive decay in the mantle causes the rock to expand and become less dense. This hot, buoyant rock then rises through the mantle, driven by its buoyancy. As it rises, it cools and becomes denser, eventually sinking back down to the bottom of the mantle. This circulation of hot and cold rock creates a convective cell, which drives the movement of the tectonic plates.
Effects of Mantle Convection
Mantle convection has a profound impact on the Earth’s surface. It is responsible for the creation of mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. The movement of the tectonic plates driven by mantle convection leads to the formation of these geological features. For example, the collision of two plates can lead to the formation of a mountain range, while the movement of a plate over a hotspot can lead to the formation of a volcano.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, mantle convection is a complex and fascinating process that drives plate tectonics and shapes the Earth’s surface. Understanding the mechanisms and processes of mantle convection is essential for predicting geological events and mitigating natural hazards. Further research is needed to fully understand the dynamics of mantle convection and its impact on the Earth’s surface. By continuing to study this process, we can gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s interior and its role in shaping our planet.
What drives mantle convection?
+Mantle convection is driven by the heat generated by the Earth’s core and radioactive decay in the mantle.
What are the two primary types of mantle convection?
+The two primary types of mantle convection are whole-mantle convection and layered convection.
What is the impact of mantle convection on the Earth’s surface?
+Mantle convection is responsible for the creation of mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes, and plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s surface.