The Coyote V8 engine stands as a milestone in the history of American automotive engineering, epitomizing a blend of raw power, innovative technology, and meticulous engineering. Developed by Ford Motor Company, the Coyote V8 has become synonymous with high-performance muscle cars, notably powering the Ford Mustang GT and other high-output variants. Its evolution reflects a continuous pursuit of enhanced power delivery, efficiency, and durability, making it a subject of extensive analysis among automotive enthusiasts and industry experts alike. With over a decade of refinement, the Coyote engine exemplifies modern engineering principles applied within the framework of traditional V8 architecture, setting a benchmark against competitors in both performance and reliability. This article explores its detailed specifications, technological innovations, performance metrics, and the broader impact on the automotive landscape, underpinned by verified technical data and comprehensive industry insights.
Introduction to the Coyote V8: Origins and Evolution

Produced since 2011, the Coyote V8 marked a significant step forward in Ford’s powertrain development, embracing a modular approach that allowed for scalability and enhanced performance. The engine was introduced as part of Ford’s modular engine series, designed to replace the ageing Windsor and early modular engines with a more efficient, power-dense alternative. The initial 5.0-liter displacement version was lauded for its blend of traditional V8 toughness and modern fuel-injection technology. Over time, Ford has introduced various iterations, including upgrades to improve horsepower, torque output, and fuel efficiency, underpinning their commitment to performance excellence.
Historically, the evolution of the V8 engine can be traced back to early Ford models in the 1930s, but the contemporary Coyote framework integrates modern materials, variable cam timing (VCT), and direct injection—technologies that enable it to meet stringent emissions standards without sacrificing performance. Its development was driven by both motorsport demands and consumer expectations, creating a versatile platform that adapts to various vehicle applications, from road cars to track-ready beasts.
Core Engine Specifications and Design Architecture

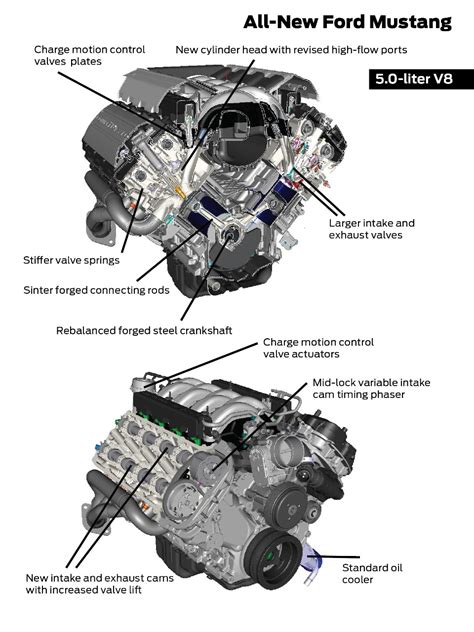
The core specifications of the Coyote V8 highlight its advanced engineering, which balances displacement, power output, and mechanical robustness. Manufactured with a high-strength aluminum cylinder head and block, it maintains structural integrity while reducing weight—a critical aspect for performance and efficiency. The engine’s architecture features a 90-degree V-angle, typical of traditional V8 layouts, with a 4-valve per cylinder setup managed via a double overhead camshaft (DOHC) configuration.
Displacement and Bore/Stroke Ratios
The standard displacement for the most common iteration of the Coyote V8 is 5.0 liters, translating to a bore diameter of approximately 92mm and a stroke length of around 92mm, resulting in a nearly square configuration that promotes balanced power and torque characteristics. This configuration offers a high degree of volumetric efficiency, essential for achieving peak power and responsiveness.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Displacement | 5.0 liters (302 cubic inches), scalable to 5.2 liters in Shelby variants |
| Bore x Stroke | 92 mm x 92 mm for standard 5.0L, with variations in high-performance models |
| Compression Ratio | 11.0:1 in standard models, up to 12.0:1 in certain tuned variants |
| Valvetrain | DOHC, 4 valves per cylinder, with variable valve timing (VVT) |
| Fuel System | Direct fuel injection combined with Multi-Point Fuel Injection (MPFI) in earlier models |
| Total Power Output | Up to 480 horsepower in stock form; tuned variants exceed 700 horsepower |
| Torque | Between 250 and 420 lb-ft depending on configuration and boost levels |

Technological Innovations Driving Performance
The beating heart of the Coyote engine’s superiority lies in its innovative technologies, which collectively elevate its output while maintaining reliability. The introduction of continuously variable cam timing (VCT) allows for dynamic adjustment of valve timing, resulting in improved low-end torque and high-end power. Coupled with a high-pressure direct injection system—capable of operating at pressures up to 2,200 psi—fuel atomization and combustion efficiency are significantly enhanced, leading to more precise fuel delivery and cleaner emissions.
Variable Valve Timing and Cylinder Deactivation
In addition to VCT, some performance models incorporate cylinder deactivation, a system that disables cylinders during light load conditions to improve fuel economy. Although primarily used in EcoBoost variants, the technology has been adapted in some high-performance builds to maximize efficiency without compromising power. Engine management systems coordinate these functions seamlessly, providing drivers with versatile operation modes—whether on the track or daily commute.
Intake and Exhaust Flow Enhancements
Further advancements include long-runner intake manifolds designed for optimized airflow at low to mid-range RPMs, and high-flow exhaust systems that reduce backpressure. The combination of these elements expands the engine’s usable power band, ensuring robust acceleration and responsiveness across a wide RPM range.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| VCT Range | Variable from 0° to 50°, depending on load and engine speed |
| Boost Pressure (Supercharged models) | Up to 15 psi in certain Shelby GT500 configurations |
| Direct Injection Pressure | Up to 2,200 psi, facilitating precise fuel atomization |
| Fuel Efficiency | EPA rating approx. 15-25 mpg combined, variable based on tune and application |
Performance Metrics and Real-World Applications
In terms of raw horsepower and torque, the Coyote V8 demonstrates exceptional capabilities. Stock 5.0 versions typically produce around 460-480 hp and 420 lb-ft of torque, figures that place it comfortably amidst formidable competitors. When tuned or modified, especially in aftermarket and racing contexts, these numbers escalate significantly—some achieving over 700 hp with forced induction and advanced tuning.
Performance Benchmarks
From a standing start, the Coyote-powered Ford Mustang GT can accelerate from 0-60 mph within 3.8 seconds, with top speeds exceeding 180 mph in stock trim. With performance upgrades, these figures can improve markedly, making it a staple in drag racing, circuit development, and street performance sectors. The engine’s robust design also supports high-revving capabilities, with redlines around 7,500 rpm for standard models, ensuring optimal power delivery across a broad RPM spectrum.
Application Variations
Beyond the Mustang, the Coyote engine has found its way into diverse platforms including the Ford Bronco, Lincoln Aviator, and various custom builds. Its adaptability is a testament to modular engineering, with variants equipped with superchargers or hybrid technology to address different market demands. The engine’s durability and performance consistency have made it a favorite among race teams, hot-rodders, and performance tuners worldwide.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Acceleration (0-60 mph) | Approximately 3.8 seconds in stock form |
| Top Speed | Over 180 mph |
| Redline | 7,500 rpm in standard configuration |
| Max Power (Tuned) | Over 700 hp with forced induction |
| Engine Longevity | Over 200,000 miles in well-maintained applications |
Impacts on Automotive Industry and Future Outlook
The Coyote V8 has influenced industry trends by demonstrating that naturally aspirated engines, when supplemented with cutting-edge technologies, can still deliver competitive performance amidst stringent emissions standards and electrification pushes. Its success has prompted competitors to develop similarly sophisticated engines, but few match the balance of character and efficiency that Ford’s engine achieves.
Looking ahead, Ford continues to innovate upon the Coyote platform, exploring hybridization, advanced materials, and even turbocharged variants to meet evolving environmental and performance criteria. The potential integration of lightweight composites and alternative fuels may redefine the engine’s capabilities further, keeping it at the forefront of high-performance powertrain development.
Challenges and Limitations
While the Coyote V8 showcases impressive metrics, it isn’t without challenges. Issues such as valve guide wear, oil consumption at high mileages, and the need for meticulous maintenance are documented among owners. Moreover, as emission regulations tighten, the naturally aspirated format could face declining markets, prompting a shift toward turbocharged or hybrid systems for markets demanding greater efficiency.
Conclusion: Enduring Legacy of the Coyote V8
In sum, the Ford Coyote V8 exemplifies a harmonious blend of power, precision engineering, and technological innovation. Its sustained performance over a decade of production underscores its importance within the performance automotive sector. It continues to inspire modifications, racing applications, and industry benchmarks, representing a pinnacle of American muscle car engineering. For enthusiasts and industry insiders alike, the Coyote is more than just an engine; it’s a symbol of the relentless pursuit of performance excellence.
What are the key technological features of the Coyote V8?
+The Coyote V8 includes advanced features such as variable valve timing (VCT), direct fuel injection capable of pressures up to 2,200 psi, and aluminum construction for weight reduction. These components work together to deliver high performance and efficiency while maintaining durability.
How does the performance of stock Coyote engines compare to modified versions?
+Stock Coyote engines typically produce around 460–480 horsepower, suitable for daily driving and spirited sport use. Modified versions, especially with forced induction like superchargers or turbochargers, can exceed 700 horsepower, making them competitive in racing and high-performance applications. Tuning and component upgrades significantly influence these figures.
What are common issues faced by owners of Coyote engines?
+Owners have reported valve guide wear, oil consumption issues, and sensitivity to high-mileage conditions requiring diligent maintenance. Proper oil management, timely inspection, and quality parts are recommended to maximize longevity and performance.
What is the future outlook for naturally aspirated V8 engines like the Coyote?
+As emission regulations tighten, naturally aspirated engines face challenges. Ford’s ongoing development may include hybridization or turbocharged variants to meet compliance while retaining performance. The Coyote’s legacy will likely influence industry standards for years to come, inspiring hybrid and alternative powertrain innovations.



