Calculating the area of a cylinder is a fundamental concept in geometry, crucial for various applications in engineering, architecture, and design. The cylinder, a three-dimensional shape with two parallel and circular bases connected by a curved lateral surface, requires a comprehensive approach to calculate its total area. This involves understanding the formulas and techniques applicable to different parts of the cylinder, including the two bases and the lateral (side) surface area. In this article, we will delve into the methods for calculating the area of a cylinder, emphasizing the importance of precise mathematical formulas and their applications.
Understanding the Components of a Cylinder
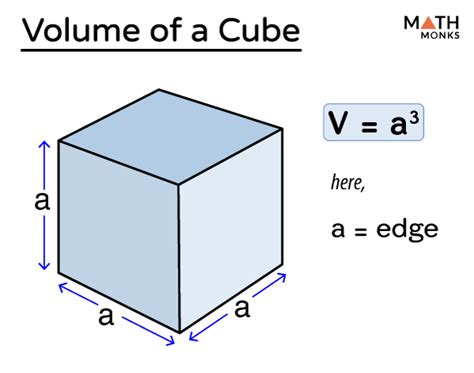
Before diving into the calculation methods, it’s essential to understand the components of a cylinder. A cylinder consists of two circular bases and a curved lateral surface. The area of the cylinder is the sum of the areas of the two bases and the lateral surface area. The formulas for calculating these areas are based on the radius of the circular bases and the height of the cylinder.
Key Formulas for Cylinder Area Calculation
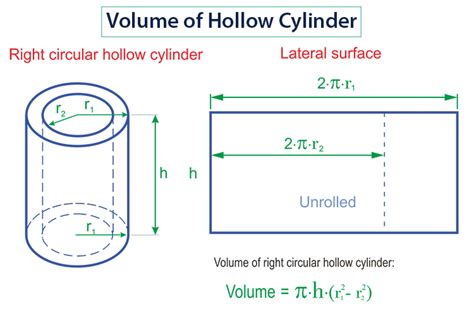
The total surface area (TSA) of a cylinder can be calculated using the formula: TSA = 2πr^2 + 2πrh, where “r” is the radius of the circular base, “h” is the height of the cylinder, and “π” (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159. This formula combines the areas of the two bases (2πr^2) and the lateral surface area (2πrh).
5 Methods to Calculate Cylinder Area

Here are five approaches to calculating the area of a cylinder, each highlighting a different aspect or application of the formulas:
- Basic Formula Application: The most straightforward method involves directly applying the formula for the total surface area: TSA = 2πr^2 + 2πrh. This requires knowing the radius and height of the cylinder.
- Calculating Base and Lateral Areas Separately: Sometimes, it's useful to calculate the areas of the bases and the lateral surface separately. The area of one base is πr^2, and since there are two bases, their total area is 2πr^2. The lateral surface area is 2πrh. This approach can be helpful for understanding the contribution of each component to the total area.
- Using the Slant Height for Lateral Area: In some cases, the slant height (the height of the lateral surface) is known instead of the actual height of the cylinder. The lateral surface area can also be calculated using the slant height (l) with the formula: Lateral Area = 2πrl. This requires calculating the slant height using the Pythagorean theorem: l = √(h^2 + r^2), where "h" is the height of the cylinder and "r" is the radius.
- Approximating π for Simplified Calculations: For quick estimates or when working without a calculator, approximating π as 3.14 can simplify calculations. However, this method may not be suitable for applications requiring high precision.
- Calculating Area for Specific Applications: Different applications might require calculating the area of a cylinder for specific purposes, such as determining the amount of material needed to cover the surface or calculating the volume of a cylinder (which requires the base area). Understanding the context of the application can guide the choice of formula and method.
Practical Applications and Examples
Calculating the area of a cylinder has numerous practical applications. For instance, in construction, knowing the surface area of cylindrical pillars or tanks is crucial for estimating the amount of material (like paint or steel) needed. In engineering, the surface area of cylindrical components in machines or vehicles affects heat transfer and stress calculations.
| Component | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Total Surface Area | TSA = 2πr^2 + 2πrh | Combines areas of bases and lateral surface |
| Area of Bases | 2πr^2 | Total area of the two circular bases |
| Lateral Surface Area | 2πrh | Area of the curved surface |
Key Points
- The total surface area of a cylinder is calculated by adding the areas of the two bases and the lateral surface area.
- Understanding the formulas and being able to apply them correctly is essential for accurate calculations.
- Different applications may require calculating the area of a cylinder in various contexts, from construction to engineering.
- Approximations of π can be used for quick estimates but may not be suitable for all applications.
- The choice of method depends on the known dimensions (radius, height, slant height) and the specific requirements of the application.
In conclusion, calculating the area of a cylinder involves understanding and applying specific mathematical formulas, each suited to different aspects of the cylinder's geometry. By grasping these concepts and methods, individuals can accurately determine the surface area of cylinders for various applications, contributing to more precise designs, estimates, and analyses in their respective fields.
What is the formula for the total surface area of a cylinder?
+The formula for the total surface area (TSA) of a cylinder is TSA = 2πr^2 + 2πrh, where “r” is the radius and “h” is the height of the cylinder.
How do you calculate the lateral surface area of a cylinder?
+The lateral surface area of a cylinder is calculated using the formula: 2πrh, where “r” is the radius and “h” is the height of the cylinder.
What is the significance of calculating the area of a cylinder in real-world applications?
+Calculating the area of a cylinder is crucial for estimating material requirements, understanding heat transfer, and performing stress calculations in various engineering and architectural applications.