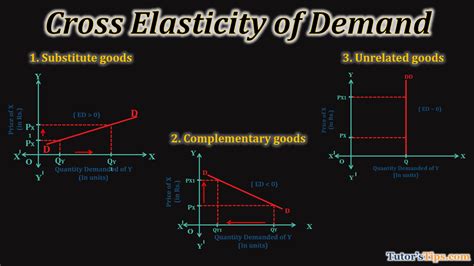
The concept of cross elasticity of demand is a fundamental principle in microeconomics, enabling businesses and policymakers to understand the intricate relationships between different products and services in the market. This concept is crucial for making informed decisions regarding product development, pricing strategies, and market forecasting. In this article, we will delve into the world of cross elasticity of demand, exploring its definition, types, calculations, and real-world applications.
The cross elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of one product to changes in the price of another product. It is an essential tool for analyzing the substitutability or complementarity of goods and services. A positive cross elasticity of demand indicates that the two products are substitutes, meaning that an increase in the price of one product leads to an increase in the demand for the other product. On the other hand, a negative cross elasticity of demand suggests that the products are complements, meaning that an increase in the price of one product leads to a decrease in the demand for the other product.
Key Points
- The cross elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of one product to changes in the price of another product.
- A positive cross elasticity of demand indicates that the two products are substitutes.
- A negative cross elasticity of demand suggests that the products are complements.
- The calculation of cross elasticity of demand involves the percentage change in the quantity demanded of one product and the percentage change in the price of another product.
- Understanding cross elasticity of demand is crucial for businesses to develop effective pricing strategies and for policymakers to make informed decisions about taxation and regulation.
Types of Cross Elasticity of Demand
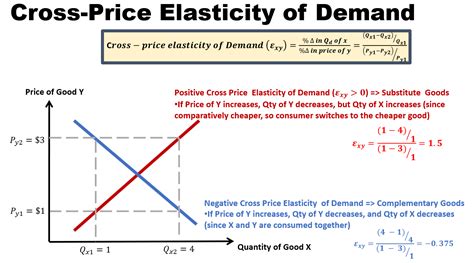
There are two primary types of cross elasticity of demand: positive and negative. A positive cross elasticity of demand occurs when an increase in the price of one product leads to an increase in the demand for another product. This is often seen in the case of substitute goods, such as Coca-Cola and Pepsi. If the price of Coca-Cola increases, consumers may switch to Pepsi, leading to an increase in the demand for Pepsi.
On the other hand, a negative cross elasticity of demand occurs when an increase in the price of one product leads to a decrease in the demand for another product. This is often seen in the case of complementary goods, such as cars and gasoline. If the price of cars increases, consumers may be less likely to purchase a car, leading to a decrease in the demand for gasoline.
Calculation of Cross Elasticity of Demand
The calculation of cross elasticity of demand involves the percentage change in the quantity demanded of one product and the percentage change in the price of another product. The formula for calculating cross elasticity of demand is:Cross Elasticity of Demand = (Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded of Product A) / (Percentage Change in Price of Product B)
For example, suppose we want to calculate the cross elasticity of demand between Coca-Cola and Pepsi. If the price of Coca-Cola increases by 10% and the quantity demanded of Pepsi increases by 5%, the cross elasticity of demand would be:
Cross Elasticity of Demand = (5% / 10%) = 0.5
This means that for every 1% increase in the price of Coca-Cola, the quantity demanded of Pepsi increases by 0.5%.
| Product | Price Change | Quantity Demanded Change |
|---|---|---|
| Coca-Cola | 10% | -5% |
| Pepsi | 0% | 5% |

Real-World Applications of Cross Elasticity of Demand

The concept of cross elasticity of demand has numerous real-world applications. Businesses use this concept to develop pricing strategies, identify new market opportunities, and forecast demand. For example, a company that produces both coffee and tea may use cross elasticity of demand to determine the optimal price for each product. If the cross elasticity of demand between coffee and tea is positive, the company may increase the price of coffee and decrease the price of tea to maximize revenue.
Policymakers also use cross elasticity of demand to make informed decisions about taxation and regulation. For example, if the cross elasticity of demand between gasoline and cars is negative, policymakers may implement policies to reduce the demand for gasoline, such as increasing the tax on gasoline or promoting the use of electric vehicles.
Limitations of Cross Elasticity of Demand
While the concept of cross elasticity of demand is a powerful tool for analyzing the relationships between different products, it has several limitations. One of the primary limitations is that it assumes that the relationship between the two products is linear, which may not always be the case. Additionally, cross elasticity of demand can be affected by various factors, such as changes in consumer preferences, income, and technology.What is the difference between positive and negative cross elasticity of demand?
+A positive cross elasticity of demand indicates that the two products are substitutes, while a negative cross elasticity of demand suggests that the products are complements.
How is cross elasticity of demand calculated?
+Cross elasticity of demand is calculated using the formula: Cross Elasticity of Demand = (Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded of Product A) / (Percentage Change in Price of Product B)
What are the real-world applications of cross elasticity of demand?
+Cross elasticity of demand has numerous real-world applications, including developing pricing strategies, identifying new market opportunities, and forecasting demand.
In conclusion, the concept of cross elasticity of demand is a fundamental principle in microeconomics that enables businesses and policymakers to understand the intricate relationships between different products and services in the market. By analyzing the cross elasticity of demand, businesses can develop effective pricing strategies, identify new market opportunities, and forecast demand. Policymakers can also use this concept to make informed decisions about taxation and regulation. While the concept of cross elasticity of demand has several limitations, it remains a powerful tool for analyzing the relationships between different products and services.
Meta Description: Understand the concept of cross elasticity of demand, its calculation, and real-world applications. Learn how businesses and policymakers use this principle to make informed decisions about pricing, market forecasting, and regulation.