The creatine kinase (CK) blood test is a diagnostic tool used to measure the levels of creatine kinase in the blood. Creatine kinase is an enzyme found in the heart, brain, skeletal muscle, and other tissues, playing a crucial role in energy production and muscle contraction. The CK blood test is essential in diagnosing and monitoring various muscular and neurological disorders, as well as assessing tissue damage.
In healthy individuals, the levels of creatine kinase in the blood are relatively low. However, when muscle or tissue damage occurs, CK is released into the bloodstream, leading to elevated levels. The CK blood test is commonly used to diagnose conditions such as muscular dystrophy, myocardial infarction (heart attack), and rhabdomyolysis (a condition characterized by the breakdown of skeletal muscle tissue). The test can also help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and detect potential complications.
Key Points
- The creatine kinase blood test measures the levels of creatine kinase in the blood to diagnose and monitor muscular and neurological disorders.
- Elevated CK levels can indicate tissue damage, muscular dystrophy, myocardial infarction, or rhabdomyolysis.
- The test is essential in assessing the effectiveness of treatment and detecting potential complications.
- CK has three main isoforms: CK-MM (skeletal muscle), CK-MB (heart muscle), and CK-BB (brain and smooth muscle).
- Normal CK levels in the blood are typically less than 200 U/L, but can vary depending on the laboratory and individual factors.
Understanding Creatine Kinase Isoforms
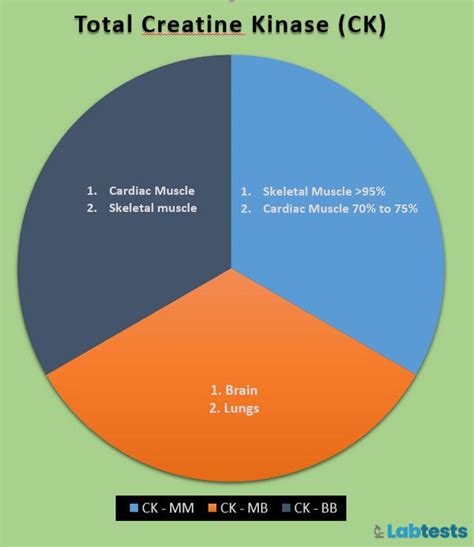
Creatine kinase has three main isoforms, each with specific tissue distribution: CK-MM (skeletal muscle), CK-MB (heart muscle), and CK-BB (brain and smooth muscle). The CK-MM isoform is the most abundant, accounting for approximately 90% of total CK activity in healthy individuals. The CK-MB isoform is primarily found in the heart muscle, while the CK-BB isoform is present in the brain and smooth muscle. Measuring the levels of each isoform can help diagnose specific conditions, such as myocardial infarction (elevated CK-MB) or skeletal muscle damage (elevated CK-MM).
CK Blood Test Procedure and Interpretation
The CK blood test is a relatively simple procedure, involving a venipuncture (blood draw) from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are typically reported in units per liter (U/L), with normal values varying depending on the laboratory and individual factors. In general, normal CK levels in the blood are typically less than 200 U/L. Elevated CK levels can indicate tissue damage or disease, while decreased levels may suggest muscle atrophy or neurodegenerative disorders.
| CK Isoform | Tissue Distribution | Normal Range (U/L) |
|---|---|---|
| CK-MM | Skeletal muscle | 50-150 |
| CK-MB | Heart muscle | 0-5 |
| CK-BB | Brain and smooth muscle | 0-2 |
Clinical Applications and Limitations

The CK blood test has various clinical applications, including diagnosing and monitoring muscular dystrophy, myocardial infarction, and rhabdomyolysis. The test can also help assess the effectiveness of treatment and detect potential complications. However, the CK blood test has some limitations. For example, elevated CK levels can be seen in various conditions, making it essential to consider clinical presentation, medical history, and other diagnostic tests when interpreting results.
Diagnosing Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and degeneration. The CK blood test is a valuable tool in diagnosing and monitoring muscular dystrophy. Elevated CK levels, particularly CK-MM, can indicate muscle damage and degeneration. The test can also help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and detect potential complications, such as respiratory or cardiac involvement.
What is the normal range for creatine kinase levels in the blood?
+Normal CK levels in the blood are typically less than 200 U/L, but can vary depending on the laboratory and individual factors.
What are the clinical applications of the creatine kinase blood test?
+The CK blood test has various clinical applications, including diagnosing and monitoring muscular dystrophy, myocardial infarction, and rhabdomyolysis.
Can the creatine kinase blood test be used to monitor treatment effectiveness?
+Yes, the CK blood test can help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and detect potential complications.
In conclusion, the creatine kinase blood test is a valuable diagnostic tool used to measure the levels of creatine kinase in the blood. The test is essential in diagnosing and monitoring various muscular and neurological disorders, as well as assessing tissue damage. By understanding the different isoforms of creatine kinase and their tissue distribution, healthcare professionals can accurately interpret CK blood test results and provide effective treatment and management plans.



